
News • Rehabilitation medicine
TBI: study reveals lasting impairments
People who suffer from a traumatic brain injury (TBI) often have lasting difficulties returning to work and may need long-term, multidisciplinary care, a new study shows.

People who suffer from a traumatic brain injury (TBI) often have lasting difficulties returning to work and may need long-term, multidisciplinary care, a new study shows.

Not all cancer mutations are equal: new research shows that a single mutation hotspot can generate a rich diversity of tumour behaviours. This could lead to more personalised cancer treatments.
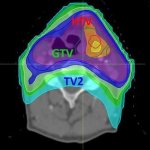
Beyond "one-size-fits-all": A new strategy that combines two types of PET scans can guide personalized radiotherapy for head and neck cancers, according to new research.
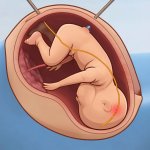
Northwestern University researchers have developed the first device that can continuously track a fetus’s vital signs while still in the uterus — a feat that previously has not been possible.

Why does Huntington’s disease begin at very different ages? Using advanced AI techniques, neuroscientists from the University of Barcelona found a way to better answer this question.
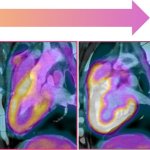
A widely used chemotherapy drugs used in cancer treatments can cause heart damage, new research shows. This could be used to adapt treatment regimens - especially in patients with high blood pressure.

Scientists have overturned a long-held belief in genetics: that inheriting two harmful variants in the same gene always worsens disease. Instead, this can actually restore normal protein function.

TV depictions of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest may mislead viewers about who is most likely to need cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and where it’s needed, new research reveals.

Gene-editing technologies show great promise for medical treatments and research, with the potential to cure thousands of genetic diseases. At the 2025 World Medical Innovation Forum in Boston, leading experts explored the possibilities and challenges of these rapidly advancing tools. The case of Baby KJ Muldoon – an infant treated with a personalised CRISPR therapy developed in just seven…
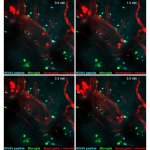
Scientists from Northwestern University have developed an injectable regenerative nanomaterial that helps protect the brain during the vulnerable window after a stroke.
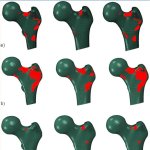
To predict the risk of hip fracture, only 7% of the bone mass needs to be analysed, a new study finds. Scientists have identified these critical areas to improving diagnostic methods.

A simple blood test that can very accurately predict the chance of survival with good recovery could be of great significance for patients in intensive care after a cardiac arrest.

A first-of-its-kind study could lead to quicker and more targeted support for vulvodynia - a painful chronic condition estimated to affect more than one in 10 women with no known cause.

Facing a mental health crisis, more and more people turn to chatbots and AI characters. While they offer new possibilities, they also pose great risks, especially for vulnerable users, experts warn.

Many women over 50 schedule mammograms for breast cancer but miss out on CT lung cancer screenings they're also eligible for. Targeted outreach coul help change this, a new study shows.

At the 2025 Journées Francophones de Radiologie (JFR), novelist, diplomat, and physician Jean-Christophe Rufin took the stage to remind an audience of radiologists that medicine, at its core, is a human story – one that needs to be told, felt, and shared. Beneath the cold light of MRI scanners and the hum of technology, he reintroduced something fragile yet essential: empathy.
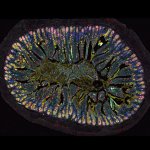
New insights into the intestinal nervous system – or "gut brain" – open new avenues for advancing therapies for allergies, chronic inflammatory bowel diseases and irritable bowel syndrome.
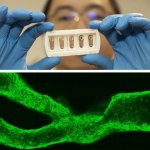
Researchers have developed a new 3D printing technique for blood vessels on glass. This could be a tool for studying stroke causes and testing patient-specific medications without animal testing.
Philips and Cortechs.ai have extended their collaboration to integrate AI-enabled quantitative neuroimaging analytics directly into MR systems. The partnership aims to provide radiologists with automated, objective measurements of brain structures and lesions to support diagnosis and monitoring of neurological conditions.

University of Delaware researchers use robotic testing to spot an often overlooked sensory deficit in stroke survivors – proprioception, the body's ability to sense movement and position.

A new study shows how AI could transform medical education, while calling for stronger collaboration across schools, hospitals, and regulators to make it safe, responsible, and effective.
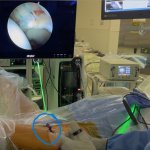
Engineers have developed a new surgical device for hip arthroscopy which they hope will completely change procedures in the hip region, making them safer and more efficient than before.
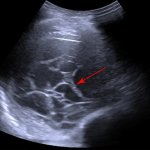
Has organ imaging using ultrasound arrived at the same level as cross-sectional imaging? At the annual conference of the German Society for Internal Medicine (DGIM), PD Dr Corinna Trenker presented new technological developments and their diagnostic significance. Despite numerous innovations such as multiparametric protocols and AI support, she made it clear that the human factor remains one of…

Not all PCOS is the same: Researchers identified four subgroups with distinct symptoms and different responses to treatment – opening the door to precision medicine for millions of women worldwide.

Climate change is claiming millions of lives every year, a new global report finds. The rate of heat-related casualties alone has climbed to 546,000 per year – more than one death every minute.

Newly discovered blood biomarkers may offer new options to track Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) in a less invasive way than physical tests or biopsies. This could support more tailored treatments.

Researchers identified a targeted way to protect the brain from harmful side effects of cranial radiation therapy, potentially preserving the quality of life for millions of brain cancer survivors.
A novel imaging solution, called PSMA PET scanning, can more effectively detect the recurrence of prostate cancer compared to standard methods, and is associated with improved survival outcomes.
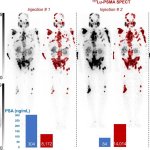
A new type of SPECT imaging provides strong prognostic information to guide prostate cancer treatments according to tumor evolution, significantly impacting patients' overall survival.

An expert summit for craniomaxillofacial (CMF) care brought together leading surgeons to explore how digital technologies are reshaping surgical planning, precision, and patient outcomes.

Chronic fatigue (ME/CFS) affects millions worldwide, but is poorly understood and has long lacked reliable diagnostic tools. Now, a new blood test claims to diagnose the condition with 96% accuracy.

Stroke patients in four NHS hospitals are now receiving genetic tests that determine whether a commonly prescribed drug will work for them – a breakthrough that could transform treatment for millions. Digital approaches are spearheading a drive to help make genomic medicine part of everyday care. The role of digital tools was a central theme at the HETT (Healthcare Excellence Through…

This year, the Journées Francophones de Radiologie (JFR) will carry a clinical ambition as simple as it is essential: to shine a spotlight on those who are often overlooked. Under the presidency of Professor Mathieu Lederlin, thoracic radiologist at Rennes University Hospital, vulnerable patients will be at the heart of the annual meeting of the French Society of Radiology that will unfold…

Asking people how much money they would accept to experience pain again can provide a more accurate and comparable measure of pain levels than the familiar 1–10 scale, according to new research.

Children with asthma using at-home monitoring are around half as likely to visit the ED or be hospitalised, compared to those only receiving care from their medical team, new research shows.
Hospitalists frequently discuss the risks associated with tests, treatments, and/or surgical procedures with their patients. But is everyone in the clear on what a “slight risk of complications” actually means? A session on the meaning of risk to patients and how to effectively communicate risk was discussed at SHM Converge 2025, the annual meeting of the Society of Hospitalist Medicine held…

International research led by Leipzig and Ulm universities creates first standardized leptin reference values for all ages and weight classes, advancing personalized medicine
Study of 3.7 million children reveals small but significant increased risk of blood cancers from medical imaging radiation, with CT scans posing highest risk

University of Stuttgart scientists develop enhanced CRISPR technique that makes genetic loss-of-function analyses more efficient and reproducible for medical research.

An ultrasound examination performed by a robot can cause distress in some patients. Munich researchers have now developed a VR avatar system that makes the process feel more human.

Wrong equipment, inadequate posture, unusual behavior: Only 1 in 7 online stock photo images of blood pressure monitoring correctly show how blood pressure should be measured, a new study finds.

Systematic screening and support for mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, or PTSD should become normalised in cardiovascular care, cardiologists urge in a new Consensus Statement.

The European Society of Cardiology (ESC) has awarded Roxana Mehran, MD, from Mount Sinai, with its top honor, the “ESC Gold Medal”, during a special ceremony at the ESC Congress in Madrid.
A novel procedure at UC San Diego Health uses a combination of artificial intelligence and 3D printing to develop a customized implant for the spine during fusion surgery.
Patient communication facilitated by chatbots, image quality optimized by machine learning: Artificial intelligence (AI) is entering radiology at breakneck speed, transforming the specialty almost beyond recognition. So, how will the future of diagnostic imaging under AI look like, and which role will humans still play in it? At the ECR congress in Vienna, experts explored the societal and…

The mere fact of being exposed to a sick avatar in a virtual reality environment triggers a measurable immune response in humans, a multidisciplinary research team discovered.

Breastfeeding women often choose not to take their medications because they worry about their baby; or stop breastfeeding because of their medicines. However, new research suggests that this is often unnecessary.

Type 2 diabetes greatly increases the risk of heart attacks, strokes, anginas, and other coronary heart diseases. Therefore, biomarkers to predict individual risk are needed, experts say.

A new ventilation mode called proportional assist ventilation (PAV+) could improve outcomes for patients in the intensive care unit (ICU) who require help breathing, a new study finds.

When should preventive mastectomy be offered for women at higher risk of breast cancer? A new evaluation model defines thresholds at which risk reducing surgery should be recommended.

Saving money, at a cost: To undergo bariatric and weight reduction surgery, more and more patients turn to institutions outside their home country – potentially putting their health at risk.

At Medical Taiwan 2025, manufacturers attracted attendees with a wide range of innovations. We took a closer look at some of the most exciting companies and their products on display at the medical, health and care expo.

An implantable device could save diabetes patients from life-threatening hypoglycemia. Remaining under the skin, it can be triggered to release glucagon when blood sugar levels get too low.

Medical Taiwan has long been a showcase for cutting-edge healthcare solutions, but this year marked a pivotal moment. Visitors of the latest edition of the medical, health and care expo in Taipei witnessed a particularly noticeable step forward: the definitive transition of medical AI from promising research to actual clinical practice. Organized by the Taiwan External Trade Development Council…

Starting fecal immunochemical testing (FIT) early significantly reduces both the incidence and mortality of colorectal cancer. These results of a new study support earlier screening.

Too many medicines, too many hospital visits: Inappropriate polypharmacy is a major driver of emergency hospital admissions among adults aged 65 and over, according to a new study.

Molecular markers in saliva could reveal the risk of a person developing major diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes and neurodegenerative diseases, new research finds.
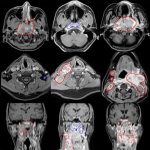
Molecular profiling of over 1,000 nasopharyngeal cancer (NPC) tumours reveals distinct differences in tumour microenvironment of locoregionally advanced NPC, supporting personalised treatment.

Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death in the EU, yet no organized screening program exists to detect the disease before symptoms appear. This September, France will strike back with an ambitious pilot program that could boost European lung cancer screening. Professor Marie-Pierre Revel presented the details at the French Thoracic Imaging Society Spring Days in Marseille, highlighting…

What if every radiographer could help combat climate change while performing their daily work? Following the congress theme of ECR 2025, experts revealed how small changes – from education initiatives to simple workflow adjustments – can collectively transform the environmental impact of radiology.
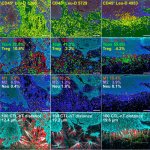
Tongue squamous cell carcinoma, the most common type of oral cancer, is a challenging target for immunotherapies. Researchers now identified five immunotypes to better predict treatment response.

Microbiota composition can help prevent pathogenic bacteria from proliferating, known as the barrier effect. Now, scientists have identified seven bacteria involved, paving the way for new therapies.

Newborns, especially those born prematurely, are vulnerable to conditions such as sepsis. A new device profiles an infant’s immune function from a single drop of blood to improve neonatal care.

Nuclear medicine specialist Daniela Oprea-Lager has been appointed Professor of Theranostics at Radboudumc / Radboud University. Her research focuses on the combination of diagnostics and treatment using radioactive substances, with particular interest for urological tumors, especially prostate cancer.

When it comes to breast cancer, ethnic differences matter, putting some women at a significantly higher risk, a new study finds. Genetic ancestry should therefore be considered as a risk factor.

From personalized medical guides and implants to advanced surgical planning solutions: 3D printing and visualization has seen considerable growth over the past years and is already making a significant impact in healthcare. AI, cloud, and virtual/augmented reality technologies show promise to further advance the number of applications.

Does having blood type A increase the risk of breast cancer? A new systematic review and meta-analysis involving more than 13,000 breast cancer patients suggests a connection.

People at risk of cardiovascular disease could be identified a decade before they have a heart attack or stroke, a new University of Dundee study has discovered.
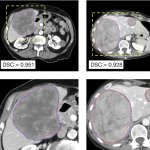
Results of a new retrospective study demonstrate the potential of a novel, CT-based deep learning-driven tool to enhance liver cancer diagnosis, treatment planning, and response evaluation.

Researchers from Université Laval discovered that the retina of people with Parkinson's disease responds differently to light than that of healthy people. This offers new diagnostic options.

A new approach enables the detection of even trace amounts of cancer cells. The method leverages SERS for signal amplification, eliminating the need for fluorescent dyes.

Molecular testing provides a more convenient, personalized way of monitoring of heart transplant recipients, according to insights shared at the Annual Meeting and Scientific Sessions of the ISHLT.
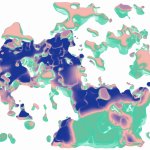
Unprecedented insights into the inner workings of an early-stage lung tumor: An international research team describes a new method for 3D mapping cellular interactions in the tumor microenvironment.

Working conditions for scientists in the field of medicine are becoming increasingly difficult in the USA. A new funding initiative offers outstanding scientists a new perspective in Germany.

Breast MRI has emerged as a powerful diagnostic tool, particularly for women with dense breast tissue where traditional mammography faces limitations. In her presentation at ECR 2025, radiographer Hanna Kalliomäki highlighted several technological advances transforming breast cancer detection and diagnosis. From time-saving abbreviated protocols and AI-assisted analysis to contrast-free…
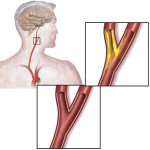
A risky carotid artery operation may no longer be necessary for patients who suffer a stroke due to carotid artery narrowing, research suggests. Instead, medication-only treatment may also be viable.

The new national Precision Omics Initiative Sweden (PROMISE) aims to generate and integrate extensive molecular data to create a model for precision medicine implementation for Sweden.

An international research team has developed an intelligent device capable of monitoring the skin continuously and accurately detect temperature variations associated with inflammation and infection.
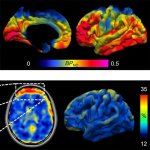
Using the COX-2 enzyme, a new PET imaging approach offers a never-before-seen view of inflammation in the brain, opening the door for clinical and research settings for various brain disorders.

Losing weight is a great way to improve one's overall health. But, are these benefits gone once a person is gaining weight again? Not necessarily, a new study points out.

Giving separated blood plasma improves outcomes in patients with traumatic brain injury (TBI) or shock, whereas unseparated or “whole” blood may be best for patients with traumatic bleeding.

Chronic pain is more common among women, but why is that? New research explores sex-specific differences in pain signal communication in the nervous system to help answer this question.
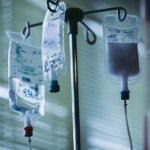
A new analysis of commercial IV fluid bags reveals that they often contain microplastics that, upon infusion, would enter the recipient’s bloodstream and potentially cause negative health effects.
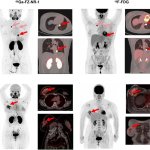
A new PET tracer has the potential to play a critical role in the diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of aggressive triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), improving clinical outcomes for patients.

The boom in interventional radiology procedures has enabled great strides in ischemic stroke management. But while a myriad of techniques are available, the challenge remains in choosing the most appropriate thrombectomy treatment on the spot, according to Jordi Blasco Andaluz, a neuroradiologist at Hospital Clinic Barcelona. The new ROSSETTI registry is designed to change this.

Nuclear cardiology is a specialised field in nuclear medicine that evaluates the heart function to help diagnosing conditions such as coronary artery disease and to assess treatment efficacy, whilst minimising invasive procedures like biopsies. More recently, clinicians have increasingly opted for nuclear imaging over endomyocardial biopsy to diagnose cardiac amyloidosis, allowing for earlier…

New research highlights the potential of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) analysis as a non-invasive method to identify actionable biomarkers for breast cancer, enabling individualized therapies.

Medical imaging has come a long way in the past four decades: Advances have been made in the digitization of images, but also towards more gender equality in a once male-dominated field. We talked with Katherine P. Andriole, Ph.D., a leading expert and one of the first women to enter the field, about the evolution of medical imaging informatics, experiences she has had, and her advice to those…

Microbiologists have just shown that people with diabetes are more likely to develop antibiotic-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus, a leading cause of AMR-associated infections and deaths.

Certain gene alterations can serve as a prognostic and predictive biomarker for prostate cancer. Now, researchers confirm the feasibility of using NGS on this marker for precise patient stratification and treatment selection.
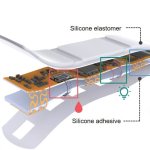
Researchers developed a smart patch capable of real-time biometric signal monitoring and drug delivery. Potential applications include glucose management, pain relief, and chronic disease treatment.
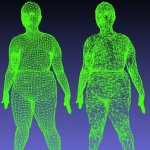
Using 3D imaging and deep learning AI, researchers have developed a new way to accurately assess body fat and muscle distribution, which are crucial for understanding health risks.

A new blood test that detects a specific brain protein may help doctors determine the type of a stroke faster and allow them to start safe treatment for people before they get to the hospital.

Self-reported, persisting health problems after Sars-CoV-2 infection are commonly described. However, the long-term prognosis of post-Covid-19 syndrome is unknown. A new study aims to change this.

The vaccine to protect against Hepatitis E is given in a 3-dose regimen. However, in an epidemic setting, two doses have also proven effective, a new study shows.

A new personalised oncology platform has been tested to detect circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA) in patients with lung adenocarcinoma before surgery, to predict their risk of cancer relapse.
Tongue cancer cells can become resistant to chemotherapy under certain circumstances. Investigating these mechanisms, researchers shed light on promising avenues toward new treatments for this cancer.
A premiere that brings hope for fertility restoration to men who underwent chemotherapy during childhood: Researchers reintroduced cryopreserved immature testicular tissue taken 16 years prior.

Can an AI determine whether or not a person drinks beer by looking at their knee X-rays? It can't – but the claim shows why “shortcut learning” is such a dangerous mechanism in medical AI.
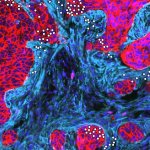
Research offers new insights into harnessing the immune system to combat ovarian cancer. The findings could lead to personalized therapies that target the right patients at the right time.

Experts have used magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to better understand the impact a gluten free diet has on people with celiac disease, which could be the first step towards new treatments.

Large language models (LLM) show promise in detecting hospital patients at risk of committing suicide. This could help warn medical staff in time while maintaining the patients' privacy.

In the world of theatre, the ‘deus ex machina’, the god from the machine, is a dramaturgical trick to resolve seemingly unsolvable conflicts. Can artificial intelligence (AI) also be such a universal problem solver for internal medicine? At the Annual Congress of the German Society of Internal Medicine (DGIM), Dr Isabella Wiest explored the potential – and limitations – of AI helpers.

Who should contribute to decisions about health care space design? A new publication discusses the benefits of professional diversity in hospital design working groups.

The current rise in antibiotic resistance is once again sparking interest in phage therapy. Now, scientists developed a new tool that recommends the best possible phage cocktail for a given patient.

“There’s nothing else we can do”, “Why did you wait so long to come?” – doctors should avoid using such phrases. A new study points out the destructive potential of “never words”.

Skills shortages and digitalization, trends in cardiology and oncology, future prospects in laboratory medicine, and healthy aging – these pressing topics are at the forefront of discussions at this year’s Medica Labmed Forum.

Women with type 1 or type 2 diabetes often have difficulty getting pregnant, due to complications from the disease, being obese or seriously underweight, or having conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome. Once pregnant, they face challenges of having a safe pregnancy and delivering a healthy baby. Recent advances in diabetes technology, including continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) and most…

Research shows a one-third chance of restoring blood circulation during cardiac arrest, regardless of whether the medication is administered into the bloodstream or bone marrow.
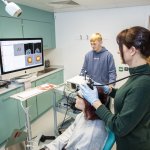
New research suggests that transcranial ultrasound stimulation (TUS) could be used to help people with pain, alcoholism, OCD, and Parkinson’s disease, without drugs or surgery.
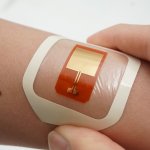
Rsearchers developed a novel bioelectronic device that taps into the natural electrical activity of certain bacteria found on our skin, paving the way for a drug-free approach to managing infections.
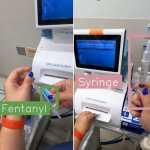
A newly-developed wearable camera system is designed to detect potential errors in medication delivery by identifying contents of vials and syringes with the help of deep-learning AI.

Immunotherapy has become the most promising strategy for treating several cancers, but its effectiveness is still very uneven. Three researchers explain how research is being done to change this.

A European research team has now shown that dietary measures are more effective in IBS patients with defects in carbohydrate digestion genes than in those without these changes.

The gut microbiome varies from person to person in terms of the bacterial species represented and their colonization density. Segatella copri is the most prominent germ. Researchers at the Helmholtz Centre for Infection Research goal to clarify its health significance.
A new study found that measuring circulating tumor cells (CTCs), rare cancer cells shed from tumors into the blood, is a reliable way to predict later treatment response and survival prospects with metastatic prostate cancer.
Minimally invasive surgical interventions, innovative imaging and the use of AI: At the upcoming EUSOBI congress in Lisbon, experts present and discuss the latest advances in breast imaging. We spoke with Tanja Brycker from Hologic ahead of the event about new trends in women’s health, the company’s investment in innovation and education, and what the future of mammography looks like with the…
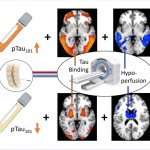
Researchers have identified biomarkers that, in conjunction with PET imaging, enable doctors to reliably distinguish between primary 4-repeat tauopathies and Alzheimer's disease.

A new type of magnetically controlled prosthetic hand allows amputees to reproduce all movements simply by thinking and to control the force applied when grasping fragile objects.

A US-Swiss team leverages AI and molecular simulations to uncover new pathways for precision cancer treatments, paving the way for more effective, personalized therapies.

A new method of analysing the crystals in dehydrated blood could lead to a quicker, cheaper and less painful technique to diagnose, early detect, and monitor prostate cancer.
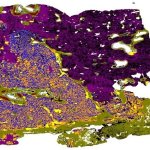
Cologne researchers have developed an AI-based digital pathology platform to enable extremely fast and accurate fully automated analysis of tissue sections from lung cancer patients.
New research sheds light on the tradeoffs between survival and time spent in inpatient care that dialysis might entail. This could help patients with kidney failure make more informed decisions.

Can a mouthwash-based test help predict head and neck cancer recurrence? A new study suggests it might.
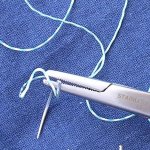
Korean researchers have developed a new type of 'smart' surgical suture that monitors the recovery process of a wound. This could improve orthopedic or general medical rehabilitation, the team hopes.
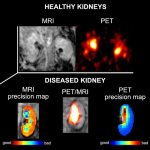
A new type of contrast agent for use in both MRI and PET imaging has the potential to significantly enhance diagnosis and subsequent treatment, particularly for kidney diseases and tumors.
A band-aid for the heart? US researchers have developed a new way to 3D print material that is at once elastic, tough, and shapable enough to fit a patient’s unique heart or joint defects.

The pace of artificial intelligence (AI) adoption in personalised medicine is unsettling for great parts of the public. A new survey reflects the worried state of mind in the UK.
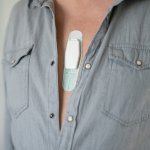
Diagnosis and monitoring medical conditions, including cancer, diabetes, heart disease, and infections: In this opinion article, Alix Joseph (Linxens) explores the potential of sweat analysis.
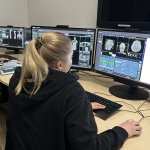
As opportunities for teleoperations rapidly expand within radiology, the concept is being deployed across an array of modalities to deliver more efficient healthcare. A range of speakers covered the topic of ‘Teleoperations in radiology’ at ECR2024, discussing its benefits in applications in MRI, ultrasound, during the social restrictions of the Covid-19 pandemic and military use. However,…
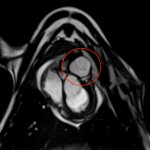
A new heart valve comprised of biological material obtained from human cells, opens up new therapeutic avenues for patients with paediatric heart diseases, such as tetralogy of Fallot.

Using advanced technology from the automotive and manufacturing industries, researchers are driving medical advancement to create ‘personalised’ hip replacements.

As demand for innovative healthcare solutions is at an all-time high, Medical Taiwan once again attracted a record number of visitors for its 2024 edition. The show’s organizer, the Taiwan External Trade Development Council (TAITRA), proudly reported an increase in attendance by 10% compared with the previous year. During the three-day event in Taipei, the audience was treated to a wide range…

The nuclear medicine global market is projected to see a significant increase in the coming years, with the lion's share being attributed to radiotherapeutics. So, how to set up a dedicated theranostics centre? At the annual meeting of the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) in Toronto, Ontario, an entire session was dedicated to planning logistics, radiation safety, and…

What is an advanced clinical practitioner (ACP) and why should nuclear medicine technologists strive to become one? At the 2024 annual meeting of the SNMMI in Toronto, ACP Luisa Roldão Pereira outlined the position and its importance in the clinical context.
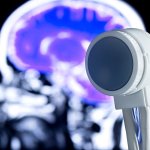
Researchers have developed a technology for targeted stimulation of the brain with ultrasound. This could be used to treat diseases and conditions such as epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, depression, addiction, and even the aftereffects of stroke.

Digital twin technology can transform clinical practice by aiding patient-specific prediction and supporting personalized treatment models. Expert speakers at an ECR 2024 session in Vienna focussed on how radiology will play a leading role in the advance through data acquisition via a range of imaging modalities.

For many, the term “metaverse” evokes images of VR headsets and the rebranded company behind Facebook – but can the digital parallel universe provide actual benefits for healthcare? Dr Anke Diehl has studied the technology intensively and recognises significant potential for medical applications. However, the expert for digital transformation at Essen University Medicine, Germany, cautions…

Researchers have succeeded in developing “pathoblockers” that provide protection against the most common pneumonia-inducing pathogens, even if they are resistant to antibiotics.

Researchers have developed a cutting-edge method for fabrication of customised pharmaceutical tablets with tailored drug release profiles, ensuring more precise and effective treatment options.

Blood cancer cells can remain in the blood of AML patients, even after chemotherapy seemed successful. Testing for these residuals before blood cell donation is a vital precaution, a new study finds.
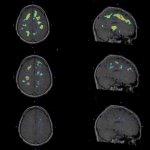
In some patients with multiple sclerosis (MS), symptoms worsen during treatment, but MRI scans do not indicate any change. In such cases, positron emission tomography could help, a new study suggests.

‘Computer, why did the doctor take that MRI scan of my leg? And what did it show?’: Popularized by OpenAI’s ChatGPT, generative artificial intelligence (AI) is already beginning to see practical applications in medical settings. The technology holds immense potential, with benefits for patients, clinicians, and even hospital administration, according to Shez Partovi, MD.
Researchers have developed a deep-learning model that predicts the transition from a normal cardiac rhythm to atrial fibrillation 30 minutes before onset, with an accuracy of around 80%.
Surgeons often suffer from back and neck pain, due to inadequate posture during surgery. A new study uses wearable technology to prevent muscoloskeletal conditions from cutting short medical careers.
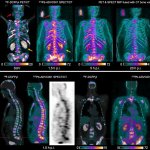
A new SPECT/CT imaging technique using lead-212 (²¹²Pb) shows promise in targeted alpha therapy (TAT) for patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.

Generalist Medical Artificial Intelligence (GMAI) models pose a significant challenge to current regulatory frameworks. Experts discuss how regulation of these models could work in the future.

Researchers discovered three distinct immunological endophenotypes of multiple sclerosis, defined by specific blood immune signatures. This opens new avenues for personalized treatment strategies.

A new bioelectronic sensor enables continuous monitoring of bladder function. This could be a game-changer for people with paralysis, spina bifida, bladder cancer or end-stage bladder disease.

Using 3D bioprinting to accurately replicate the biological environment surrounding gastric cancer cells, researchers predicted a patient’s response to anticancer drugs during the preclinical stage.
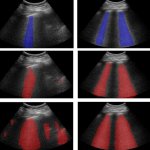
Using ultrasound imaging to detect Covid-19 infections, a new automated detection tool could help doctors in the emergency room diagnose patients quickly and accurately.

A team of Northwestern University scientists has developed the first wireless, implantable temperature sensor to detect inflammatory flareups in patients with Crohn’s disease.
Radiologists and AI don’t always work well together: New research finds that the benefits of using AI tools appear to vary, boosting performance of some clinicians, but hurting others'.

Some year in this decade, AI tools will become ubiquitous within clinical laboratories. AI has the potential to increase the accuracy of laboratory testing and improve the quality and efficiency of operations and service of testing labs.

A person’s age, sex and location are correlated with the chance that they have a bloodstream infection that is resistant to antibiotics, according to a new study.

An ageing population and modern lifestyle conditions have greatly increased the case numbers for hip arthroplasty. To prevent complications, it is important for orthopaedic surgeons to identify high-risk patients and take proper precautions. At the Heraeus symposium at DKOU, two experts explored the special measures that should be taken to ensure better outcomes for elderly and frail patients.

Striking the balance between diagnostic efficacy and patient safety remains critical when utilising iodinated contrast media to deliver the best imaging outcomes. While playing a crucial role in diagnosis and treatment of disease, CT expert Efthimios Agadakos believes the medical profession has a duty to do its utmost to minimize patient risk from contrast media.

Medical Taiwan, the premier international expo for medical, health, and care industries organized by TAITRA, is scheduled to be held at Taipei Nangang Exhibition Center Hall 2 (TaiNex2) from June 20th to 22nd, 2024.

Why are we doing what we are doing to stop surgical infections? A new research review in the run-up to the ECCMID congress 2024 will look at improving preventive measures.

New study results explore the long-term effects of infection with Sars-CoV-2, and challenge the idea that vaccine immunity fades quickly.
Ordering preoperative breast MRI exams of diagnosed breast cancer patients used to be controversial: Did they aid surgical planning better than the combination of mammography and breast ultrasound? Or did their findings cause overtreatment, specifically mastectomy, when breast-conservation surgery would have sufficed? New research has now settled the issue.

Researchers present new 3D-printable materials that can be easily monitored using X-ray or CT imaging. This has great potential to expand the possibilities of reconstructive and plastic surgery.
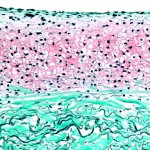
Patients suffering from cartilage defects in the knee may benefit from a new method in development: Using cartilage from the nose, researchers grow a tailor-made implant.

Researchers have developed a 3D-bioprinted, miniaturized chip to advance the understanding of cardiovascular disease and aid in the development of new precision treatments.

In a new article, digital health experts discuss how medical data from citizens could be used for research in the future while respecting personal rights.
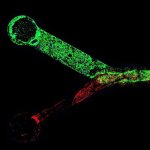
Chemotherapy can be toxic to heart cells. To help protect the hearts of cancer patients, Cedars-Sinai investigators have created a three-dimensional “heart-on-a-chip” to evaluate drug safety.

During the Covid-19 pandemic, Switzerland relied on contact tracing to identify people likely to have been contaminated by an acquaintance. A research team assessed the effectiveness of this method.

AI technology holds promise for personalised cancer therapies. However, rigid and slow approval requirements impede its introduction, say experts – and point out how this might be changed.
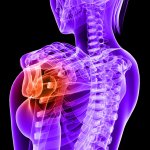
Bone fractures caused by osteoporosis are a common major global health risk. The International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) reports that one in three women over the age of 50 will sustain a potentially life-threatening fragility fracture in their remaining lifetimes. Early diagnosis and proactive treatment to keep bones healthy, including prescription medication and lifestyle changes, has the…

A team comprising obstetricians, gynecologists, pediatricians, and biomedical engineers has found the key determinants for digital health solutions that support women from pre- to post-pregnancy.

As a result from better living standards and medical advances, population longevity increases – a development which, paradoxically, current healthcare systems are ill-prepared for, Sir John Bell points out. The UK’s Our Future Health programme, which he chairs, exemplifies the paradigm shift to a prevention-centered healthcare approach.

UK law changes threaten the security of messaging apps – and their use in the NHS. Doctors warn that patient care will suffer if they can no longer use apps such as WhatsApp to share information.

A new soldering technique developed by Empa researchers is expected to prevent wound healing disorders and life-threatening complications from leaking sutures.

If healthcare professionals could get support making fast-paced, life-critical decisions from an AI tool, more lives could be saved, according to new research results from Sweden.
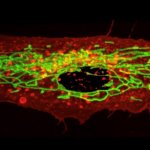
A new US study suggests a new way to personalize mental health care: They found compounds in the blood of people with depression and suicidal ideation that could be detected using a blood test.

While genetic information may lead to better treatments, promises of cost savings are unfounded. Instead, a large additional bill is more likely, according to University of Copenhagen researchers.
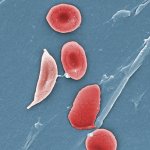
It's an important milestone for gene editing technology: a novel treatment for sickle cell disease utilizing CRISPR-Cas9, has now received FDA approval – a first for this type of therapy.

When a person has a cardiac arrest, using an automated external defibrillators (AED) can be life-saving. New research shows that AED delivery via drone is often quicker than an ambulance.
A multinational study confirms a strong and clear association between exposure to radiation from CT scans in young people and an increased risk of blood cancers.
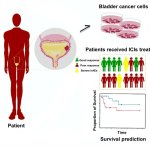
In a new study, researchers from Fudan University have developed a novel urine-based prognostic model that promises to transform the management and treatment of bladder cancer.

Sure, AI still has a long way go. But maybe one day in the not-so-distant future, AI will provide us with information about our current state of health, such as the number of red blood cells, cholesterol levels, fat percentage, and how many seconds last night's beer will shorten our life expectancy.

Bioethics researchers call on medical societies, government leaders, clinicians, and researchers to work together to ensure AI-driven healthcare preserves patient autonomy and respects human dignity.

Machine learning and AI are playing an increasingly important role in medicine and healthcare, and not just since ChatGPT. This is especially true in data-intensive specialties such as radiology, pathology or intensive care. The quality of diagnostics and decision-making via AI, however, does not only depend on a sophisticated algorithm but – crucially – on the quality of the training data.

A collaborative study, led by Cima Universidad de Navarra, has identified key epigenetic targets for the treatment of hepatoblastoma, the most frequent liver cancer in childhood.

Stark inequalities in diagnosis and treatment of four of the most common heart conditions in the UK have been revealed in new research led by a team at the University of Leeds.

New research led by Brigham and Women’s Hospital unveils that women who struggle with getting enough sleep might be at greater risk of developing hypertension, or high blood pressure.

Using placebos in primary care to reduce overprescribing, conserve existing antibiotics and limit further resistance, is publicly acceptable, a new study shows.
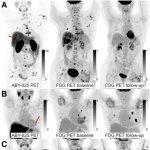
A new imaging agent can predict early metabolic response to HER2-targeted treatment in metastatic breast cancer patients, according to new research published in the Journal of Nuclear Medicine.

When celebrities admit to having undergone cosmetic surgery on social media, the nubmer of procedures increase. But why is that? Australian researchers looked deeper into this phenomenon.

A genetic test for BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutations may drive women to undergo breast cancer surgery, even though their risk might not even be drastically affected by this, a new study finds.
A new type of microdevice could offer new ways to treat brain cancer. The shape and size of a grain of rice, it is implanted into a tumor to study the effects of ongoing therapies.
New research finds the use of an electric field a promising means to prevent aerosol spread of viruses in healthcare environments, for example during surgery.

When faced with an unfamiliar task, many people rely on the voice assistants in their smartphone to help them out. However, when it comes to CPR, these AI companions cannot always be counted on.
Using a defibrillator for a cardiac arrest victim improves 30-day survival even with ambulance response times as short as two minutes, according to research presented at ESC Congress 2023.

The 2023 AACC meeting saw two exciting AI applications in lab medicine: a predictive algorithm for MS, and machine learning for detecting contaminated lab samples.

Women with a history of endometriosis had higher concentrations of cadmium in their urine compared to those without that diagnosis, a new study finds, linking the toxic metal to the condition.

A new study by investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital demonstrates the potential for restoring fertility when the ovaries have stopped working.
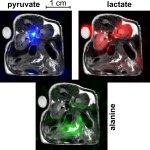
A new imaging method devised by German researchers offers a fast and cost-effective way to observe abnormal metabolic processes live in the MRI scanner.
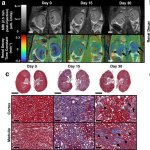
University of Ottawa scientists have introduced a metal-free MRI dye capable of mapping kidney function with unprecedented accuracy — a promising technique for more personalized care.
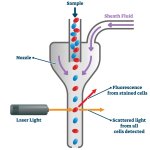
Plastics are a part of everyday life, and an increasingly concerning factor of global environmental pollution. They also have infiltrated our bodies as microparticles (MPs) and nanoparticles (NPs), found even in placentas supporting foetal life. And they are in our blood. Now, researchers in Spain have developed a new method to detect and measure nanoparticles in human peripheral blood that is…

By using genetic data on multiple traits from people of non-European ancestry, scientists have improved the accuracy of polygenic scores in predicting disease risk for all.

AI, robotics, climate change and more: Swedish researchers outline emerging technologies and trends that may define what the healthcare industry looks like in the next 50 years.

Post-pandemic problems, ageing societies, the impact of climate change on human health: To find solutions for new and ongoing healthcare challenges, thinking outside the box is crucial. This year’s Medical Taiwan Health & Care Expo took this approach to heart: True to its motto “beyond healthcare”, the event showcased a wide range of innovative products, promising start-up presentations…

From current mixed reality assistance, technological advances could soon make fully digital autopsies a reality. This could enhance efficiency and legal certainty, and also benefit training.

A new study from Munich reveals: Whether patients are able to correctly assess risks depends partly on how physicians convey statistical information to them.

New research suggests that combining blood biomarkers with genomic information more accurately, cost-effectively predicts the risk of developing diseases.

Chatbots are increasingly becoming a part of health care around the world, but do they encourage bias? New research from the University of Colorado School of Medicine hints at this possibility.

Unanswered questions are hampering clinicians in their efforts to get the best out of a precision medicine approach for their patients. Speaking at the Genomics and Precision Medicine Expo in London at the end of May, cancer educator Dr Elaine Vickers said the benefits of being matched to an investigational drug remain questionable for most people with advanced cancer.
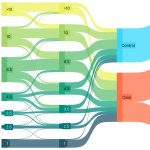
The accuracy of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening can be improved by including genetic factors that cause changes in PSA levels not associated with cancer, according to a multi-center study.

British societies BCS and BJCA publish a joint policy statement to stamp out bullying, harassment, and discrimination in the specialty, endorsed by 19 affiliated organisations.

People with strong legs are less likely to develop heart failure after a heart attack, according to research presented at the Heart Failure 2023 scientific congress in Prague.
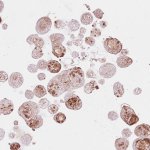
Researchers from the Organoid group (Hubrecht Institute) and UMC Utrecht have developed a biobank with organoids derived from patients with head and neck cancer (HNC).

A new online ‘European Cancer Pulse’ tool, created to compare cancer data across Europe, has highlighted that only 12 of the 27 EU Member States have an up-to-date national cancer control plan.

A new review has shown how medical professionals in cardiology can help reduce healthcare's carbon footprint, by making small, low-cost changes in how they work.

Women with triple-negative breast cancer who received multiple antibiotic prescriptions within three years after their cancer diagnosis were more likely to experience disease recurrence and to die from their cancer.

Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a developmental disorder associated with difficulties in interacting with others, repetitive behaviors, restricted interests and other symptoms that can impact academic or professional performance.
Genes are full of clues about a person's health and might also show the way for stroke recovery.

Doctors across all disciplines, with assistance from artificial intelligence, may soon have the ability to quickly consult a patient's entire medical file against the backdrop of all medical health care data and every published piece of medical literature online.

As ChatGPT becomes more popular among those seeking health advice, researchers try to find out whether the information provided by the AI chatbot is reliable and accurate.
A new study led by the University of Edinburgh has identfied areas of the brain susceptible to damage from high blood pressure, affecting memory loss, thinking skills and dementia.

An international study has shown how a decision tool for health professionals has proved capable of halving the use of antibiotics against urinary tract infections while maintaining patient safety.
New research has debunked the idea of an “obesity paradox”, whereby overweight or obese patients with heart failure are less likely to end up in hospital or die than people of normal weight.

Interactive mobile apps have become ubiquitous in daily life. The Covid-19 pandemic has escalated the use of disease-specific monitoring apps. Mobile apps enabling cancer patients to self-manage their physical condition and symptoms can help them to evaluate toxic side effects of their treatments, offer artificial intelligence (AI)-generated recommendations to minimize them, and alert them to…

Patients immersed in virtual reality, while undergoing wide-awake surgery experience more joy and less anxiety than those in a traditional operating room setting, according to a new study.

True or false: Webcams have only recently been introduced in neonatology and are a patient-side component of the Digital Health Portfolio. False! Already in 1989, Professor Dr Roland Wauer at Charité Berlin built his DIY system to transmit images from the neonatology ward.

60 percent of all administered drugs do not have the desired therapeutic effect. Even worse: in Germany alone about 60,000 deaths per year are caused by medication. With these shocking statistics Professor Dr Christian Franken started his presentation on “Pills from the 3D printer” at last year’s Medica in Düsseldorf. He hopes that his vision of personalized medication based on 2D and 3D…

US researchers are developing a highly accurate machine learning model for early detection of mild cognitive impairment and dementia in older drivers.

January 28 saw the celebration of the “Data Protection Day” as it is called in Europe, or respectively the “Privacy Day” as it is referred to outside of Europe. It marks the date on which the Council of Europe’s data protection convention, known as “Convention 108” was opened for signature back in 1981. According to the Council of Europe, it is the ‘only international,…

A new study confirms that haematopoietic stem cell transplantation can be used to cure patients with HIV infections. This third successful case gives new insights into the underlying processes.
Philips is an active participant in the new European Federation for Cancer Images consortium (EUCAIM) – a project launched in the run-up to World Cancer Day 2023.

Combining single-cell data with a self-learning algorithm reveals how structural changes in chromosomes can trigger cancer. This could pave the way for personalized cancer treatments.

High-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) ablation is a noninvasively treatment for benign thyroid nodules that are causing distress to patients. Brian H. H. Lang, MD, Clinical Professor in the Department of Surgery at the University of Hong Kong, and chief of the Division of Endocrine Surgery at Queen Mary Hospital, is a preeminent investigator, proponent, and pioneer of this technique. He…

The Netherlands Cancer Institute (NKI) will deploy a diagnostic platform from digital and computational pathology solutions provider Proscia, the company announced.

Researchers generated human mini bones in the lab which mirror the composition and function of human bone - a step toward the development of future patient-tailored models of bone cancers and tumors.
Some hospitalized patients’ infections may develop from their own bacteria, new research results suggest. The study in mice indicates that medical interventions can awaken dormant, hidden bacteria.

A more accurate approach to predicting fractures due to osteoporosis could help protect patients, particularly people with multiple health conditions, according to new research.

Both hot and cold environments trigger a stress response and can lead to cardiovascular problems. Results of a new study are especially interesting in light of the current multiple global crises.

Identification of elderly persons at risk of developing cognitive impairment and dementia could be made possible by examining ergothioneine levels in the blood, researchers from Singapore find.

Prolonging life may not be a top priority for everyone: New research finds that patients with neuroendocrine tumours and their doctors often disagree when it comes to treatment goals.

In their pursuit of solutions for pandemic challenges, a US hospital system applied telemedicine principles to respiratory therapy – with impressive results.
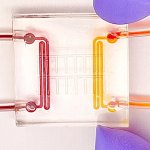
Researchers have developed a so-called “heart attack on a chip”, which could one day serve as a testbed to develop new heart drugs and even personalized medicines.

A pioneering ‘smart contact lens’ to test the eye in a quick, non-invasive way could prevent deaths caused by fungal eye infections in developing countries.

Researchers use AI to develop personalized 3D-printed joint implants so that these delicate finger parts can be replaced when necessary (e.g. after illness or injury).
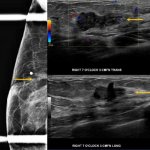
The need for breast cancer screening of transgender individuals has been a topic of uncertainty until recently, due to lack of reliable patient data, consensus by radiologists, published research, and recommended guidelines. A 2021 survey of Society of Breast Imaging (SBI) members revealed that ‘breast radiologists differ in their practice and knowledge regarding screening of transgender…

Eunsin Bae, M.D. specializes in laboratory medicine and leads the Institute of Clinical Research at Seegene Inc. Her research focuses on microbiology, molecular biology, and hematology. Dr. Bae is currently working toward implementing a global clinical study and establishing an international network of clinical investigations.
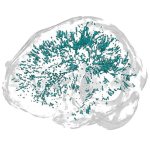
For the first time, a new study has identified enlarged perivascular spaces in the brains of migraine sufferers. Results of the study will be presented at the annual RSNA meeting.

Innovative gastrointestinal imaging, medical panel PCs with hygiene optimisation, smartphone-based diagnostic tools, and sustainable hardware setups: At Medica 2022, manufacturers from Taiwan again showed their capability to adapt and provide solutions for a world radically changed by the Covid-19 pandemic. Under the “Taiwan Excellence” banner, outstanding products from the island nation’s…

It is the size of a common pencil eraser, but it could have a huge impact on the therapy of glioblastoma: Scientists in Virginia have developed a novel 3D tissue-engineered model of the brain tumour microenvironment, which can be used to assess how the glioma cell invades healthy tissue, proliferates, and reacts to chemotherapy drugs.
Despite treatment, chronic lung diseases such as COPD or cystic fibrosis can become so severe that a lung transplant is necessary. Dr Urte Sommerwerck explains which patients might be considered for transplantation and why follow-up is as important as the surgery itself.
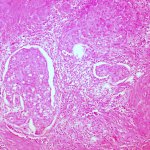
Scientists have discovered that cervical cancer can be divided into 2 distinct molecular subgroups – one far more aggressive than the other – as part of the largest ‘omics’ study of its kind.