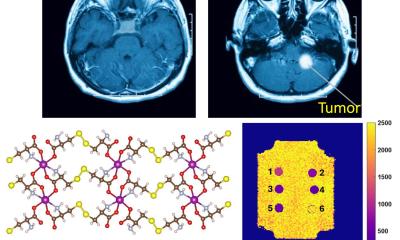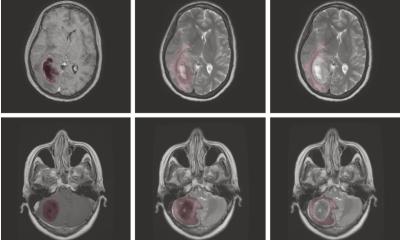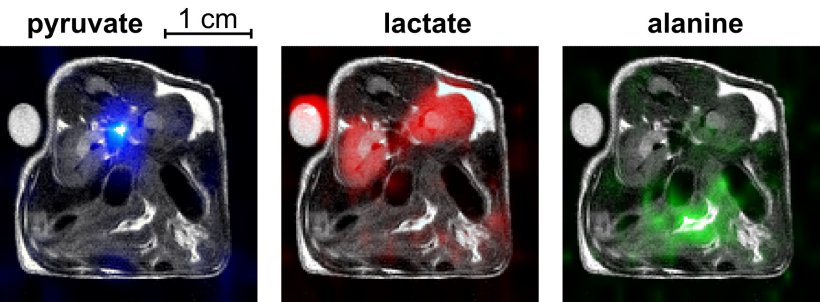
Image source: University Medical Center Freiburg; adapted from: de Maissin et al., Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2023 (CC BY-NC 4.0)
News • Production of biological contrast agents
Hyperpolarized MRI to advance cancer imaging
A team of scientists from the University Medical Center Freiburg, the German Cancer Consortium (DKTK), and other locations has achieved a significant breakthrough in live observation of metabolic processes in the body using metabolic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
They have developed a method to modify naturally occurring molecules in the body in an affordable, safe, and rapid manner, significantly enhancing their visibility in MRI scans. This plays an important role in personalized cancer diagnostics, among other applications. The results of their study were published in the journal "Angewandte Chemie International Edition".
"We have found a way to produce biological contrast agents simply, quickly, and safely, which even make metabolism visible. This allows us to observe cancer metabolism in real-time, opening up entirely new perspectives for personalized cancer medicine," says lead investigator Dr. Andreas Schmidt, Head of the "Hyperpolarization and Metabolic MRI" research group in the Department of Medical Physics at the Clinic for Radiology, Medical Center - University of Freiburg, Germany.
How Metabolic MRI Works:
In MRI, the magnetic properties of molecules are detected. During hyperpolarization, these properties are significantly amplified for a certain period, resulting in a much stronger signal than usual. Biologically, the molecules behave as before. Thus, metabolic processes can be observed non-invasively. "Moreover, this approach is safe, radiation-free, and metabolic MRI only takes a few minutes. These aspects are particularly important for patients requiring regular follow-up examinations," explains co-investigator Dr. Stephan Knecht, Director of MR development with NVivion Imaging Technologies GmbH.
The study results encompass two significant milestones:
- Successful production of highly polarized pyruvate in a biocompatible, aqueous solution. Pyruvate is a common molecule in the body and is involved in central metabolic processes. The team used the innovative SABRE method (Signal Amplification By Reversible Exchange) to enhance the pyruvate signal. This process allows for the production of highly sensitive biological contrast agents in a few minutes, at low cost, and without chemical modification. So far, SABRE has not been efficient enough as a method, and it was not previously possible to produce contrast agents in aqueous solutions with sufficient purity. In contrast, with the currently established method, the production of contrast agents took approximately an hour or longer and was technically very demanding.
- With the developed highly sensitive biological contrast agents, the conversion of pyruvate into lactate and alanine was successfully demonstrated in an animal model. These conversions in energy metabolism have already been identified as helpful diagnostic markers in previous studies.
The collaboration between the DKTK partner sites (Medical Center - University of Freiburg and University of Freiburg, Klinikum rechts der Isar Munich) and partners in Göttingen (Max Planck Institute for Multidisciplinary Sciences), Kiel (University Medical Center Schleswig-Holstein), Ulm (NVision Imaging Technologies), and Detroit (Wayne State University) has led to this significant progress. "I would like to express my gratitude to all project participants for their valuable collaboration and contribution to this groundbreaking research," concludes Schmidt.
Source: Universitätsklinikum Freiburg
17.07.2023