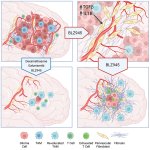
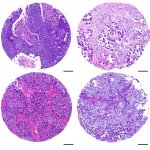
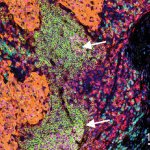
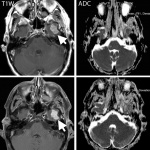
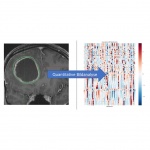
News • CTNNB1 in focus
Mutation strength may hold key to personalized cancer treatment
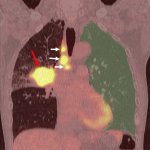
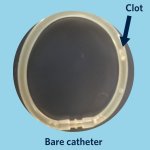
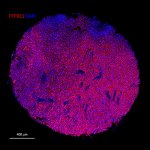
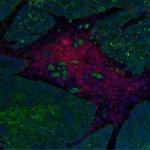
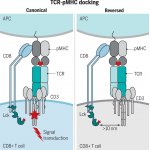
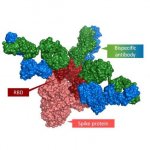
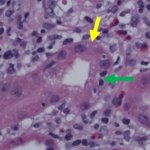
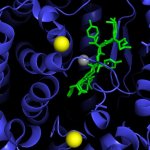
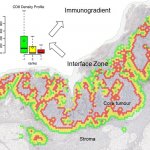
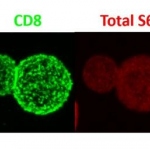
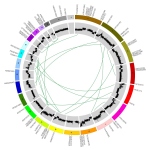
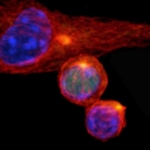
Not all cancer mutations are equal: new research shows that a single mutation hotspot can generate a rich diversity of tumour behaviours. This could lead to more personalised cancer treatments.