© Dr Eva Conde
News • Promising results pave way for trial
A vaccine against allergic asthma: reseachers report new milestone
To combat allergic asthma, which affects millions of people worldwide, scientists from Inserm, CNRS and Université Toulouse III-Paul Sabatier at the Infinity laboratory, Institut Pasteur and French company Neovacs are developing and testing a new vaccine.
In their previous study, the teams had shown it to be effective in producing antibodies capable of neutralizing human immune proteins that play a key role in triggering allergic asthma, cytokines IL-4 and IL-13. The results, published in Allergy, pave the way for the organization of a clinical trial.
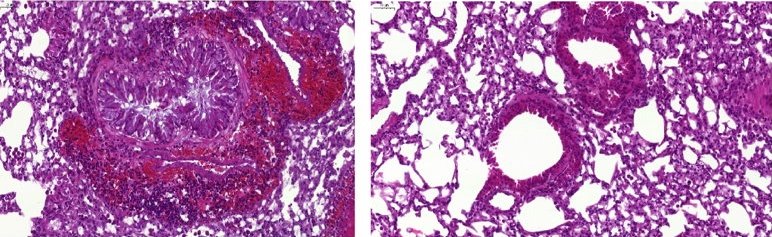
Asthma is a chronic disease that affects around 4 million people in France and 340 million worldwide. Allergic asthma, which accounts for around 50% of asthma cases, is characterized by inflammation of the bronchial tubes and respiratory discomfort caused by the inhalation of allergens, most often dust mites. This exposure to dust mites and other allergens triggers the overproduction of antibodies called immunoglobulin E (IgE) and proteins called type 2 cytokines (particularly interleukin-4 (IL-4) and IL-13) in the airways. This phenomenon leads to a cascade of reactions resulting in hyperresponsiveness of the respiratory tract, overproduction of mucus, and eosinophilia (when there are too many eosinophils, a type of white blood cell, in the airways).
Vaccination against allergic asthma represents the hope of a long-term treatment for this chronic disease and the prospect of reducing allergy symptoms related to other factors
Pierre Bruhns
At present, inhaled corticosteroids are the gold standard for controlling asthma. However, in the case of severe allergic asthma, this treatment is not always sufficient. Therapeutic monoclonal antibody treatments are then required in order to target the IgE or the IL-4 and IL-13 pathways. However, these are very costly and require patients to inject for years or even throughout their lives. For several years now, Inserm research director Laurent Reber and his colleagues at the Infinity laboratory in Toulouse, along with Pierre Bruhns’ team at Institut Pasteur, have been working in collaboration with Neovacs to develop a vaccine to open up new therapeutic avenues for patients with severe allergic asthma.
In a previous study, the researchers had showed the efficacy in mice of a conjugate vaccine called Kinoïde. The results suggested that this vaccine induced the sustained production of antibodies directed specifically against murine IL-4 and IL-13, as well as a reduction in the symptoms of allergic asthma in those animals.
Following these encouraging early data and in order to envisage clinical trials in humans, it was necessary to develop a vaccine that is also capable of neutralizing human IL-4 and IL-13 cytokines. In order to test the efficacy of this new vaccine, the scientists this time used a model of house dust mite allergic asthma in “humanized” mice, whose genes encoding murine cytokines IL-4 and IL-13 were replaced with the respective human genes.
Again, the results are promising: vaccination induced a major antibody response, capable of neutralizing human IL-4 and IL-13 cytokines, with no reduction in the efficacy of the vaccine, up to three months after injection (time corresponding to the total duration of this study). A significant effect on asthma symptoms was also observed: in the animals studied, vaccination was associated with reduced IgE and eosinophilia levels as well as reduced mucus production and airway hyperreactivity.
“This study provides proof of concept of the vaccine’s efficacy in neutralizing human proteins that play a key role in allergic asthma, bringing us closer to its testing in humans. We are currently in discussion with the various project partners regarding the set-up of these clinical trials,” concludes Reber. “Vaccination against allergic asthma represents the hope of a long-term treatment for this chronic disease and the prospect of reducing allergy symptoms related to other factors, since this vaccine targets molecules involved in different allergies,” points out Pierre Bruhns, head of the Antibodies in Therapy and Pathology unit at Institut Pasteur.
Source: Inserm
09.03.2023





