Image source: Vall d’Hebron Institute of Oncology
News • Voxel-wise classification
Deep learning tool uses MRI to enhance brain tumor diagnosis
Jointly developed by investigators of the Vall d’Hebron Institute of Oncology’s (VHIO) Radiomics Group and the Bellvitge University Hospital’s Neuro-Radiology Unit, the Diagnosis in Susceptibility Contrast Enhancing Regions for Neuroncology (DISCERN) is an open access, deep learning tool based on the training of patterns using artificial intelligence models from information of standard magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Published in the journal Cell Reports Medicine, results of a VHIO-led study demonstrate the feasibility and accuracy of DISCERN as an enabler of accurate brain tumor diagnosis from perfusion MRI, outperforming conventional methods.
Glioblastoma multiforme, brain metastasis from solid tumors, and primary central nervous system lymphoma account for up to 70% of all malignant brain cancers. Given that each of these malignancies require a distinct therapeutic approach, differential diagnosis between these different malignancies represents an unmet clinical need. “The non-invasive differential diagnosis of brain tumors is currently based on the assessment of magnetic resonance imaging before and after contrast administration. However, a definitive diagnosis often requires neurosurgical interventions that compromise the quality of life of patients,” said Raquel Perez-Lopez, Head of VHIO’s Radiomics Group and corresponding author of this present study.
Validating this deep learning tool in more than 500 additional cases, results of this present study demonstrate 78% accuracy in the classification of these tumors, surpassing conventional methods
Raquel Perez-Lopez
“This work is the result of more than five years’ research focused on the identification of innovative magnetic resonance perfusion imaging biomarkers to enable the differential diagnosis of brain tumors. This present study integrates insights generated by other previous research projects on artificial intelligence, resulting in the development of software that automates presurgical diagnostic classification with very good precision, while facilitating its clinical applicability with a user-friendly interface for clinicians,” added Albert Pons-Escoda, a Clinical Neuroradiologist and Investigator of the Neuroradiology at the Bellvitge University Hospital, and co-author of this study.
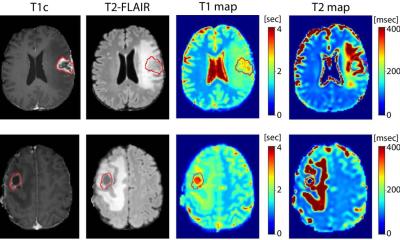
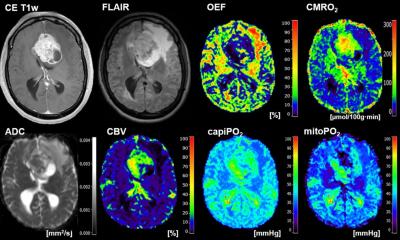
This novel deep learning tool leverages the full spatial and temporal information of conventional MRI to identify behavioral patterns on imaging specific to each tumor. “Deep learning teaches the machine the characteristics of each tumor detected by magnetic resonance imaging of already diagnosed patients. For example, if we show the machine thousands of images of dogs and cats, it will learn the distinct and defining characteristics of both species, and when it sees a new image, it can differentiate between the two,” added Alonso García-Ruiz, a PhD Student of VHIO’s Radiomics Group and first author of this study.

Image source: Vall d’Hebron Institute of Oncology
In this case, the learning units are voxels which represent the minimum measurement of volume to study MRI scans and are equivalent to pixels, but three-dimensional display elements. The investigators trained DISCERN to learn the characteristics of these three most common brain malignancies on 50,000 voxels from 40 diagnosed patients. “Validating this deep learning tool in more than 500 additional cases, results of this present study demonstrate 78% accuracy in the classification of these tumors, surpassing conventional methods,” observed Perez-Lopez
“DISCERN is a computerized diagnostic support tool that facilitates the classification of brain tumors to help guide medical decision making by multidisciplinary teams regarding the need for and type of surgery required to confirm diagnosis,” said Carles Majós, Clinical Neuroradiologist and Investigator of the Neuro-Rdaiology at the Bellvitge University Hospital, and a co-author of this study.
To enhance study reproducibility and accelerate its adoption in clinical studies, the proposed method developed by VHIO’s Radiomics Group, in close collaboration with investigators of HUB’s Neuro-Radiology Unit, has been implemented on the user-friendly, open access DISCERN application. For demonstrative and research purposes, the DISCERN app can be accessed here.
This study was carried out in collaboration with colleagues at the Neuro-Radiology Unit of the Bellvitge Biomedical Research Institute – IDIBELL and Clínic Hospital (Barcelona, Spain), and HT Medica (Andalucia, Spain), and Radiation Medicine and Applied Sciences and Bioengineering Departments of the University of California (San Diego, USA). This work has been carried out thanks to the support received from the CRIS Cancer Foundation, FERO Foundation, and “la Caixa” Foundation, which fund research of VHIO’s Radiomics Group through various initiatives.
Source: Vall d’Hebron Institute of Oncology
13.03.2024