Image source: Unsplash/Ryan Cryar
News • Neurology
The 'thermostat' that prevents our brain from overheating
The mechanisms by which the body measures temperature and regulates its own body heat are vital, but still poorly understood. The discovery of the first heat sensor on nerve cells in the skin, for which the U.S. molecular biologist David Julius received this year's Nobel Prize for Medicine, was therefore pioneering.
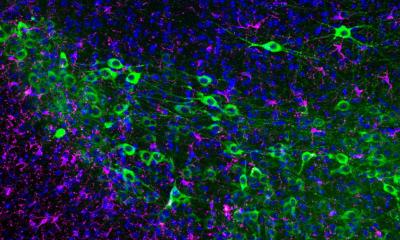
However, a very similar heat sensor, the protein TRPM2, is active not only in the skin, but also in the brain , as scientists from the Pharmacological Institute at Heidelberg University Hospital have already discovered. Now they have further elucidated the mechanism surrounding the sensor protein TRPM2 in mice and published their findings in the scientific journal "Neuron". They showed: TRPM2 is "outsourced". It does not sit on the heat-sensitive neurons themselves, but is distributed more widely at the contact sites of neighboring neurons. This means - technically speaking - more adjustment options on the body's own thermostat.

Image source: Heidelberg University Hospital
"Placing the heat sensors at the sites of signal transmission between the nerve cells, the synapses, allows fine-tuning of thermoregulation," explains research group leader Prof. Jan Siemens, PhD, who spent four years conducting research in Nobel Prize winner Julius' lab at the University of California, San Francisco. Synapses are wafer-thin, widely ramified cell extensions through which nerve cells make contact with their neighbors and transmit signals from one cell to another. In the hypothalamus, the brain region that acts as a thermostat, when the temperature rises, TRPM2 on the surface of these synapses itself triggers a signal to the heat-sensitive nerve cells, as the scientists discovered to their surprise in experiments with cells from this brain region.
Surprisingly, TRPM2 plays no role inside the neurons that are actually heat-sensitive. "Whether heat-sensitive neurons pass on the signal to cool down and with what urgency probably results from the sum of all incoming activating and inhibitory signals from the network," Siemens surmises. "This is because, for example, signals on energy balance or hormone status, which also have an influence on thermoregulation, arrive simultaneously and are offset against each other." Thanks to the outsourced heat sensors, it is not the limited number of heat-sensitive neurons that determines heat sensitivity, but the entire network of surrounding neurons. This makes thermoregulation more adaptable to individual needs, he said.
If the temperature in the brain exceeds a value that is still healthy for the body, the hypothalamus, or more precisely its preoptic region, gives the signal to cool down. If the current body temperature deviates from the set point, which can differ slightly from species to species, the body initiates appropriate countermeasures. In 2016, the team led by Prof. Siemens found the first heat sensor in the form of the protein TRPM2, which enables the body's own thermostat to detect impending overheating at all: TRPM2 causes calcium to flood into the synapses in mice from around 39 degrees Celsius, as it probably does in humans, and sets a signaling chain in motion that ultimately leads to the body dissipating heat, for example through dilated blood vessels in the skin. The exact processes are still poorly understood. The findings from Heidelberg are helping to elucidate the mechanisms piece by piece.
Source: Heidelberg University Hospital
25.10.2021