© Sebastian Kaulitzki – stock.adobe.com
News • Aortic analysis
Exploring the aorta's "weak spots" for aneurysms
The sites where vascular aneurysms typically form have a predilection from the outset, even in healthy people. This is shown by a study conducted by medical researchers from Bochum and Bonn.
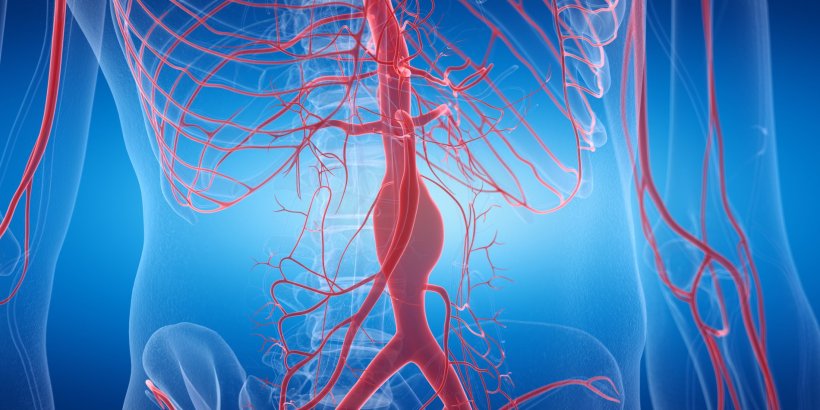
A vascular dilatation in the aorta can be life-threatening if it bursts. These so-called aortic aneurysms typically form in the same sites of the large blood vessel: either on the upper arch or in the abdominal cavity. “We wanted to understand why it is always these sites that are affected. What is it that sets them apart from others?” points out Professor Daniela Wenzel, Head of the Department of Systems Physiology at Ruhr University Bochum, Germany. Research into the gene activity of the innermost vascular layer showed that even in healthy mice abnormalities occur at precisely these sites. The research team published their findings in the journal Angiogenesis.

© RUB, Marquard
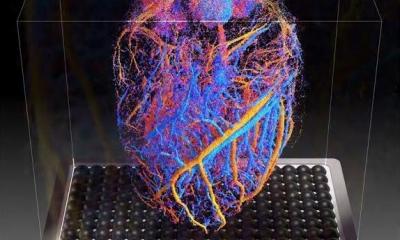
In order to find out what distinguishes the repeatedly affected vascular regions from others, Daniela Wenzel and her team from Bochum and Bonn, which is part of the Collaborative Research Center/Transregio 259 “Aortic Diseases”, developed a method to specifically examine the endothelium of the aorta: the innermost layer of the blood vessel. “We know from other vascular diseases such as arteriosclerosis that there are changes in this innermost layer long before symptoms appear,” says the researcher.
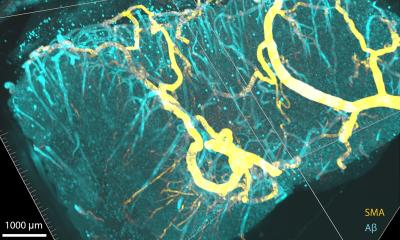
The researchers succeeded in isolating only the endothelial cells of the aorta of healthy mice using a stamping technique under extreme cold. From these small samples, which only comprised around 350 individual cells, they could isolate and examine the RNA. They analyzed the gene activity at different sites of the aorta and compared the sites where aneurysms frequently form with those that don’t show this tendency.

Image source: RUB; photo: private
“We identified certain patterns of upregulated genes in the sites where dilatations frequently form,” explains Alexander Brückner, a PhD student in the working group at the Institute of Physiology I at the University Hospital Bonn and the University of Bonn and first author of the study. “These remarkably active genes affect, for example, changes in the extracellular matrix, the formation of new blood vessels and some inflammatory reactions.” Such genetic abnormalities are also found in tissue from human aneurysms. Together with cooperation partners from the Institute of Physiology at the University of Lübeck, the researchers also determined the stiffness of the endothelium in the healthy aortic samples. The less elastic the endothelium, the more detrimental it is to vascular health. They proved that the endothelium was stiffer in the sites where aneurysms frequently develop than in the control areas.
In the next step, the team used an established model of a knock-out mouse that tends to form aneurysms due to a targeted genetic modification. If high blood pressure is additionally induced in these mice, aortic aneurysms form. They compared the genetic activity in the aortic endothelium of the genetically modified mice without aneurysm with that of mice that had developed an aneurysm due to added high blood pressure. “In the mice with aneurysms, we found a much greater degree of gene alterations that belong to the same category as the gene alterations in healthy mice,” says Brückner. “In the mice with an aneurysm, the vessel wall was also altered.”
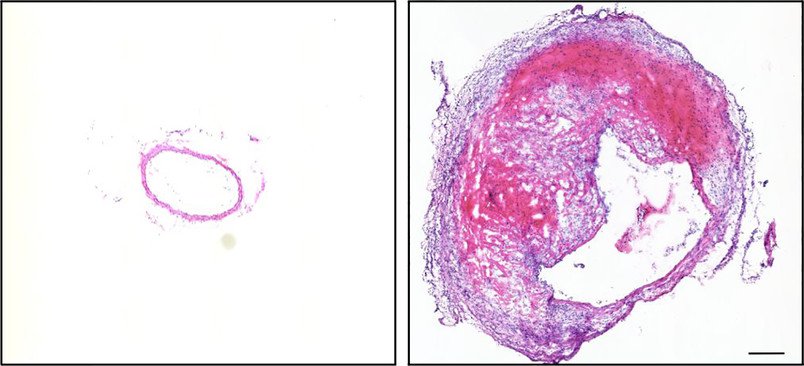
© Daniela Wenzel
The researchers conclude that the sites where aneurysms frequently form are weak points from the outset. “We don’t know exactly why this happens – perhaps it has to do with the mechanical conditions and the blood flow there, or perhaps the altered gene activity at these sites is inherited from birth,” explains Daniela Wenzel. The latter seems plausible, as the aorta develops at different heights from different embryonic precursor cells. “If risk factors are added to this – such as smoking and high blood pressure – these sites are particularly susceptible to the formation of a vascular aneurysm,” outlines the physician. She hopes that basic research will result in a better understanding of the processes that contribute to the formation of an aneurysm and that this will eventually lead to new approaches for drug treatment.
Source: Ruhr University Bochum
08.07.2024