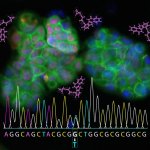
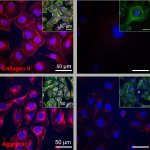
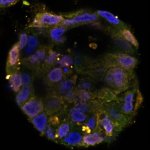
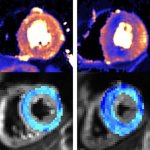
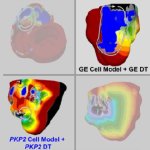
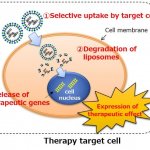
News • Disease tolerance and infection pathogenesis
Different age, same infection treatment? Not a good idea, study finds
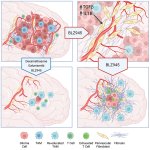
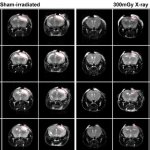
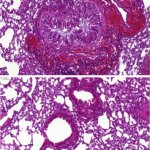
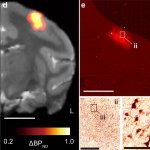
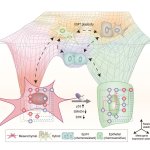
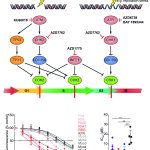
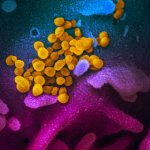
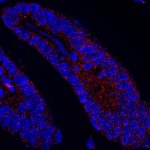
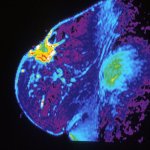
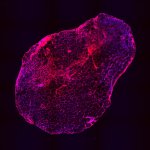
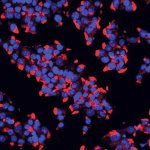
Should younger and older people receive different treatments for the same infection? New research suggests that age-specific treatments may be necessary in ongoing antibiotic resistance crisis.