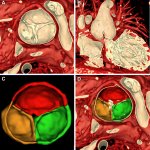
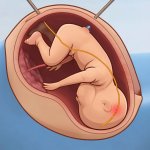
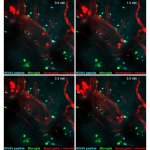
News • Critical role of NFAT
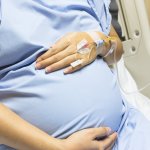
Preventing pregnancy complications with new immune insights
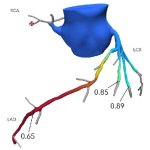
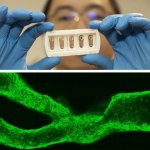
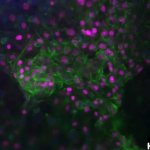
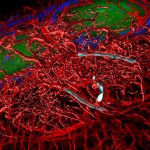
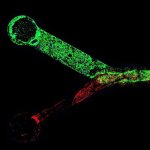
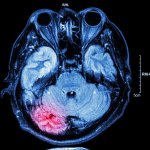
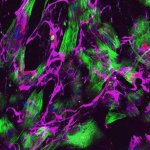
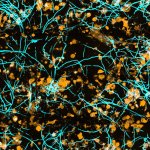
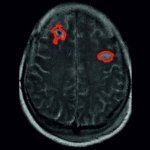
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Researchers have discovered a crucial immune switch that sheds light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure.