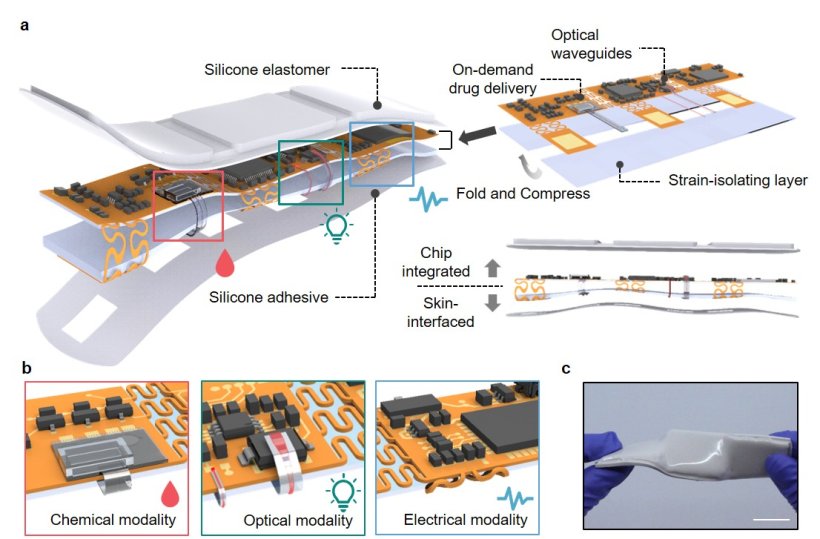
Image source: DGIST; adapted from: Lee H, Song S, Yea J et al., Nature Communications 2025 (CC BY 4.0)
News • Multifunctional wearable
Smart patch combines health monitoring and drug delivery
The Department of Robotics and Mechatronics Engineering research team at the Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST), led by Professor Kyung-In Jang, has developed a smart patch capable of real-time biometric signal monitoring and drug delivery.
This patch integrates various sensors and a drug delivery system into a single unit using a foldable structure, enabling real-time cardiovascular health monitoring and immediate drug administration when necessary. The research team expects this technology to be widely applicable across multiple medical fields, including glucose management, pain relief, and chronic disease treatment.
The findings were published in the journal Nature Communications.
Moving forward, we plan to further develop this technology into an intelligent healthcare platform applicable to diverse medical areas
Kyung-In Jang
The researchers point out the growing importance of personalized healthcare in the context of an ageing society. Consequently, interest is growing in wearable medical devices capable of real-time health monitoring and immediate treatment. However, existing wearable devices typically provide either biometric signal detection or drug delivery, with limitations in integrating multiple functions into a thin and stable structure. To overcome these limitations, Professor Kyung-In Jang’s team designed a smart patch that integrates electrical and optical biometric signal sensors, a drug delivery system, and a wireless communication module into a foldable structure. This patch can automatically deliver drugs based on real-time biometric signals, enabling personalized treatment tailored to the user’s health condition(s).
The research team validated the performance of the smart patch through real-time biometric signal measurement and drug delivery experiments. Experimental results demonstrated successful real-time monitoring of electrocardiograms and blood flow, along with accurate analyses of heart rate variability and pulse transit time. Additionally, the team successfully implemented an automated drug delivery function based on collected biometric signals. Professor Kyung-In Jang stated, “The smart patch developed in this study integrates biometric signal measurement and drug delivery into a single system, with high applicability across various medical fields, such as blood pressure control, glucose management, pain relief, and chronic disease treatment. It enables real-time, personalized treatment.” He added, “Moving forward, we plan to further develop this technology into an intelligent healthcare platform applicable to diverse medical areas.”
Source: Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology
07.02.2025