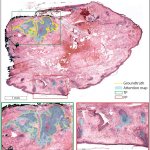
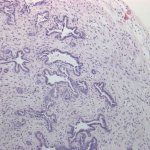
News • MRD assessment
Liquid biopsy to detect breast cancer relapse up to 5 years in advance
Newly developed technology can detect breast cancer relapses up to five years in advance. This advance could represent a turning point in post-treatment follow-up, the researchers hope.