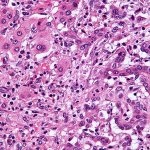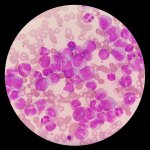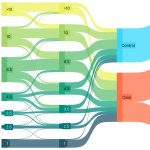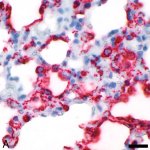
News • Tissue sample analysis
Demographic bias creeps into pathology AI, study finds
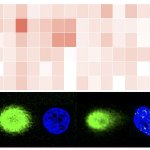
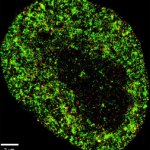
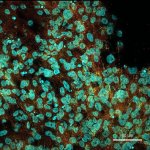
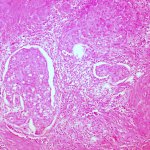
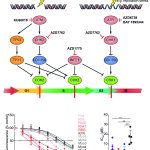
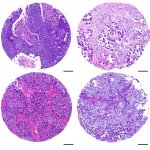
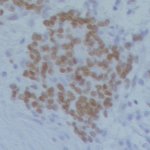
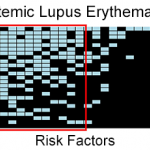
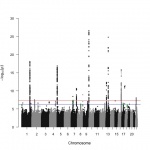
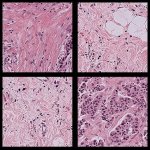
A sample of inequality: A new study shows that AI models can infer demographic information from pathology slides, leading to bias in cancer diagnosis among different populations.