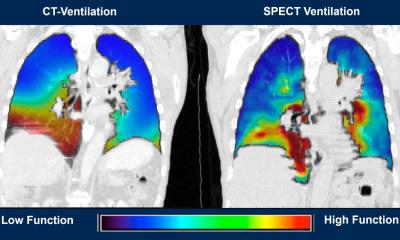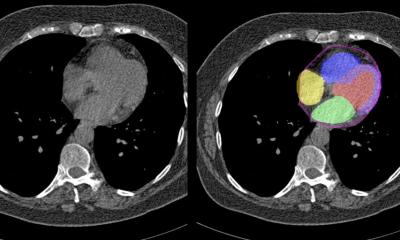
© H_Ko – stock.adobe.com
Article • Medical imaging
Contrast media utilisation: trends and breakthroughs
Striking the balance between diagnostic efficacy and patient safety remains critical when utilising iodinated contrast media to deliver the best imaging outcomes. Currently, 300 million CT exams are conducted across the world every year, with 40% contrast-enhanced exam. While playing a crucial role in diagnosis and treatment of disease, CT expert Efthimios Agadakos believes the medical profession has a duty to do its utmost to minimize patient risk from contrast media.
Report: Mark Nicholls

A session at ECR 2024 in Vienna heard about latest developments, trends and breakthroughs in contrast media utilisation in CT, MRI and ultrasound imaging, and explored the question of how dosage may be further lowered using modern protocols. Focussing on CT imaging, Agadakos offered insights into approaches he feels can contribute to enhanced patient safety and better-informed clinical decisions.
As Chief Radiographer at Laiko General Hospital in Athens, he highlighted the role of imaging in modern clinical practice, offering invaluable diagnostic information across a wide spectrum of medical specialities. ‘It can improve visualisation of anatomy and pathology, enhance lesion detection and vasculature, identify ischemic conditions, enhance surgical planning and guidance as well as monitoring treatment response,’ he said. ‘But it is imperative to acknowledge the associated risk of iodine in contrast media.’
Why a lower dose matters
Risks from radiation levels and adverse reactions mean that optimal iodine delivery is pivotal in yielding precise and reliable diagnosis, while maintaining patient safety and healthcare efficiency. Agadakos said that lower iodine dose can reduce risk of allergic reactions and contrast-induced nephropathy, decrease vascular complications, enhance patient comfort and experience, minimise radiation exposure, and optimise resource utilisation. Protocols can also be adapted for children, the elderly and for patients that need repeat CT scans.
The expert went into detail on a range of options that can be applied to help reduce iodine dose when using CT. These include tube voltage selection (automated or manual), iterative reconstruction algorithms, cinematic rendering, Dual Energy CT, AI applications, Photon-counting CT, personalized protocols and smart injection systems. ‘Iterative reconstruction algorithms enable the use of lower tube currents or voltages, driving lower iodine doses without diagnosing compromising diagnostic accuracy,’ he told delegates.1
One study using a low KV and low iodine dose with abdominopelvic CT achieved a 40% iodine dose reduction and 50% radiation dose reduction.2 ‘Meanwhile, dual-energy CT allows for better iodine contrast enhancement at lower doses, thus reducing the total iodine load on the patients,’ added Agadakos.3
Perfect timing
Artificial Intelligence applications assist in reducing need for IVCM (intravenous contrast media) by analysing patient data such as weight, age, renal function and medical history to tailor personalized contrast doses for optimal imaging, and minimise the contrast-induced risks.4
Machine learning algorithms can predict the required iodine dose and flow weight, select low KV or dual-energy CT scanning based on individual patient characteristics. When using personalized protocols, he said bolus triggering is a “must” with contrast-enhanced CT as it facilitates ‘perfect timing for contrast enhancement, produces accurate imaging and reduces the need for higher iodine concentrations.’ Meanwhile, photon counting CTA facilitates lower iodine dose by enhancing the detection of contrast media, particularly in small vessels, he added.5
Recommended article
News • Angiography advances
Photon-counting CT enables lower contrast media for aortic imaging
Photon-counting detector CT reduces the amount of contrast needed for CT angiography (CTA) while maintaining image quality, according to a new study published in Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging.
Finally, advanced contrast injectors equipped with intelligent technologies offer precise management of contrast administration. Agadakos said the aim is to strike a balance between diagnostic efficacy, image quality and patient safety and comfort. ‘By embracing the latest advancements in CT technology and adopting tailored strategies for iodine dose reduction, we can push the boundaries of diagnostic excellence while prioritizing patient safety,’ he continued. ‘But we must continue to collaborate, innovate, and elevate the standard of patient-centred care in medical imaging, ensuring that every patient receives the highest quality of care and a positive and reassuring experience in the CT department.’
The session also heard from Peter Murphy, Unit Manager, MRI, PET CT & DXA, Alliance Diagnostic Medical Imaging Ireland and Cork University Hospital about current issues with Gadolinium-Based agents with MRI, and Barbara Kraus from Wolkersdorf, Austria, speaking on indications and protocols for ultrasound contrast agent administration.
Profile:
Efthimios Agadakos is the chief radiographer of the Medical Imaging Department at Laiko General Hospital, Athens, Regional Director Europe ISRRT (International Society of Radiographers and Radiological Technologists) and President of the Panhellenic Society of Radiological Technologists Greece. His areas of interest are in CT, radiation protection and patient safety. Awarded a MSc in Health Services Management from the National School of Public Health in Athens, he is currently completing his PhD thesis in Medicine at the University of Athens on low radiation dose protocols in CT.
References:
- Lee T, Seeram E: The Use of Artificial Intelligence in Computed Tomography Image Reconstruction: A Systematic Review; Radiology Open 2020
- Araki K et al.: Low-voltage (80-kVp) abdominopelvic computed tomography allows 60% contrast dose reduction in patients at risk of contrast-induced nephropathy; Clinical Imaging 2018
- Tabari A et al.: Reducing Radiation Dose and Contrast Medium Volume With Application of Dual-Energy CT in Children and Young Adults; American Journal of Roentgenology 2019
- Azarfar G et al.: Applications of deep learning to reduce the need for iodinated contrast media for CT imaging: a systematic review; International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery 2023
- Higashigaito K et al.: CT Angiography of the Aorta Using Photon-counting Detector CT with Reduced Contrast Media Volume; Radiology. Cardiothoracic Imaging 2023
08.03.2024