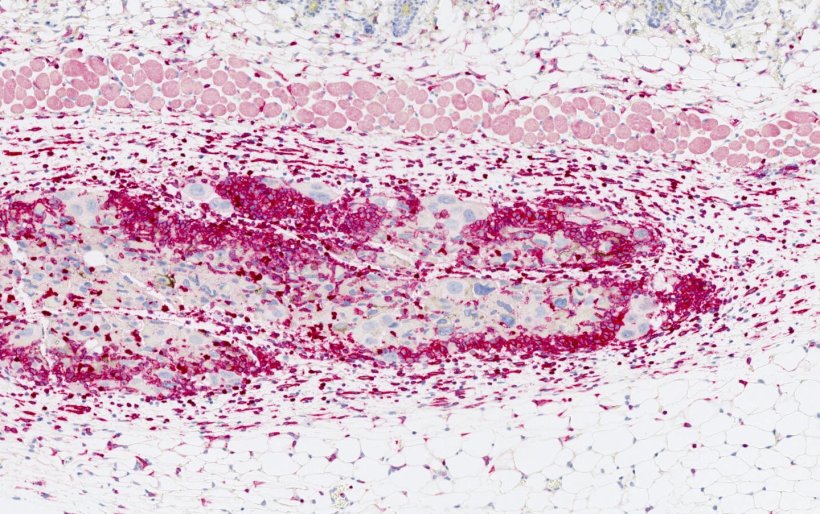
Image source: IRB Barcelona
News • Immune systems timulation
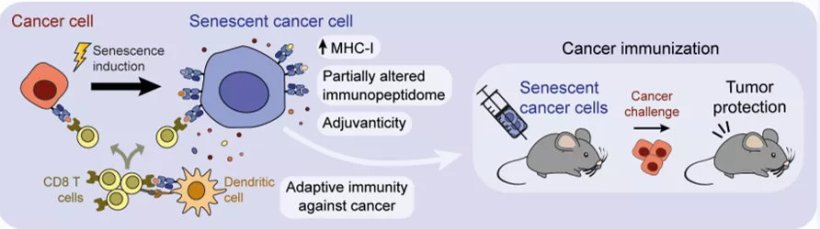
Using senescent cells as anti-cancer vaccines
Cancer cells have a series of features that allow the immune system to identify and attack them. However, these same cells create an environment that blocks immune cells and protects the tumour. This means that immune cells cannot reach the cancer cells to remove them. The scientific community has been working for years to increase the effectiveness of the immune system against cancer by using vaccines based on dead tumour cells.
Scientists at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB) Barcelona, led by ICREA researcher Dr. Manuel Serrano, and Dr. Federico Pietrocola, now at the Karolinska Institutet, in Sweden, have studied how inducing senescence in cancer cells improves the effectiveness of the immune response to a greater degree than the dead cancer cells. After vaccinating healthy mice with senescent cancer cells and then stimulating the formation of tumours, the researchers observed that the animals did not develop cancer or that the number that do is significantly reduced. They also analysed the efficacy of vaccination in animals that had already developed tumours. In this setting, although the results were more moderate due to the protective barrier of the tumour, improvements were also observed.
The study has been published in the journal Cancer Discovery.
"Our results indicate that senescent cells are a preferred option when it comes to stimulating the immune system against cancer, and they pave the way to considering vaccination with these cells as a possible therapy," explains Dr. Serrano, head of the Cellular Plasticity and Disease lab at IRB Barcelona.
The researchers tested the technique in animal models of melanoma, a type of cancer characterised by high activation of the immune system, and also in pancreatic cancer models, which present strong barriers against immune cells. Prophylactic vaccination therapy with senescent cancer cells was effective against both types of tumors. They also complemented the study with tumour samples from cancer patients and confirmed that human cancer cells also have a greater capacity to activate the immune system when they are previously rendered senescent. The group is now studying the combined efficacy of vaccination with senescent cells and immunotherapy treatments.
Our study concludes that the induction of senescence in tumour cells improves the recognition of these cells by the immune system and it also increases the intensity of the response they generate
Inés Marín
Senescence is a state of latency reached by damaged or aged cells in which they do not reproduce but do not disappear either. Senescent cells emit information signals into their environment, which warn of their presence, stimulating an inflammatory response and tissue regeneration. In the context of cancer, the researchers led by Dr. Serrano have discovered that senescent cells, due to their characteristics, are a good option for activating the immune system and improving its response to the tumour. On the one hand, because they are living cells, senescent cells remain in the body longer than dead ones and are thus able to stimulate the immune system for longer. On the other hand, as these cells do not divide, they cannot regenerate the tumour. "Our study concludes that the induction of senescence in tumour cells improves the recognition of these cells by the immune system and it also increases the intensity of the response they generate. So our findings are very positive,” explains Inés Marín, a doctoral student from the same laboratory and first author of the study.
As observed in this study, senescent cells present unique signals, which stimulate recognition by and activation of the immune system, and which differ from those presented by cells before senescence has been induced.
The discovery made by the Cellular Plasticity and Disease laboratory has been published simultaneously and in the same journal as another article led by the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) in New York and completed in collaboration with IRB Barcelona. The latter, which is authored by Dr. Direna Alonso-Curbello, now head of the Inflammation, Tissue Plasticity & Cancer laboratory at IRB Barcelona, and Dr. Scott W. Lowe, reaches complementary conclusions, despite studying the subject using a very different approach.
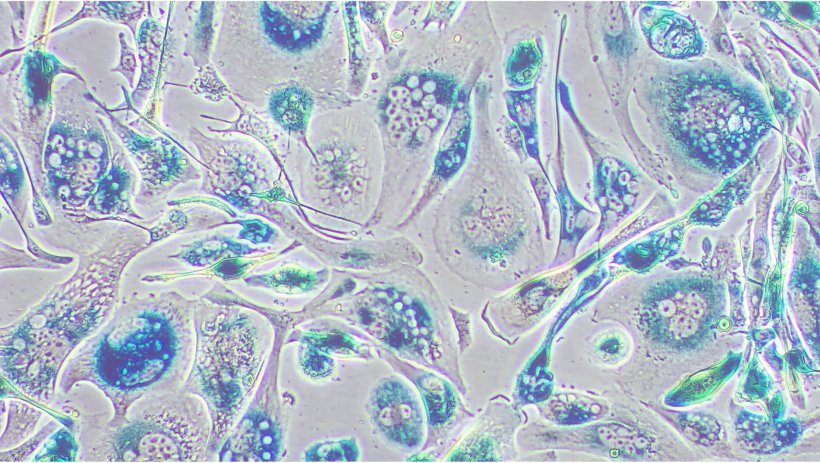
Image source: IRB Barcelona
In short, the work started at the MSKCC focused on describing how the induction of senescence in tumour cells alters the molecular programs that mediate communication between the tumour and the immune system. “Until now, most studies have focused on the ability of senescent cells to "send" inflammatory signals to their environment. Our work shows that this communication is bidirectional, revealing that senescence increases the ability of cells to "receive" signals from their environment that activate key pathways for their recognition and destruction by cytotoxic T cells," explains Dr. Alonso-Curbelo.
This work demonstrates that the ability to "receive" signals from the environment, which is increased by the induction of senescence, amplifies the anti-tumour effects of signals such as interferon, making tumour cells more visible to the immune system and reactivating anti-tumour immunity in liver cancer models.
Other diseases related to ageing and those in which there is a prevalent presence of senescent cells, such as atherosclerosis, could also benefit from possible vaccines with senescent cells. In this regard, the scientists for IRB Barcelona also report that senescent cells can be mistakently recognized by immune cells as if they were foreign cells. These findings are in line with those reported by other researchers working on cells subjected to stress, which can also be mistaken as foreign cells.
Source: Institute for Research in Biomedicine Barcelona
07.11.2022