News • New biomaterials
Building durable, infection-resistant implants with liquid metal
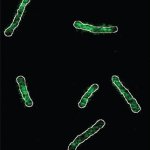
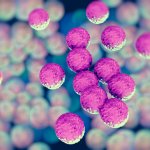
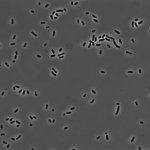
Integrating liquid metal nanomaterials into a ceramic scaffold could improve the durability and biocompatibility of orthopedic implants, while also combatting antimicrobial resistance.