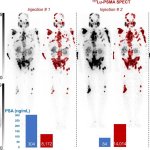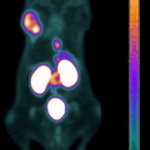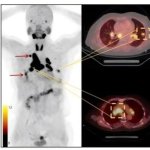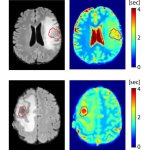
News • Differentiation after radiotherapy
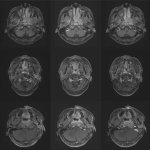
Brain tumour or radiation necrosis? AI can tell them apart
A novel AI-based method can distinguish between progressive brain tumours and radiotherapy-induced necrosis on advanced MRI. This could help clinicians more accurately identify and treat the issues.