Deadly 2011 E. coli Strain Decoded
The secret to the deadly 2011 E. coli outbreak in Germany has been decoded, thanks to research conducted at Michigan State University.
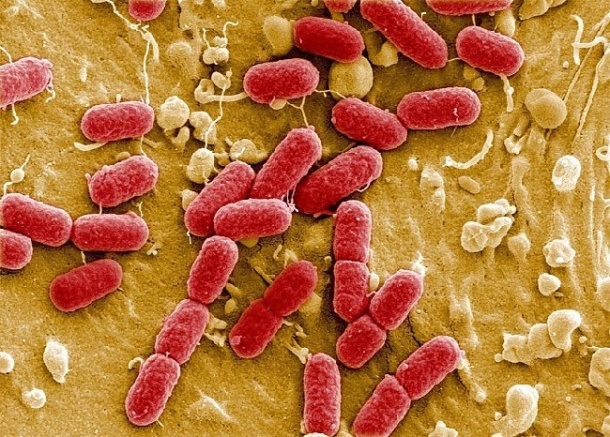
The deadliest E. coli outbreak ever, which caused 54 deaths and sickened more than 3,800 people, was traced to a particularly virulent strain that researchers had never seen in an outbreak before. In the current issue of the academic journal PLoS ONE, a team of researchers led by Shannon Manning, MSU molecular biologist and epidemiologist, suggests a way to potentially tame the killer bacteria.
The strain, E. coli O104:H4, shares some characteristics as other deadly E. coli bacteria, but its combination is novel. Researchers haven't determined the mechanism it uses to cause disease, although Manning and her team were able to find the strain's Achilles heel - its biofilm.
By focusing on the bacteria's biofilm, the grouping of many E. coli bacteria that stick to a cell's surface and grow encased in a self-produced protective coat, Manning and colleagues were able to determine why it was so deadly. When the bacterium found in Germany forms a biofilm, it begins to make more toxic genes like the Shiga toxin.
Increased production of the Shiga toxin is the probable culprit that contributed to so many incidents of kidney damage and death during the 2011 outbreak, Manning said.
"What made the German outbreak so different is that many victims suffering from kidney failure were adults," she said. "Rather than attacking adults, other types of E. coli that produce Shiga toxins typically damage kidneys of children under 10."
In addition, the incubation period was considerably longer among individuals infected with the German outbreak strain compared to individuals infected with E. coli O157, a similar bacterium that can also cause illness and death. Manning believes this is because the German strain needs a longer period of time to form a biofilm, whereas biofilms are not important for O157 infections.
"Our research demonstrates that biofilm formation is critical for toxin production and kidney damage," she said. "If we can block the bacteria from forming a stable biofilm, then it is likely that we can prevent future E. coli O104:H4 infections."
The next phase of Manning's research is already focusing on creating mutant strains in an effort to prevent the bacterium from forming a biofilm. This would prevent the disease completely since the conditions would not be favorable for bacterial growth.
30.07.2012





