News • Treatment for muscle loss injuries
Researchers make bacteria produce tissue-healing hydrogel
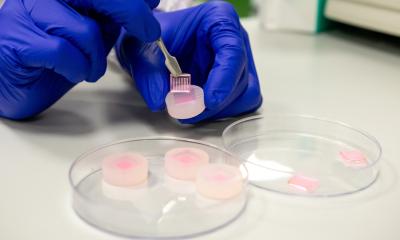
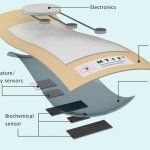
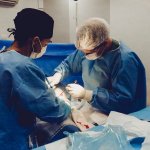
Researchers explore the native bioproduction facilities in bacteria to synthesize a new biopolymer with tissue-healing properties. The resulting hydrogel could be used for muscle tissue regeneration.