News • Scaffold-free approach
Researchers create cartilage tissue out of stem cells
Researchers at the University of Southampton have invented a new way to generate human cartilage tissue from stem cells. The technique could pave the way for the development of a much-needed new treatment for people with cartilage damage.
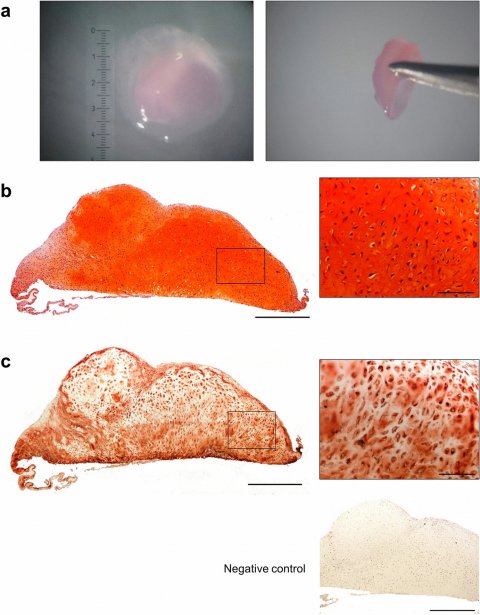
Image source: Griffith et al., Scientific Reports 2021 (CC BY 4.0)
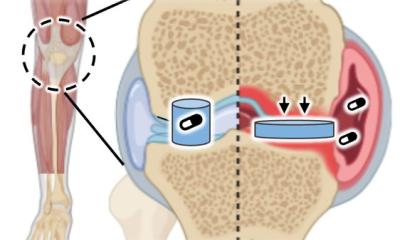
Cartilage acts as a shock absorber in joints, but it is susceptible to damage through daily wear-and-tear, or trauma from sports injuries and falls. The current gold-standard surgical approach to restore regions of damaged cartilage, using cartilage cells, is not wholly successful. This is because survival of the repair tissue, generated by cartilage cells at the site of damage, has been shown to decrease significantly after 5-10 years. As such, there is a need for a new way to promote robust, long-term repair through the implantation of cartilage tissue, as opposed to cartilage cells, at the site of damage.
Scientists at the Centre for Human Development, Stem Cells and Regeneration think they may have found the answer. They generated cartilage tissue in the laboratory by successfully differentiating embryonic stem cells into cartilage cells, and then used these to generate three-dimensional pieces of cartilage tissue without any synthetic or natural supporting materials. This is known as a ‘scaffold-free’ cartilage tissue engineering technique. The generated cartilage tissue is structurally and mechanically comparable to normal human cartilage with the potential to form a stable and longer lasting repair than current treatment options available to patients.
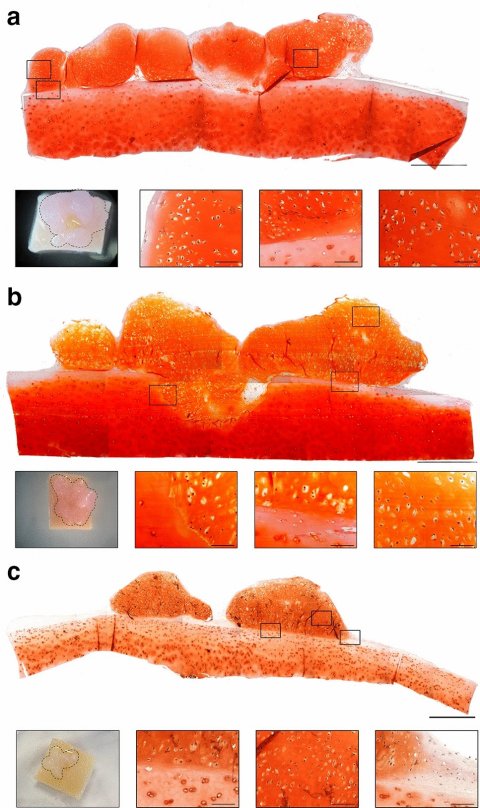
Image source: Griffith et al., Scientific Reports 2021 (CC BY 4.0)
The researchers are the first to use the scaffold-free technique to generate cartilage tissue, which is scaled up beyond 1 mm without adversely affecting its structural and mechanical properties. The team hopes that eventually, after more research is conducted, this lab created tissue could be routinely used in surgery to mend damaged cartilage.
The interdisciplinary study, published in the journal Scientific Reports, was led by Dr Franchesca Houghton and Dr Rahul Tare from the Faculty of Medicine at the University of Southampton. Dr Houghton said: “This research is exciting as our ability to generate cartilage with properties akin to normal human cartilage has the potential to provide a robust tissue engineered product for cartilage repair.” Dr Tare adds: “This tissue-based approach of replacing ‘like-for-like’ has the potential to constitute a step-change improvement in current cell-based surgical approaches for repairing damaged cartilage and improve long-term patient outcomes.”
Source: University of Southampton
30.09.2021