News • Therapy-resistant cells
Von Hippel-Lindau: How to kill hereditary cancer
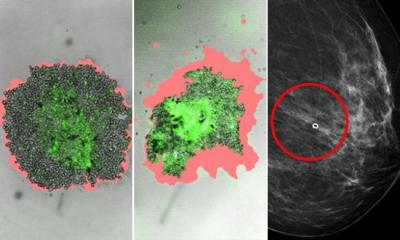
Researchers identified how to kill therapy-resistant cells in hypoxic tumors and in cells arising in the von Hippel-Lindau hereditary cancer.

In a recent publication in PNAS, the Susanne Schlisio group at Department of Microbiology, Tumor and Cell Biology (MTC) in Collaboration with Cancer Center Karolinska (CCK) at Karolinska Institutet, the Edinburgh Cancer Research UK Centre, and the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute present their findings. Many strategies have been proposed to eradicate cancer cells that have become resistant to therapies. Despite substantial research in this area, relapse caused by drug-resistant cells occurs in most patients. Tumor hypoxia is a barrier to radiotherapy and chemotherapy in cancer. Despite substantial research in this area, resistant cells occur in most patients. They identified how to kill therapy-resistant cells in hypoxic tumors and in cells arising in the von Hippel-Lindau hereditary cancer.
Image credit: National Eye Institute, National Institutes of Health
VHL disease has an incidence of one in 36,000 births. There is over 90% penetrance by the age of 65. Age at diagnosis varies from infancy to age 60–70 years, with an average patient age at clinical diagnosis of 26 years. Tumors usually first appear in young adulthood. The types of tumors associated with VHL disease include hemangioblastomas (slow-growing tumors of the central nervous system); kidney cysts and clear cell renal cell carcinoma (most common death in these patients); pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors and pheochromocytomas. The identification of HIFα as a VHL substrate provided the first and direct link between tumor suppressor function and oxygen sensing (27634319, Cell 2016).
However, regulation of HIFa by VHL could not explain the complex genotype-phenotype manifestation within the VHL disease. In this project the researchers try to resolve the conundrum created by type 2C VHL mutants, which cause pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma despite repressing HIFa, and provide further insights into the link between pheochromocytoma and mutations that impinge upon neuronal apoptosis. They describe a novel oxygen sensing pathway that is abolished by VHL type 2C mutations. VHL type 2C mutants fail to bind to the hydroxylated pro-apoptotic protein BIM-EL, despite their ability to bind hydroxylated HIFa.
The study provides evidence that pheochromocytoma linked to VHL mutations are caused by defects in EglN3-induced apoptosis because of a failure to stabilize BIMEL. By unraveling the precise molecular mechanism of BIM-EL stabilization by VHL and EglN3, the researchers provide further insights into the chemoresistance that is typical of tumors lacking VHL or oxygen. They identified an acquired vulnerability to treat therapy-resistant tumors arising in the von Hippel-Lindau hereditary cancer syndrome. Combinatorial treatment using ERK kinase inhibitor resensitizes VHL- and EglN3-deficient cells that are otherwise cisplatin resistant.
Source: Karolinska Institutet
08.08.2019