News • Research on metastasis mechanism
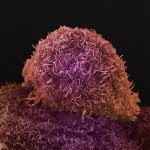
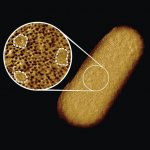
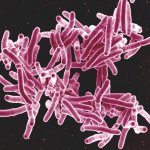
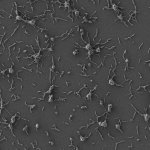
How ovarian cancer hijacks abdominal cells as an invasion force
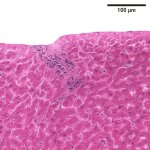
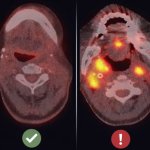
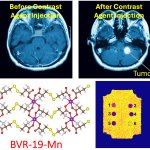
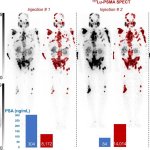
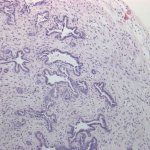
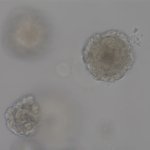
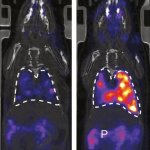
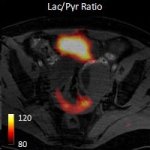
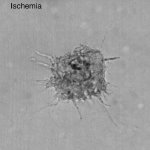
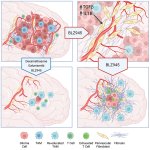
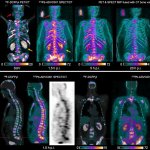
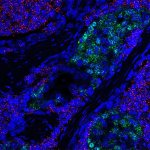
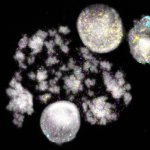
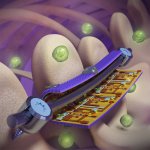
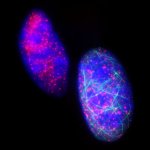
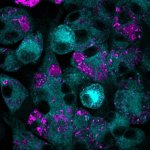
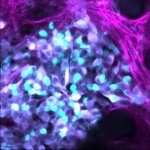
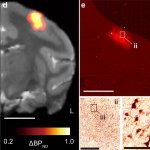
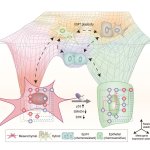
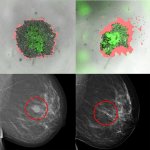
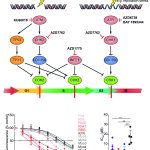
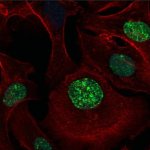
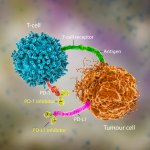
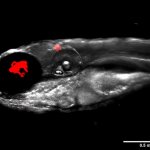
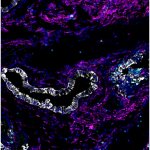
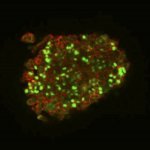
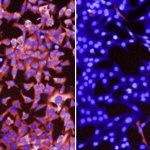
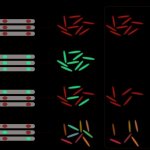
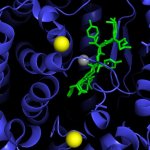
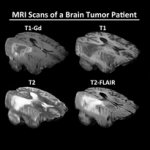
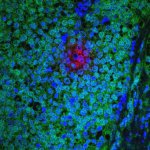
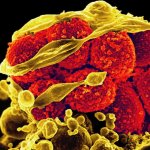
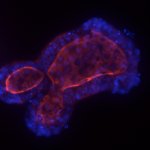
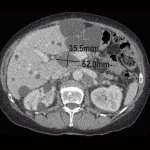
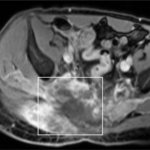
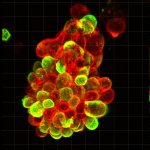
Due to its rapid spread in the abdomen, ovarian cancer is often only detected at an advanced stage. Now, scientists have discovered how this cancer takes advantage of other cells for metastasis.