News • Enhanced imaging and surgical guidance
Fluorescent bacteria light up tumors like a neon sign
Accurate removal of tumors is the most critical aspect of cancer surgery, yet it remains a significant challenge in clinical practice.

Image source: Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST)
In breast cancer, for example, the positive margin rate—where cancer cells remain at the surgical boundary—can reach up to 35%, often requiring reoperation and increasing the risk of recurrence. Preoperative imaging or ultrasound is often insufficient to fully identify tumor boundaries, forcing surgeons to rely heavily on experience. These limitations highlight the urgent need for technologies that can provide real-time tumor visualization during surgery.
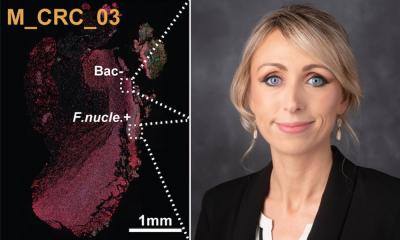
A joint research team led by Dr. SeungBeum Suh (Center for Bionics) and Dr. Sehoon Kim (Center for Chemical and Biological Convergence) at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST, President Sang-Rok Oh), and Professor Hyo-Jin Lee at Chungnam National University Hospital, has developed a next-generation intraoperative imaging platform using engineered beneficial bacteria that emit fluorescence specifically at tumor sites. This bacteria-based contrast agent illuminates tumors like a neon sign during surgery, enabling more precise resection and reducing the risk of recurrence.
The team published their findings in the journal Advanced Materials.
The researchers engineered a fluorescent bacterial system that specifically activates within tumor tissue, allowing surgeons to identify tumor location and margins in real time. The fluorescent signal remains stable in vivo for over 72 hours and clearly highlights tumor regions even within complex internal organs. Like lighting up a building on a map, this enables intuitive, visual identification of tumors with the naked eye during surgery, even under standard surgical lighting, thereby reducing surgical burden.
This study demonstrates a novel approach in which bacteria autonomously locate tumors and emit fluorescent signals, allowing real-time identification of tumor location and boundaries during surgery
SeungBeum Suh
Unlike conventional contrast agents that must be developed individually for each cancer type, this new platform exploits two common tumor microenvironment features—hypoxia and immune evasion—making it broadly applicable across multiple solid tumors. The fluorescence intensity is approximately five times stronger than conventional agents, and the system operates in the near-infrared spectrum, ensuring compatibility with existing surgical endoscopes and imaging equipment. It can also be integrated with surgical robots and intraoperative imaging systems to enhance surgical precision and shorten procedure time. The ability to interface with widely used fluorescence-guided surgical systems in hospitals further strengthens its clinical and commercialization potential.
The research team aims to expand this bacterial platform into an integrated cancer treatment system that combines diagnosis, surgery, and therapy. The engineered bacteria, which can autonomously locate tumors, may also serve as carriers for anticancer drugs or therapeutic proteins. To this end, the team is advancing the platform through convergence with medical imaging equipment, precision drug delivery systems, and comprehensive safety evaluations for clinical application.
Dr. Suh of KIST stated, “This study demonstrates a novel approach in which bacteria autonomously locate tumors and emit fluorescent signals, allowing real-time identification of tumor location and boundaries during surgery. Its applicability across a range of solid tumors positions it as a potential new standard for precision surgical imaging.”
Source: Korean National Research Council of Science & Technology
25.07.2025