News • Colorectal cancer
Harmful to women? Expert questions new screening recommendation
The British Medical Journal (BMJ) published a new recommendation on colorectal cancer screening on October 2nd, 2019. The main point: Screening participation is only recommended to people with at least a three percent chance of developing colorectal cancer in the next 15 years. As a result, the majority of women would be advised not to participate in screening – even though its benefit to them has been clearly shown.
Image source: Damato, PET-MIPS anim frame, marked as public domain, details at Wikimedia Commons
This is emphasized by Prof. Dr. Ulrike Haug, Head of the Department of Clinical Epidemiology at the Leibniz Institute for Prevention Research and Epidemiology – BIPS. She is not only critical of the recommendation itself, but also questions the methodology applied to develop it.
The new recommendation in question can be accessed here.
Most current guidelines recommend colorectal cancer screening to men and women aged 50 and over. This takes the slow development of colorectal cancer from precursors into account which allows screening to prevent cancers that would occur much later in life. However, the approach of the BMJ recommendation differed. A panel of 22 people was asked to estimate at which benefit—in absolute terms—the majority of people would choose screening. However, the answers offered were comparatively extreme. "It is therefore not surprising that ultimately the threshold was set relatively high, resulting in very restrictive recommendations," Haug criticizes. If this recommendation were applied, the majority of women would receive a recommendation against screening and screening would be shifted to older age groups.
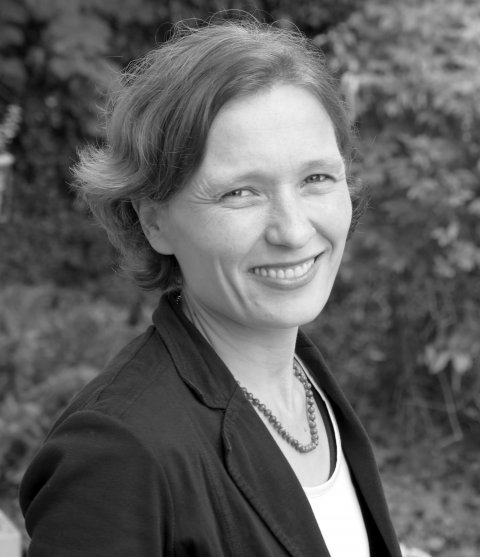

"Hardly any other cancer offers as effective screening options as colorectal cancer. It seems absurd to recommend against this, based on the assumption of a small group of experts who feel entitled to judge what the population regards as relevant benefits. In Germany, 45 percent of colorectal cancer cases occur in women. I do not think it is justifiable to advise women against colorectal cancer screening or to recommend it only at an advanced age. In that case, it may still be possible to detect colorectal cancer at an early stage but the chance of preventing the disease completely is reduced. Personally, I would much prefer not to have cancer in the first place which is probably how many people feel. However, the BMJ panel of experts regarded the benefit of preventing the occurrence of cancer as equivalent to the benefit of not dying of cancer. There is an additional problem. In order to apply the recommendation, one must determine whether the personal risk of developing colorectal cancer in the next 15 years is below or above three percent. However, the existing prediction models are flawed in this respect. For example, about two-thirds of women who will develop colorectal cancer in the next five years would mistakenly be predicted to have a risk of less than three percent – thus they would be advised against colorectal cancer screening according to the BMJ recommendation. The authors of the study stress that the BMJ recommendations are not 'strong recommendations' and that the personal decision should be made together with the doctor. Nevertheless, I worry that these recommendations will cause a great deal of uncertainty and ultimately do much more harm than good, especially for women," says Haug.
Source: Leibniz Institute for Prevention Research and Epidemiology – BIPS
04.10.2019