News • Cardiovascular care
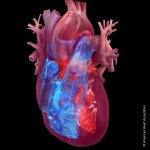
The hidden heart health risks (that don't start in the heart)
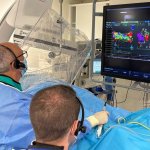
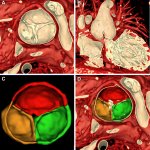
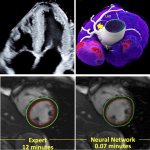
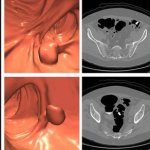
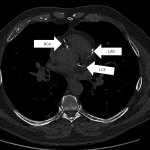
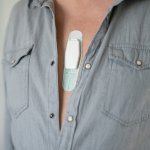
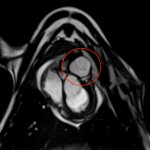
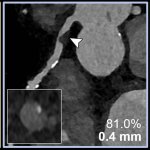
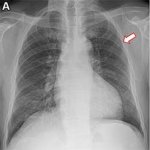
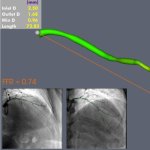
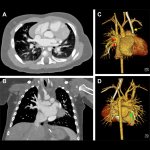
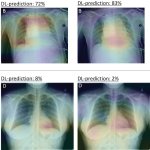
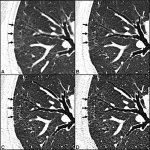
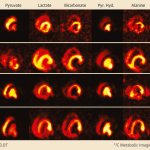
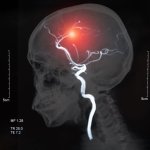
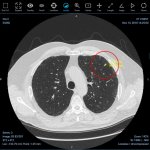
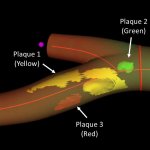
Diabetes and kidney disease are among the biggest — and most overlooked — drivers of heart disease. A new survey shows many people don't even know the connection exists.