Source: UT Southwestern Medical Center
News • Immunotherapy side effect
Hope for kidney cancer patients
An autoimmune side effect of immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) drugs could signal improved control of kidney cancer, according to a new study by researchers in UT Southwestern's Kidney Cancer Program (KCP).
The study, published today in the Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer, may have broad implications for patients being treated with ICIs, a type of immunotherapy that is used against a large number of cancers, including lung, breast, liver, and cervical.
Renal cell carcinoma, the most common type of kidney cancer, is the ninth leading cause of cancer in the U.S. Once the cancer has spread to other organs, or metastasized, the survival rate averages 12 percent at five years.
With the advent of ICIs, kidney cancer survival rates are improving. However, only a fraction of patients respond to ICIs - and who will respond is unpredictable. ICIs disable cloaking mechanisms put in place by tumors to evade killing by immune cells. But taking down these cloaking mechanisms also increases the chances that the immune system will turn against the body, causing autoimmune side effects.
KCP investigators hypothesize that kidney cancer patients whose immune system attacked their kidneys may be more likely to benefit from ICIs. Using Kidney Cancer Explorer, a proprietary tool that extracts information from electronic health records, investigators identified metastatic kidney cancer patients treated with ICIs between 2014 and 2018. Using this tool, they analyzed thousands of laboratory test results to identify patients whose kidney function became impaired. Out of 177 patients, they found 36 such patients.
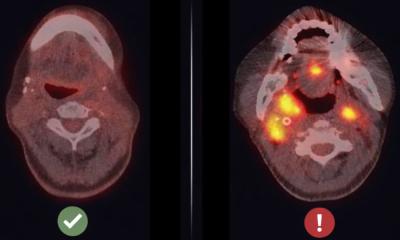
In three of the 36 patients, the impairment was due to an immune-mediated attack. A fourth more recent patient was also identified. All four patients developed acute interstitial nephritis (AIN), an autoimmune condition in which immune cells attack kidney cells, causing inflammation and swelling. While ICIs induce responses in the cancer in up to 40 percent of patients, in this case all four patients with AIN had a response.
Recommended article
News • Lipids, lysosomes, and autophagy
Researchers find the keys to preventing kidney injury
Human cells need to work like well-oiled machines to keep our bodies running as they should. Waste products such as misfolded proteins, damaged cellular components, and carbohydrates get in the way and must be quickly disposed of. Dealing with this cellular “trash” are spherical, membrane-bound organelles called lysosomes filled with a mixture of potent enzymes. In a process called autophagy,…
"For 100 percent of patients to respond is quite significant," says Roy Elias, M.D., assistant instructor of internal medicine and co-first author of the study. "If a patient develops AIN, it is a sign that the treatment may be working."
This is not the first time that a particular autoimmune effect has been linked to increased response rates to ICIs, says James Brugarolas, M.D., Ph.D., professor of internal medicine and director of the Kidney Cancer Program. In fact, patients with melanoma who developed vitiligo, a condition in which skin pigment cells are killed by immune cells, also had higher chances of response.
Upon identifying a second example of an immune attack to the tissue of origin associated with a favorable cancer response, KCP investigators propose that this finding may be generalizable to other tumor types.
"All cancer cells start out as normal cells," says Brugarolas. "Even after turning malignant, they retain some of their original traits. Thus, an attack against the tissue of origin may signal a higher chance that the immune system will also recognize and attack the cancer."
Further study will be needed to determine whether positive outcomes could be generalizable to patients with other cancers who are experiencing similar immune attacks against the cell of origin of the cancer.
Source: UT Southwestern Medical Center
08.11.2020