News • Study on bacteria composition
Antibiotics leave a lasting mark on the gut microbiome
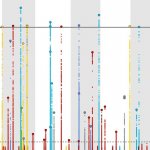
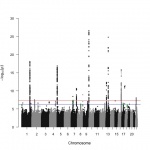
Antibiotics can affect the composition of the community of bacteria living in the gut, known as the gut microbiome, for as long as four to eight years after treatment, a new study shows.