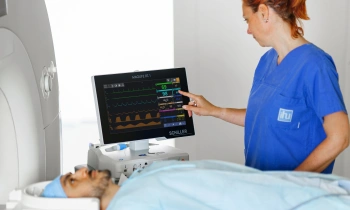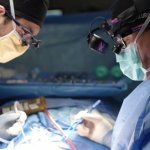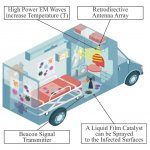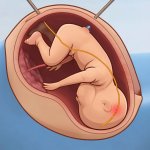
News • In utero monitoring during surgery
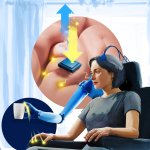
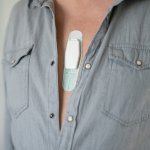
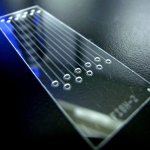
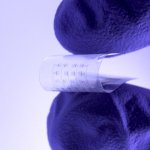
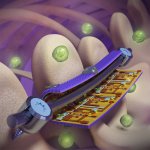
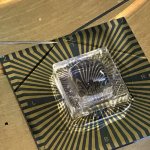
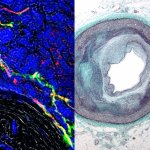
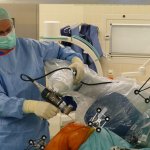
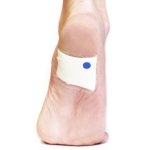
New probe tracks baby's health in the uterus
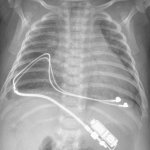
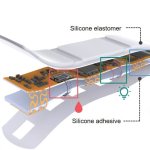
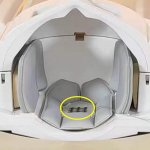
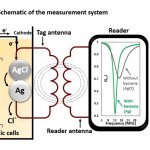
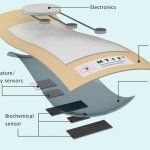
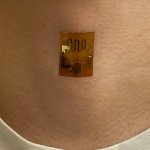
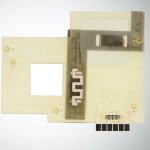
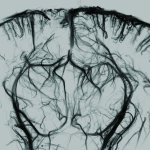
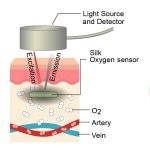
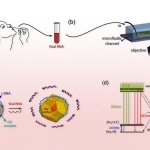
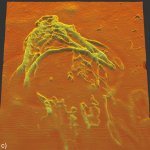
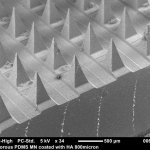
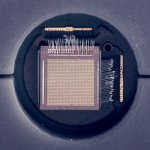
Northwestern University researchers have developed the first device that can continuously track a fetus’s vital signs while still in the uterus — a feat that previously has not been possible.