News • Faster, more accurate treatment
Basal cell carcinoma: AI support for Mohs surgery
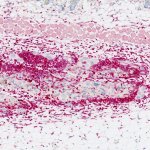
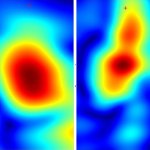
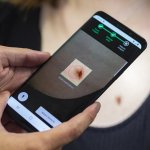
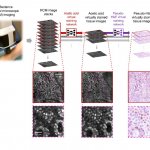
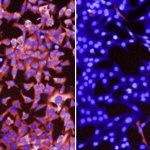
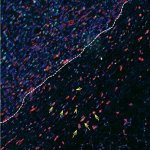
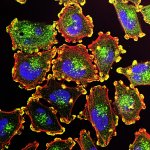
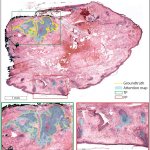
Dutch researchers have developed an AI tool to support Mohs surgery, a precise but time-consuming procedure to treat the most common form of cancer in the Netherlands: basal cell carcinoma.