Source: Plana-Ripoll O, Pedersen CB, Holtz Y, et al. Exploring Comorbidity Within Mental Disorders Among a Danish National Population. JAMA Psychiatry. Published online January 16, 2019. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2018.3658; http://nbepi.com/
News • Comorbidity
Mapping out the relationship between mental disorders
Half of those who develop a severe mental disorder such as depression prior to the age 20, will also develop an anxiety disorder within the next 15 years. This is just one of the many results on the relationship between various mental disorders mapped out.
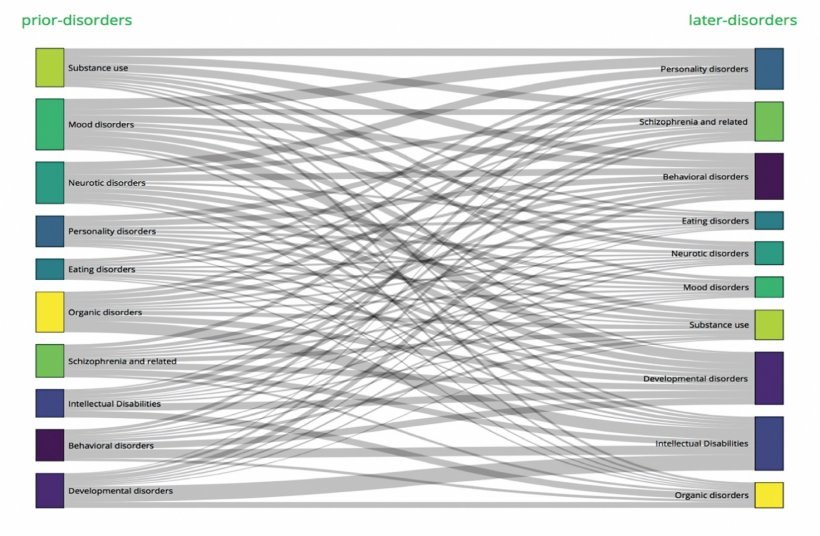
The new research from the National Centre for Register-based Research at Aarhus BSS is the first of its kind to offer a comprehensive description of the risks of double diagnosis within the ten major groups of mental disorders - also called comorbidity. Based on register data from 5.9 million people living in Denmark from 2000 to 2016, the study is the most detailed study of comorbidity ever conducted in the field of mental health. The results have just been published in JAMA Psychiatry, which is one of the world's most prestigious scientific journals in the field of psychiatry. The researchers have also developed an interactive webpage that offers professionals and the general public access to examine the risks of double diagnoses according to age, sex and type of mental disorder.
"This is the first study to provide a comprehensive description of all possible associations between pairs of mental disorders using national registers available for a whole population. We knew from previous smaller studies that some types of disorder tended to occur together. But now we can confirm that comorbidity is the rule, not the exception. Those who receive a diagnosis of a specific major mental disorder are more likely to receive diagnoses for all other types of mental disorders," says Oleguer Plana-Ripoll, who is a postdoctoral researcher at the National Centre for Register-based Research at Aarhus BSS and the main author of the study.
In the study, the researchers uncovered how different types of mental disorders accumulate across a lifespan. Due to the size of the study, the researchers were able to measure the absolute risks of people developing more than one mental disorder later in life. The study showed that people who are diagnosed with one mental disorder are not only more likely to be diagnosed with other mental disorders, but also that this risk persists for many years after the first diagnosis.
We want to 'democratice' the results so that they are more widely understood by clinicians and people with mental disorders and their caregivers
John McGrath
The study partly originates from the national psychiatric project, iPSYCH, and partly the Niels Bohr Professorship research programme at Aarhus University, which is led by Professor John McGrath and explores new innovative methods related to psychiatric epidemiology. "It is a large and comprehensive study that provides never-before-seen details of the relationship between the different mental disorders. We have provided the field with fine-grain details - for example that the risk of developing more than one mental disorder is not constant over time," says Oleguer Plana-Ripoll.
In addition to the scientific publication, all the results of the study are available on an interactive webpage that can be used by physicians and the general public. "We want to 'democratice' the results so that they are more widely understood by clinicians and people with mental disorders and their caregivers. We hope that this new information will help the clinicians to monitor the development of mental disorders. This is especially important for people who develop a mental disorder when they are young," says John McGrath.
Source: Aarhus University
18.01.2019