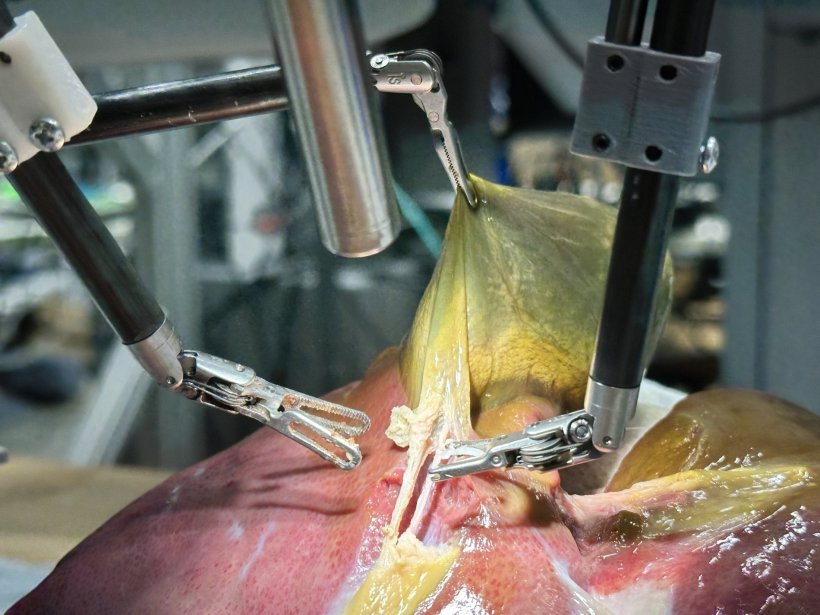
Image source: Juo-Tung Chen/Johns Hopkins University
News • Autonomous system trained on surgical videos
Robot performs realistic surgery without human help
System trained on videos of surgeries performs like an expert surgeon
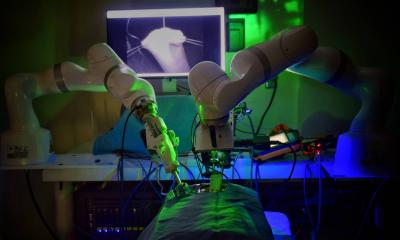
A robot trained on videos of surgeries performed a lengthy phase of a gallbladder removal without human help. The robot operated for the first time on a lifelike patient, and during the operation, responded to and learned from voice commands from the team—like a novice surgeon working with a mentor. The robot performed unflappably across trials and with the expertise of a skilled human surgeon, even during unexpected scenarios typical in real life medical emergencies.
This is a critical distinction that brings us significantly closer to clinically viable autonomous surgical systems that can work in the messy, unpredictable reality of actual patient care
Axel Krieger
The federally-funded work, led by Johns Hopkins University researchers, is a transformative advancement in surgical robotics, where robots can perform with both mechanical precision and human-like adaptability and understanding. “This advancement moves us from robots that can execute specific surgical tasks to robots that truly understand surgical procedures,” said medical roboticist Axel Krieger. “This is a critical distinction that brings us significantly closer to clinically viable autonomous surgical systems that can work in the messy, unpredictable reality of actual patient care.”
In 2022, Krieger’s Smart Tissue Autonomous Robot, STAR, performed the first autonomous robotic surgery on a live animal – a laparoscopic surgery on a pig. But that robot required specially marked tissue, operated in a highly controlled environment, and followed a rigid, predetermined surgical plan. Krieger said it was like teaching a robot to drive along a carefully mapped route.
Recommended article

News • Autonomous procedure
Robot performs first laparoscopic surgery without human help
A robot has performed laparoscopic surgery on the soft tissue of a pig without the guiding hand of a human – a significant step toward fully automated surgery on humans.
But his new system, he says, “is like teaching a robot to navigate any road, in any condition, responding intelligently to whatever it encounters.”
Surgical Robot Transformer-Hierarchy, SRT-H, truly performs surgery, adapting to individual anatomical features in real-time, making decisions on the fly, and self-correcting when things don't go as expected. Built with the same machine learning architecture that powers ChatGPT, SRT-H is also interactive, able respond to spoken commands (“grab the gallbladder head”) and corrections (“move the left arm a bit to the left”). The robot learns from this feedback.
Our work shows that AI models can be made reliable enough for surgical autonomy—something that once felt far-off but is now demonstrably viable
Ji Woong "Brian" Kim
“This work represents a major leap from prior efforts because it tackles some of the fundamental barriers to deploying autonomous surgical robots in the real world,” said lead author Ji Woong "Brian" Kim, a former postdoctoral researcher at Johns Hopkins who’s now with Stanford University. “Our work shows that AI models can be made reliable enough for surgical autonomy—something that once felt far-off but is now demonstrably viable.”
Last year Krieger’s team used the system to train a robot to perform three foundational surgical tasks: manipulating a needle, lifting body tissue, and suturing. Those tasks took just a few seconds each.
Recommended article
News • Imitation learning
Learning surgery steps: Robot see, robot do
Imitation learning could open a new frontier in medical robotics: Researchers 'taught' a robot to mimic a surgical procedure by watching the surgeons' performance.
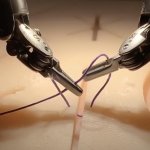
The gallbladder removal procedure is much more complex, a minutes-long string of 17 tasks. The robot had to identify certain ducts and arteries and grab them precisely, strategically place clips, and sever parts with scissors. SRT-H learned how to do the gall bladder work by watching videos of Johns Hopkins surgeons doing it on pig cadavers. The team reinforced the visual training with captions describing the tasks. After watching the videos, the robot performed the surgery with 100% accuracy.
Although the robot took longer to perform the work than a human surgeon, the results were comparable to an expert surgeon. “Just as surgical residents often master different parts of an operation at different rates, this work illustrates the promise of developing autonomous robotic systems in a similarly modular and progressive manner,” says Johns Hopkins surgeon Jeff Jopling, a co-author.
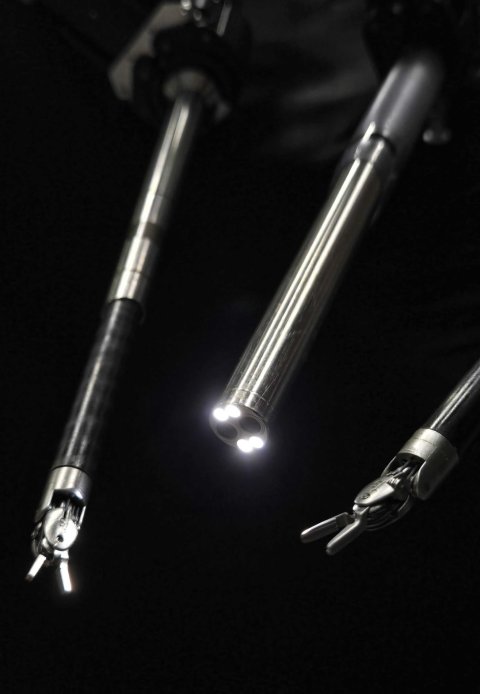

Image source: XinHao Chen/Johns Hopkins University
The robot performed flawlessly across anatomical conditions that weren’t uniform, and during unexpected detours—such as when the researchers changed the robot’s starting position and when they added blood-like dyes that changed the appearance of the gallbladder and surrounding tissues. “To me it really shows that it’s possible to perform complex surgical procedures autonomously,” Krieger said. “This is a proof of concept that it’s possible and this imitation learning framework can automate such complex procedure with such a high degree of robustness.”
Next the team would like to train and test the system on more types of surgeries and expand its capabilities to perform a complete autonomous surgery.
Authors include Johns Hopkins PhD student Juo-Tung Chen; Johns Hopkins visiting graduate student Pascal Hansen; Stanford University PhD student Lucy X. Shi; Johns Hopkins undergraduate Antony Goldenberg; Johns Hopkins PhD student Samuel Schmidgall; former Johns Hopkins postdoctoral fellow Paul Maria Scheikl; Johns Hopkins research engineer Anton Deguet; surgical fellow Brandon M. White, Stanford University assistant professor Chelsea Finn; and De Ru Tsai and Richard Cha of Optosurgical.
Source: Johns Hopkins University
10.07.2025