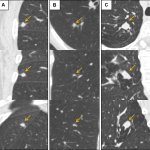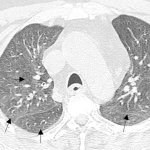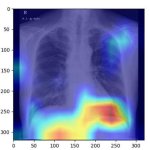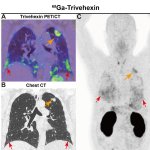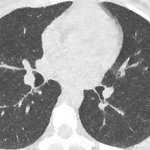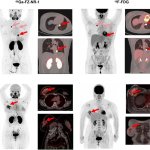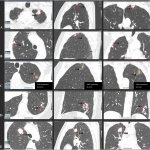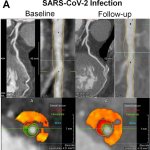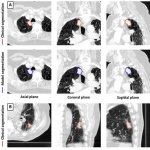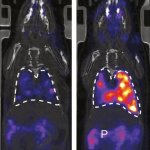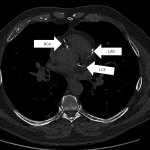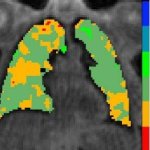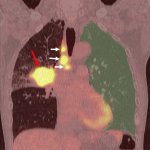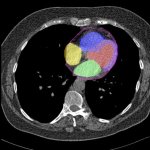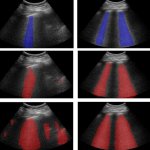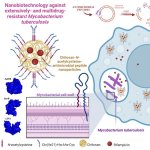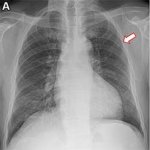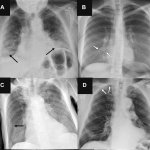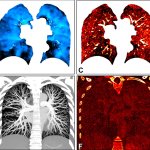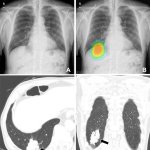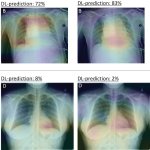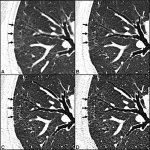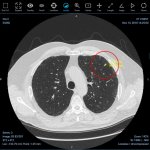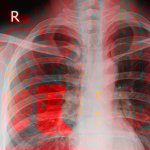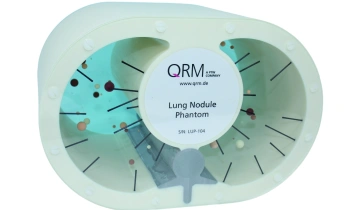
QRM Lung Nodule Phantom
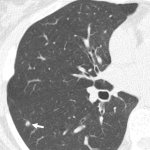
For the verification of lung-dose screening programs For the detection of various lung nodules within the lung regionFor covering diverse imaging scenarios with respect to nodule typeand grey value (e.g. ground glass opacity)For the evaluation of algorithm performance across heterogeneouspatient datasetsFor the development and validation of robust computer-aided detection and diagnosis…