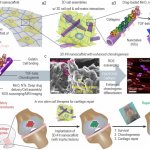
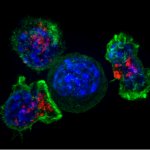
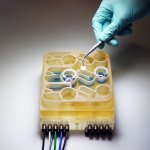
News • Adhesive microgel-based coating
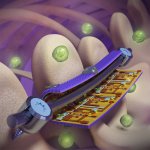
A spray-on shield to prevent transplant rejection
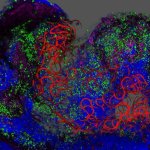
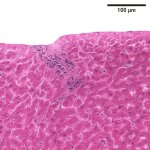
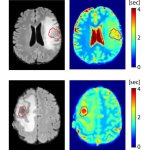
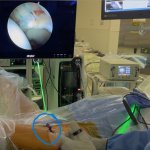
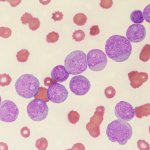
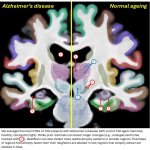
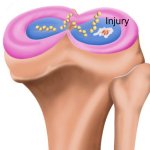
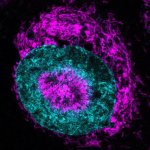
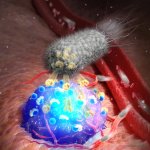
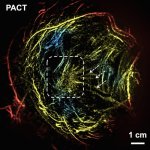
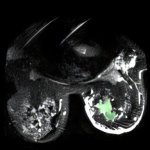
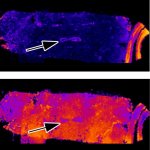
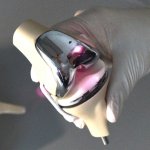
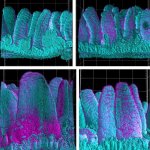
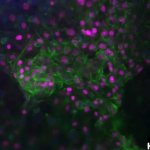
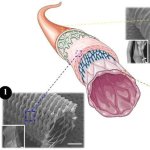
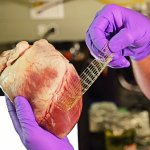
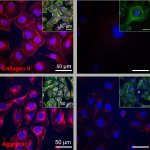
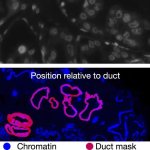
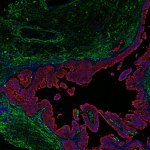
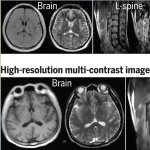
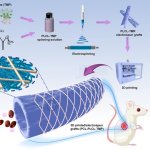
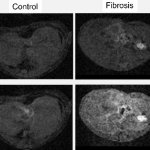
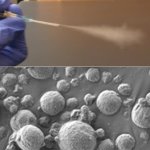
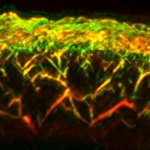
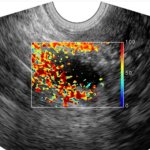
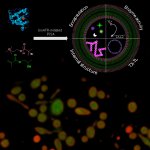
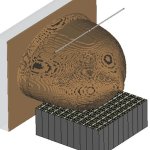
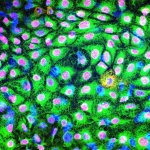
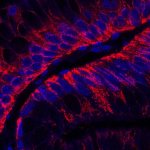
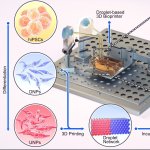
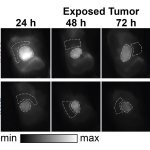
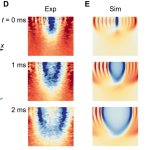
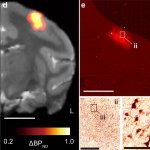
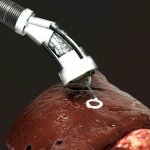
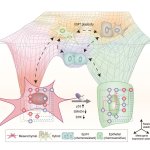
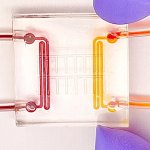
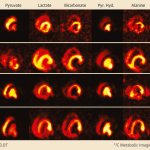
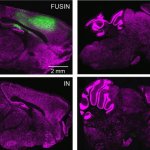
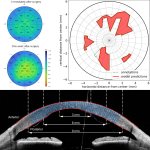
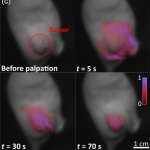
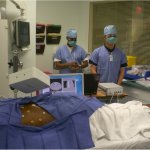
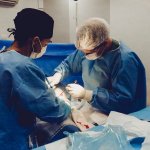
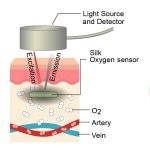
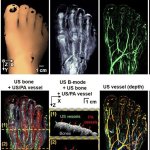
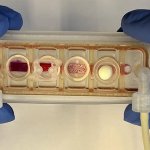
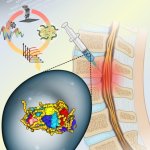
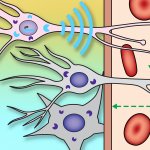
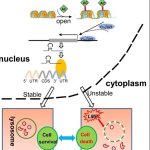
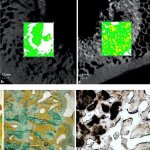
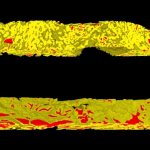
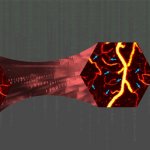
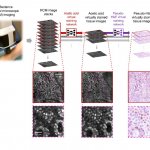
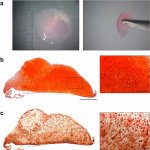
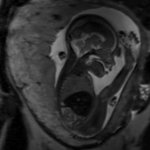
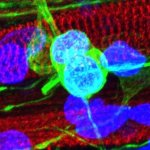
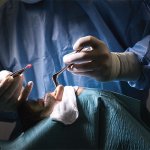
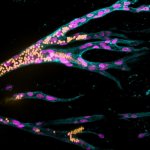
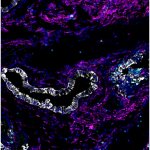
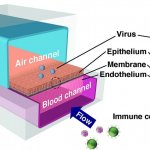
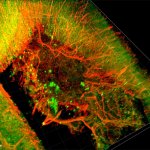
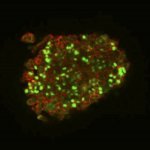
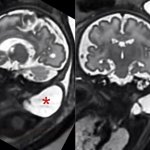
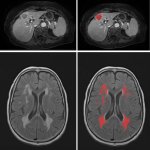
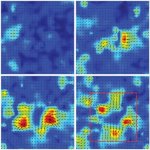
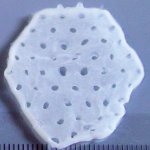
Korean researchers are developing a “spray shield that adheres to transplant organs” and reduces the burden on patients taking lifelong immunosuppressants to prevent transplant rejection.