Image source: ITEFI-CSIC
News • Inhibition of solid tumor growth
'Paralyzing' pancreatic cancer with low-intensity ultrasound
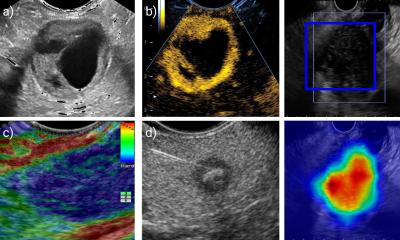
A study led by Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC) has demonstrated the efficiency of an ultrasound radiation-based therapy on the inhibition of cancer cell motion in pancreas cancer models.
This work, recently published in Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, opens a door to the development of new non-invasive treatments based on the use of the ultrasound technology to paralyze solid tumor growth. This tumor growth is accompanied by proliferation processes and migration of the cancer cells. Current therapies including ionizing radiation damage malign and surrounding healthy cells. "Our research [proposes for] the first time the possibility to develop a new therapy exclusively based on the used of low intensity ultrasounds in control conditions," the researchers explain. "This non-ionizing radiation could represent a noninvasive technology of low-cost production and easy application without collateral damage," explains Icíar González, researcher of CSIC in the Instituto de Tecnologías Físicas y de la Información "Leonardo Torres Quevedo" (ITEFI).
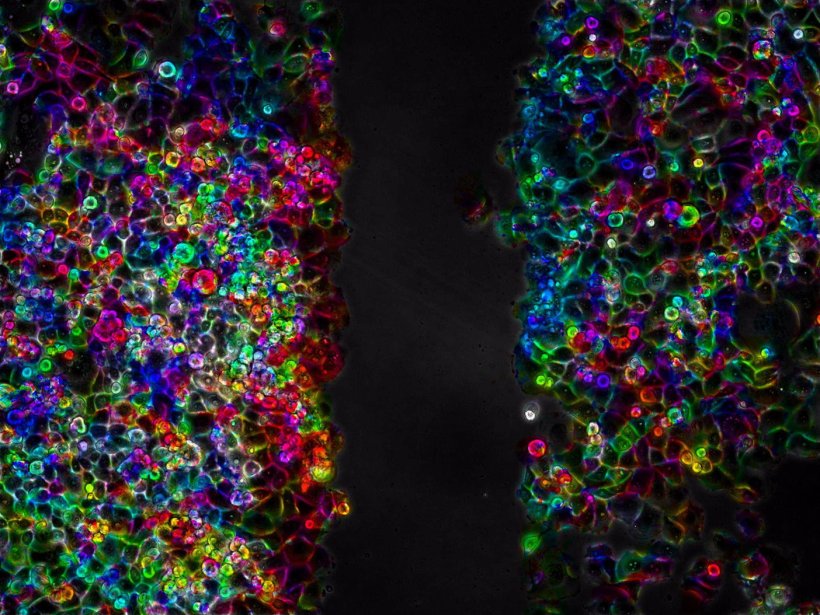
The authors have developed the experiments with in vitro pancreas samples. "The collective migration PANC-1 cell lines in monolayer is blocked during at least 2 days after applying a single dose of 20-minute low intensity ultrasound," describes González. "Application of ultrasonic waves at certain controlled acoustic conditions during short times of 15-20 minutes inhibits the ability of motion of the cells (both collective and individual) for [...] times longer than 48 hours or even 3 days after the acoustic treatment."
"We have also observed a certain inhibition on the cell proliferation as a second effect of the LICUS actuation that [is] currently being analyzed in new experiments and studies of gene expression," she says.
The next step is conducting murine in vivo tests to verify the suitability and advantages of this technology as upcoming therapy.
Source: Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas
31.01.2023