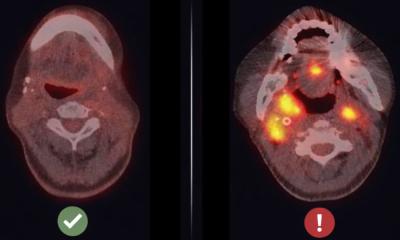
Source: Science (2021). DOI: 10.1126/science.abe9124
News • Immune system
Fundamental advance in understanding T cell immunity
Monash University researchers have provided a fundamental advance regarding how T cells become activated when encountering pathogens such as viruses.
The recent study, co-led by Professor Nicole La Gruta, Professor Jamie Rossjohn and Professor Stephanie Gras with first author Dr. Pirooz Zareie from the Monash Biomedicine Discovery Institute, have found that T Cells need to recognize pathogens in a particular orientation in order to receive a strong activating signal. T cells play a key role in the immune system by eliminating invading pathogens, such as viruses, and it is crucial to understand the factors that determine how and why T cells become activated after recognizing these pathogens.
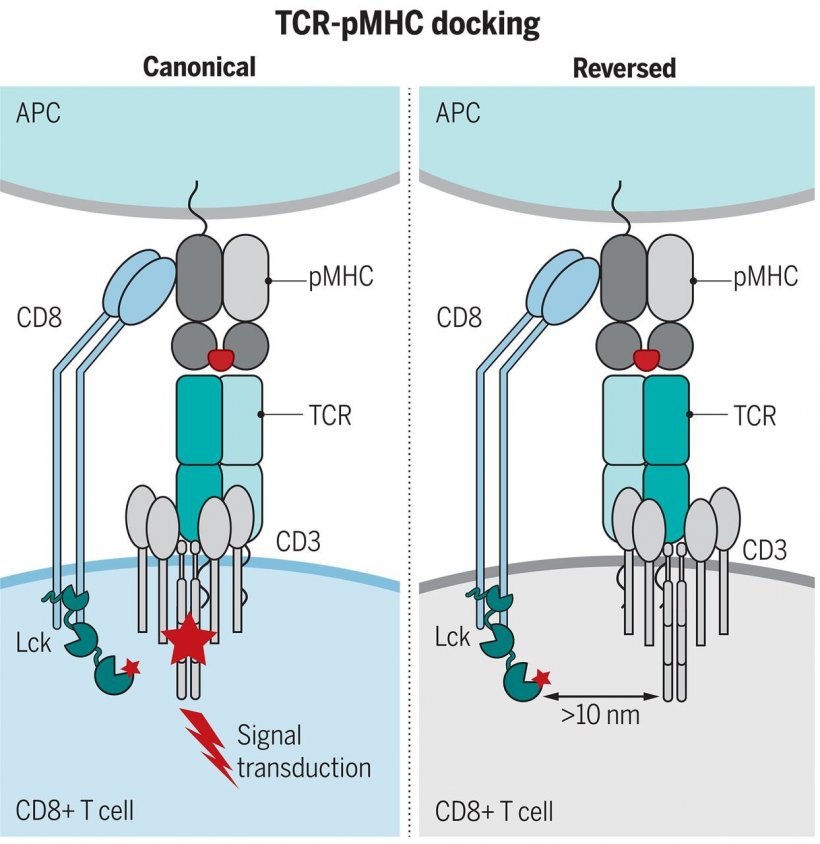
T cells express on their surface a T cell receptor (TCR) that recognizes and binds to virus fragments (antigens) presented by infected cells. This recognition event can lead to T cell activation and killing of infected cells. "The central issue is that there are millions of different T cell receptors (TCRs) in the human body, and a vast array of viruses, making it difficult to understand the rules around how T cell receptor recognition of a virus drives T cell activation. Indeed, it is a problem that has remained contentious for over 25 years," says Professor La Gruta.
This is an advance in our fundamental understanding of how a T cell needs to 'see' pathogenic antigens in order to be activated.
Nicole La Gruta
"Our study has shown that the orientation in which the T cell receptor binds is a primary factor determining whether the T cell receives an activating signal," Professor La Gruta said.
"This is an advance in our fundamental understanding of how a T cell needs to 'see' pathogenic antigens in order to be activated," she said. "It has clarified a critical mechanism essential for effective T cell immunity. It is also relevant to the ongoing development of immunotherapies that aim to boost the activation of T cells."
Dr. Pirooz Zareie stated: "a combination of technologies, including super-resolution microscopy, X-ray crystallography at the Australian Synchrotron, biochemical assays and using in vitro and in vivo experimental models from a variety of labs led to the findings."
08.06.2021