News • Plasmonic nanorods
Golden eyes: restoring vision with nanoparticles
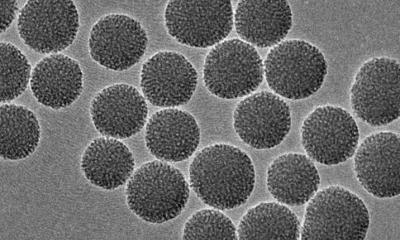
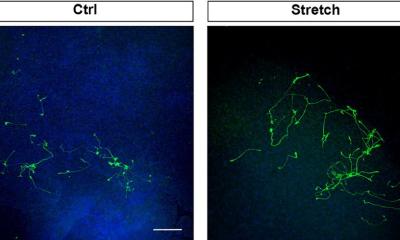
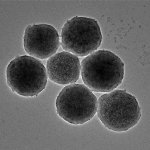
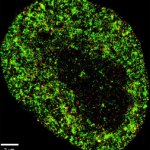
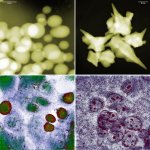
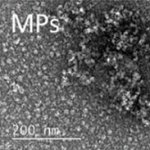
A new study suggests that gold nanoparticles — thousands of times thinner than a human hair — might one day help restore vision in people with macular degeneration and other retinal disorders.