News • Blood vessel-like coating
New material to protect devices against blood clot formation
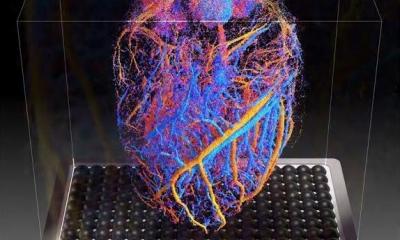
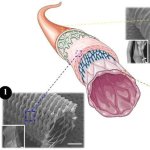
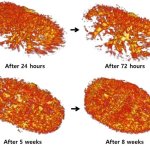
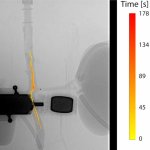
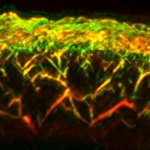
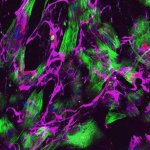
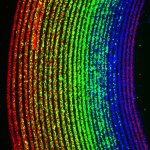
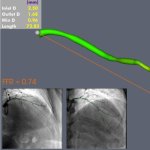
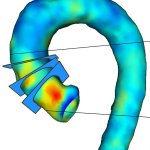
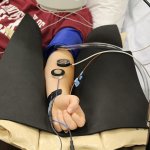
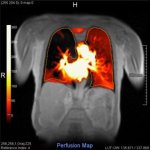
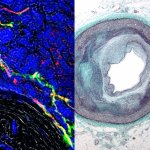
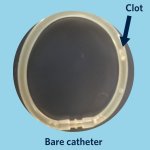
Protection against blood clots: A new material, designed to mimic blood vessels, could allow for safer use of devices like catheters, stents, blood-oxygenation machines and dialysis machines.