Image source: Radboud University
News • Ultrahigh field strength
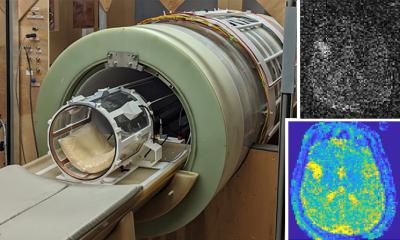
14 Tesla: Researchers to build world's strongest MRI scanner
A consortium of seven partners, led by the Donders Institute for Brain, Cognition and Behaviour (Radboud University), has received a €19 million Roadmap grant from the Dutch Research Council (NWO). It will be used to build the world's first MRI scanner with a magnetic field strength of 14 Tesla in Nijmegen.
Every two years, the Dutch Ministry of Education, Culture and Science makes funds available to NWO for the National Roadmap Large-Scale Research Infrastructure. This enables the construction or renewal of essential research infrastructure in the Netherlands. In the DYNAMIC project, researchers will build the world's first MRI scanner with a magnetic field strength of 14 Tesla. The scanner's high sensitivity will allow scientists to image the brain in more detail and thereby better understand brain function, but will also enable them to gain new insights into mechanisms of diseases and their treatment throughout the body.
'The new MRI scanner will be placed in on the Nijmegen campus, but the scanner will be a tremendous resource for the Dutch scientific community and collaborate with international partners,' stresses David Norris, project leader and Professor of Magnetic Resonance Physics at the Donders Institute of Radboud University. 'With this new sensitive scanner, we intend to open new areas of research for the entire scientific community.'
We expect that the new 14 Tesla MRI-scanner will revolutionize non-invasive neuroscience by enabling the mapping of neural circuits in humans at an unprecedented level of spatial resolution
Elia Formisano
The new scanner is of great importance for research into brain disorders, explains Anja van der Kolk, neuroradiologist/clinician-scientist at Radboud university medical centre. ‘The number of people with brain disorders is large and will only increase in the upcoming years. For many of these disorders no effective treatment is currently available, because we do not know how they develop. With the 14T MRI-scanner, we will be able to see in great detail, without needing surgery, what happens to the brain when it becomes ill, even at an early stage. With this information we hope to find new options for treatment, or even prevention, of these disorders.’
On the importance of this new scanner for the field of medicine, Dennis Klomp, professor in High precision structural and metabolic imaging at UMC Utrecht says: ‘This world's strongest MRI provides us a unique non-invasive window inside the human body to see metabolism in diseases and how this can be influenced by medication. Using the high spectral and spatial resolution of the 14T MRI, we will study the effect of new treatments in heterogeneous tissues like tumors.’
For the field of neuroscience ‘we expect that the new 14 Tesla MRI-scanner will revolutionize non-invasive neuroscience by enabling the mapping of neural circuits in humans at an unprecedented level of spatial resolution. This highly detailed data will be essential for testing existing models of neural computation and for developing and refining novel, more realistic models’, says Elia Formisano, professor for Neural Signal Analysis at Maastricht University.
The Dutch National 14Tesla MRI Initiative in Medical Science (DYNAMIC) is initiated by a consortium of seven partners: Radboud University (responsible institution), Amsterdam Medical Centre (AMC), Leiden University Medical Centre (LUMC), Maastricht University, Radboud University Medical Centre, Spinoza Centre for Neuroimaging – KNAW and University Medical Centre Utrecht (UMCU).
A total of nine projects will receive 140 million euros from NWO to set up or improve large-scale scientific infrastructure. 'Investments in large-scale infrastructure contribute to the international position of the Netherlands as a knowledge economy. Science and research cannot do without the right scientific infrastructure,' said Minister Robbert Dijkgraaf (OCW).
Source: Radboud University
20.02.2023