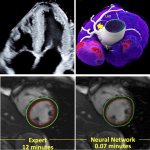
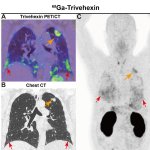
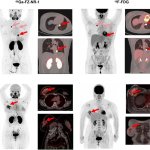
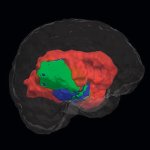
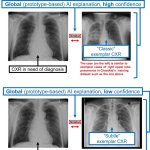
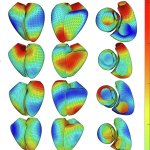
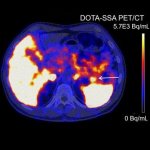
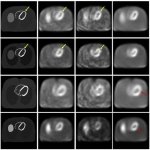
News • Common comorbidity
Researchers find genetic link between type 2 diabetes and hypertension
Type 2 diabetes and high blood pressure share a genetic link, new research from the UK and France shows. People with one condition are more likely to develop the other.