Image source: Adobe Stock/Mark Kostich
News • Clinical trial
Prostate cancer: Researchers explore new radiotherapy approach
A different way of treating people with prostate cancer will be investigated by researchers at the University of Leeds in a new clinical trial funded by Yorkshire Cancer Research.
The £1.1 million study will explore how radiotherapy can be made more effective for men whose cancer has come back following an initial course of treatment intended to cure it.
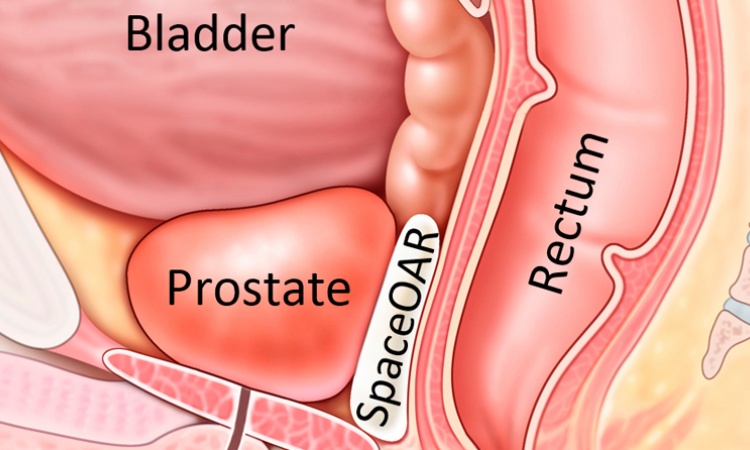
Although treatment for prostate cancer is usually successful, the cancer can sometimes return in the pelvis. When this happens, men are normally treated with very precise beams of radiation that directly target the cancer cells. However, even after this follow-up treatment, cancer can develop in other parts of the pelvis and go on to spread throughout the body.
Our new clinical trial will test whether treating a wider area of the pelvis with radiotherapy works better and can be introduced as a routine option for patients
Ann Henry
Researchers will find out if treating a wider area of the pelvis with radiotherapy, and not just the part that is directly affected by the cancer, is better at stopping the cancer from spreading. The trial, involving patients being treated at hospitals in Leeds, Sheffield and Hull, will be led by Dr Ann Henry, Associate Professor in Clinical Oncology in Leeds’s School of Medicine. She said: “Men in Yorkshire are more likely to be diagnosed with prostate cancer at a late stage when the cancer is more advanced and often more difficult to treat. This means there is a higher risk of the cancer coming back after treatment. The normal course of radiotherapy for cancer that has returned aims to target and kill only the visible cancer cells. If there are microscopic traces of cancer that remain undetected in the pelvis, these can be left to spread to other parts of the body. Our new clinical trial will test whether treating a wider area of the pelvis with radiotherapy works better and can be introduced as a routine option for patients.”
The standard course of radiotherapy is usually given in three to five treatment visits. This alternative method is usually given in 20 treatment visits, but the research team will test if it could also be given in five visits without increasing side effects. Dr Henry continued: “If the trial is successful, this treatment could be routinely offered across Yorkshire and beyond, giving patients access to a new standard of care. Being able to deliver the treatment in just five hospital visits will also offer more convenience to those taking part, increasing the number of patients who are able to take up this option.”
In Yorkshire, 4,300 men in Yorkshire are diagnosed with prostate cancer each year, making it the most common cancer among men living in the region. The new research is part of a wider £7.3m investment by the charity in new programmes across Yorkshire.
Source: University of Leeds
04.05.2022