Source: University of the West of Scotland
News • Dexterity and motor skills
Robotic sensors could help transform prosthetics
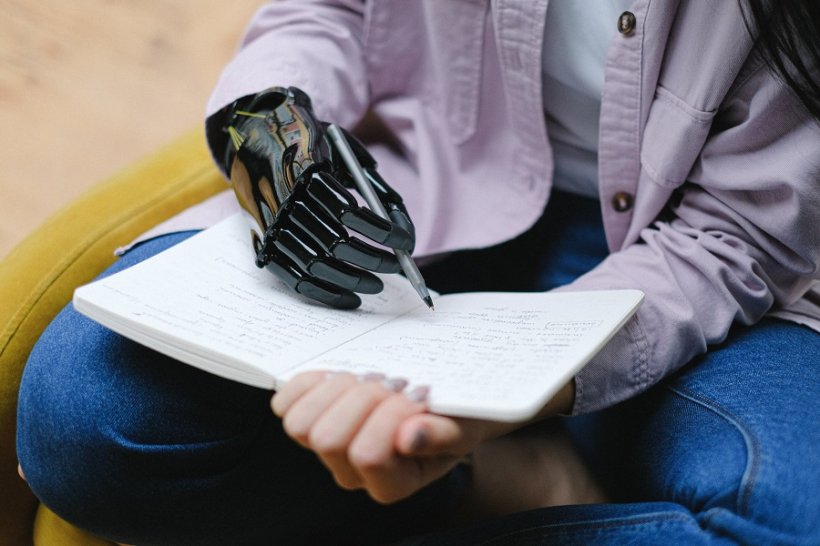
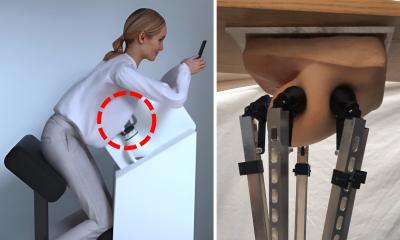
A pioneering project to develop advanced sensors for use in robotic systems, could transform prosthetics and robotic limbs. The research project aims to develop sensors which provide enhanced capabilities to robots, helping improve their dexterity and motor skills, through the use of accurate pressure sensors which provide haptic feedback and distributed touch.
Professor Des Gibson, Director of the Institute of Thin Films, Sensors and Imaging at University of the West of Scotland (UWS) and project principal investigator, said: "Over recent years the advancements in the robotics industry have been remarkable, however, due to a lack of sensory capabilities, robotic systems often fail to execute certain tasks easily. For robots to reach their full potential, accurate pressure sensors, capable of providing greater tactile ability, are required.
"Our collaboration with Integrated Graphene Ltd, has led to the development of advanced pressure sensor technology, which could help transform robotic systems."
Made from 3D graphene foam, which offers unique capabilities when put under mechanical stress, the sensors use a piezoresistive approach, meaning when the material is put under pressure it dynamically changes its electric resistance, easily detecting and adapting to the range of pressure required, from light to heavy.
Marco Caffio, co-founder and Chief Scientific Officer at Integrated Graphene said: "Gii, our novel 3D graphene foam, has the capability to mimic the sensitivity and feedback of human touch, which could have a transformative impact on how robotics can be used for a whole range of real-world applications from surgery to precision manufacturing.
"We know the unique property of Gii makes it suitable for use in other applications like disease diagnostics and energy storage, so we're always very excited to be able to demonstrate its flexibility in projects like this one."
Dr. Carlos Garcia Nunez, School of Computing Engineering and Physical Sciences at UWS added: "Within robotics and wearable electronics the use of pressure sensors is a vital element, to provide either an information input system, or to give robotic systems human-like motor skills. An advanced material like 3D graphene foam offers excellent potential for use in such applications, due to its outstanding electrical, mechanical and chemical properties. Our work shines a light on the significant potential for this technology to revolutionize the robotics industry with dynamic pressure sensors."
Claire Ordoyno, Interim Director of SRPe, said: "The SRPe—NMIS Industrial Doctorate Program brings together ground breaking academic research with industry partners to drive forward innovation in engineering. These collaborative Ph.D. projects not only enhance the Scottish engineering research landscape, but produce innovation focussed, industry ready Ph.D. graduates to feed the talent pipeline."
The next stage of the project—funded by UWS, Integrated Graphene Ltd, SRPe and NMIS—will look to further increase sensitivity of the sensors, before developing for wider use in robotic systems.
Source: University of the West of Scotland
08.08.2022