News • Cancer “chronotherapy”
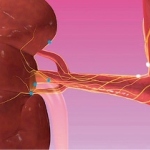
Beating cancer by the clock: Why the time of day matters for radiotherapy
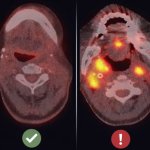
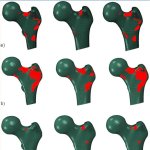
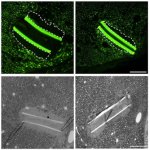
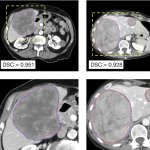
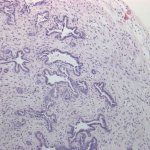
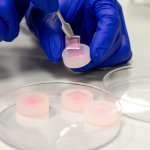
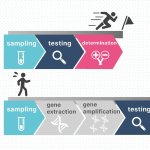
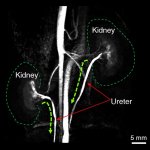
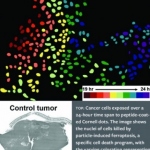
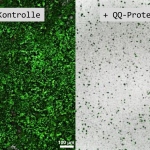
Radiotherapy is more effective when administered at the right time of day, according to new research. This discovery opens the door to cancer “chronotherapy”, the researchers hope.