News • In situ vaccination
Turning tumors into cancer vaccine factories
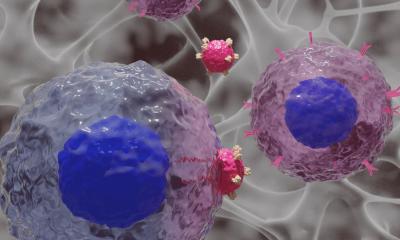
Researchers at Mount Sinai have developed a novel approach to cancer immunotherapy, injecting immune stimulants directly into a tumor to teach the immune system to destroy it and other tumor cells throughout the body.
Source: Pixabay/skeeze
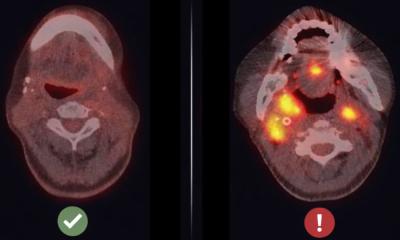
The “in situ vaccination” worked so well in patients with advanced-stage lymphoma that it is also undergoing trials in breast and head and neck cancer patients, according to a study now published in Nature Medicine. The treatment consists of administering a series of immune stimulants directly into one tumor site. The first stimulant recruits important immune cells called dendritic cells that act like generals of the immune army. The second stimulant activatesthe dendritic cells, which then instruct T cells, the immune system’s soldiers, to kill cancer cells and spare non-cancer cells. This immune army learns to recognize features of the tumor cells so it can seek them out and destroy them throughout the body, essentially turning the tumor into a cancer vaccine factory.
Recommended article

Article • Immuno-oncological biomarkers
Seeking to augment the value of tumour infiltrating lymphocytes
Measuring tumour infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) is gaining importance in immunotherapy, but other variables must also be considered to boost prognosis and prediction accuracy, a leading pathologist argued at EBCC 11 last March in Barcelona. When it comes to prognosis and prediction for immunotherapy, a potentially new variable is emerging – TILs – white blood cells that have left the blood…
“The in situ vaccine approach has broad implications for multiple types of cancer,” said lead author Joshua Brody, MD, Director of the Lymphoma Immunotherapy Program at The Tisch Cancer Institute at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. “This method could also increase the success of other immunotherapies such as checkpoint blockade.”
After testing the lymphoma vaccine in the lab, it was tested in 11 patients in a clinical trial. Some patients had full remission from months to years. In lab tests in mice, the vaccine drastically increased the success of checkpoint blockade immunotherapy, the type of immunotherapy responsible for the complete remission of former President Jimmy Carter’s cancer and the focus of the 2018 Nobel Prize in Medicine.
A clinical trial for lymphoma, breast, and head and neck cancer patients opened in March to test the vaccine with checkpoint blockade drugs. Because the combinedimmune therapy was at least three times more powerful than either checkpoint blockade or the vaccine by themselves, researchers are extremely optimistic about how effective this may be in patients in this new trial. The in situ vaccine is also being tested in the lab in liver and ovarian cancer.
Source: Mount Sinai
10.04.2019