News • Identification of high-risk CAD patients
FFR-CT: AI tool predicts heart attack risk in angina patients
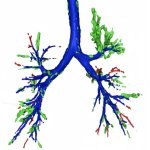
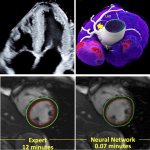
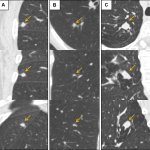
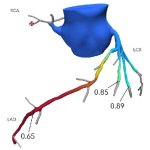
Can CT-derived fractional flow reserve (FFR-CT) be used in patients with angina to predict future major cardiovascular events? A novel AI-based approach for CCTA analysis yields promising results.