© DKFZ
News • Relapse research
Multiple myeloma: Tracking down resistant cancer cells
In multiple myeloma, a cancer of the bone marrow, relapse almost always occurs after treatment. Initially, most patients respond well to therapy. However, as the disease progresses, resistant cancer cells spread in the bone marrow, with fatal consequences for the patients.
Scientists at the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), Heidelberg University Hospital (UKHD) and the National Center for Tumor Diseases (NCT) in Heidelberg have now used single-cell sequencing to elucidate how myeloma cells with different genetic characteristics change in interaction with the surrounding immune cells in a patient during relapse. The results, published in the journal Nature Communications, point to new approaches to counteract relapse.
We can now better identify the molecular changes in individual myeloma cells that indicate emerging resistance
Marc-Steffen Raab
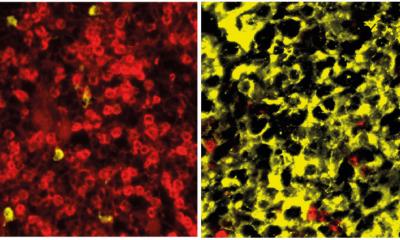
Molecular analyses of tumor genetic material typically determine an "average" of tens of thousands of cancer cells. Information on the heterogeneity of the tumor as well as the contribution of healthy cells in the sample is lost. New technologies now make it possible to sequence and quantify all mRNAs at the level of individual cells and also to identify changes in the genetic material from them. This makes it possible to follow exactly how individual subsets of cancer cells with different mutations develop during treatment. This is particularly important for understanding why patients who initially responded well to therapy relapse.
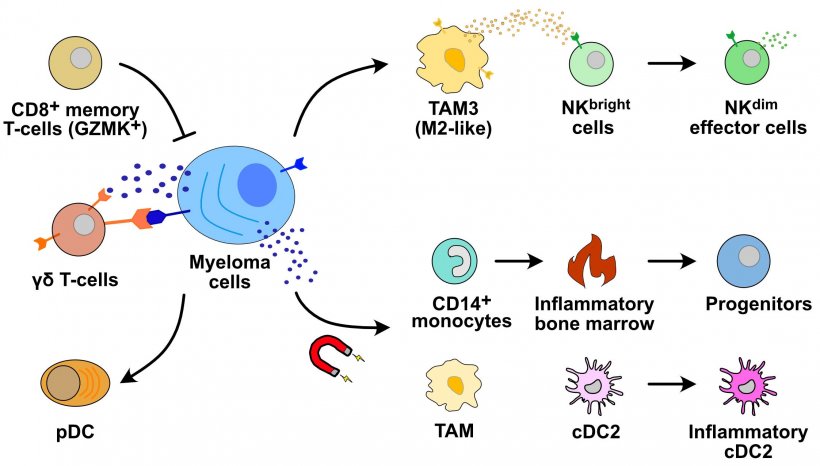
"In our current study, we analyzed the RNA sequences of about half a million individual cells. We were able to see how the composition of different cancer cell clones changes within a patient in multiple myeloma and how individual clones can reprogram the immune cells in their environment," explains Karsten Rippe, who is coordinating the study together with Marc-Steffen Raab as part of the Translational Myeloma Research Program at DKFZ and UKHD. "We can now better identify the molecular changes in individual myeloma cells that indicate emerging resistance" said Marc-Steffen Raab, clinical director of the Heidelberg Myeloma Center. "This provides new approaches to develop targeted drugs or combinations of drugs for patients to counteract relapse."
Next, the scientists want to find out how new immunotherapies affect both myeloma cells and immune cells in the bone marrow, and how single-cell sequencing can be used to better predict the success of these treatments.
Source: German Cancer Research Center
29.11.2021