
News • (B)eating cancer
Bacteria to consume tumours from the inside out
A research team led by the University of Waterloo is developing a novel tool to treat cancer by engineering hungry bacteria to literally eat tumours from the inside out.

A research team led by the University of Waterloo is developing a novel tool to treat cancer by engineering hungry bacteria to literally eat tumours from the inside out.
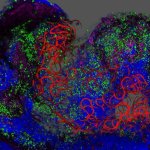
Researchers have created a ‘cyborg’ pancreas device - an ultrathin mesh of conductive wires within growing pancreatic tissue - that could open up new ways for treating diabetes.

“Each pregnancy leaves a unique mark on the female brain”: Research shows that mothers' brains distinctly change, not just during the first pregnancy, to better care for multiple children.

Clues in the CSF: Researchers have developed the first high-precision method that can theoretically diagnose common brain tumors in children and adolescents without surgery.

Type 2 diabetes and high blood pressure share a genetic link, new research from the UK and France shows. People with one condition are more likely to develop the other.
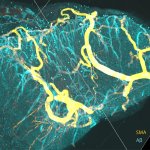
A new type of 3D imaging reveals how amyloid β (Aβ) deposits spread along blood vessels in the human brain. This could lead to targeted therapies for Alzheimer's disease and CAA.
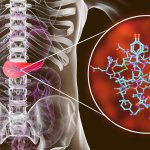
Not just linked to diabetes: For the first time, researchers demonstrated that insulin resistance is a risk factor for 12 types of cancer, including uterine and breast cancer.
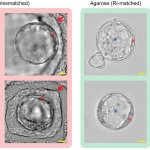
Selecting the healthiest embryo is one of the most important steps in in‑vitro fertilization, yet it remains one of the most uncertain. A new type of hydrogel offers hope for more successful IVF.
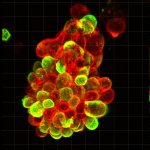
Due to its rapid spread in the abdomen, ovarian cancer is often only detected at an advanced stage. Now, scientists have discovered how this cancer takes advantage of other cells for metastasis.

Even after a blood clot is removed from a large brain artery via thrombectomy, administering the thrombolytic drug alteplase to the area may improve stroke recovery, a new trial from Spain shows.

Not all cancer mutations are equal: new research shows that a single mutation hotspot can generate a rich diversity of tumour behaviours. This could lead to more personalised cancer treatments.

An AI-assisted stethoscope could help doctors identify patients with valvular heart disease who may otherwise go undiagnosed. This could reduce hospital admissions and overall healthcare costs.
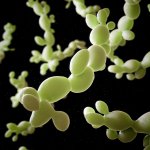
Reseachers show how Candida albicans – a fungus living in our body – can make melanoma more aggressive. The results pave the way for antifungal therapies to complement skin cancer treatments.
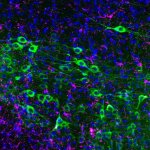
Promising new research points to a new immunotherapy approach that could help preserve viable neurons in people with Parkinson’s disease.

Rethinking ultrasound gel: To reduce patient discomfort during sonography exams, researchers from Japan propose a natural, reusable solid pad for clearer, more comfortable imaging.
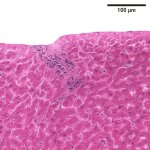
Scientists have shown that a type of laser similar to the one currently used in routine eye surgery could one day help surgeons remove unwanted tissues, such as tumours, with unprecedented accuracy.
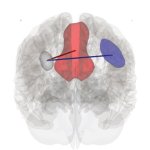
Brain fog explained: People with ME/CFS and long Covid experience a disruption to their brain connectivity during a mentally demanding task, new research finds.
A new type of lab-grown organoid that mimics the behaviour of a human stomach could boost the understanding of rare gastric diseases, researchers say.
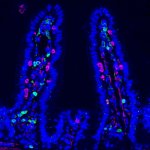
Chemotherapy does more than kill cancer cells: It reshapes the gut microbiome, making the body less permissive to metastasis. This finding opens new avenues for adjuvant strategies.