Article • Preventive cardiology
AI to measure coronary plaque in six seconds
Coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) is a non-invasive imaging test which can be used to evaluate coronary artery stenosis and measure plaques. Current plaque analysis is time-consuming and needs expert readers in order to help assess a patient’s heart attack risk. That’s about to change.
Report: Mark Nicholls

During a session focused on artificial intelligence in imaging, at the forthcoming virtual European Society of Cardiology Annual Congress 2021, Dr Andrew Lin will explain how using artificial neural networks, AI can generate automated predictions directly from medical image data. Healthcare in Europe spoke with the post-doctoral researcher about his work at the Biomedical Imaging Research Institute at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, in L.A. California. Research aims? To develop a deep learning system for plaque quantification from CCTA and compare it with expert readers and intravascular ultrasound.
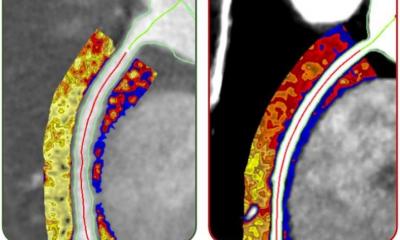
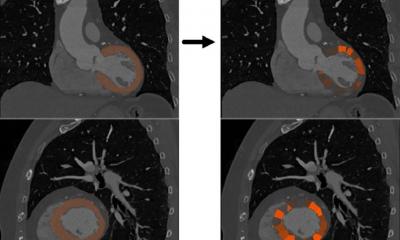
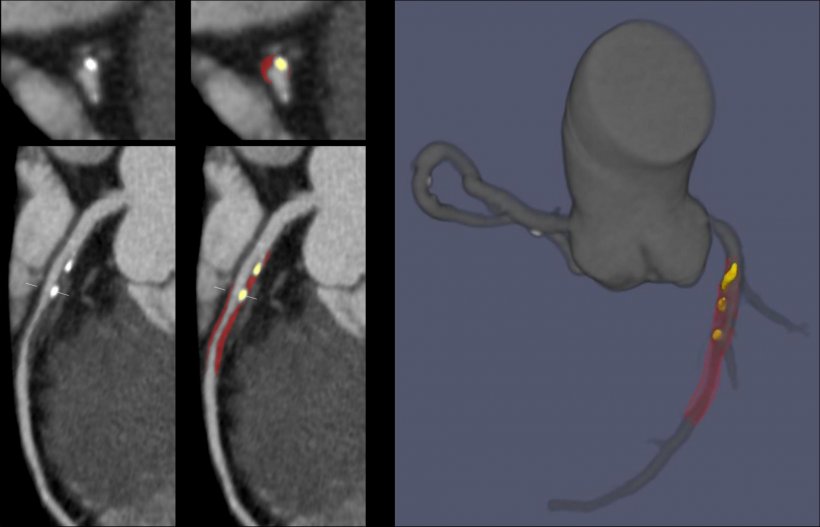
A dataset of 921 patients was used to train an automated deep learning neural network to measure plaque volume and coronary artery stenosis from CCTA images. The deep learning network was then applied to an independent test set of 275 patients, where its diagnostic performance was evaluated. ‘There was excellent agreement between deep learning and expert readers for measurements of total plaque volume and coronary artery stenosis,’ Lin confirmed. ‘Deep learning also performed in close agreement with intravascular ultrasound, which is the invasive gold standard for plaque measurements. The time taken for deep learning analysis per scan was around six seconds, compared with 25-30 minutes taken by experts.’
By providing automated and objective results, deep learning may reduce inter-observer variability and interpretative error among physicians
Andrew Lin
Deep learning offers significant promise for plaque quantification from routine CCTA images, by automatically detecting and contouring the heart arteries and underlying atherosclerotic plaques. This, Lin pointed out, enables measurements of plaque volume and coronary artery stenosis directly from standard CCTA images, with high accuracy compared to expert readers and at a fraction of the usual analysis time. Lin also noted that deep learning from CCTA agreed with the invasive reference standard of intravascular ultrasound for measurements of total plaque volume and minimum luminal area.
He now believes a deep learning system that rapidly and accurately estimates coronary artery stenosis could potentially be implemented into clinical practice as a ‘second reader’ and clinical decision support tool. ‘By providing automated and objective results, deep learning may reduce inter-observer variability and interpretative error among physicians. The system also could be used to pre-screen CCTA scans, flagging patients with obstructive disease to be prioritised for clinical reporting.’
When integrated into clinical decision-making, CCTA guides the use of preventive therapies, improves event-free survival, and reduces unnecessary downstream testing. AI-enabled image analysis has the potential to improve the efficiency of CCTA workflow and enhance patient risk stratification.
Profile:
Dr Andrew Lin is a postdoctoral researcher in the Biomedical Imaging Research Institute, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, California, (Mentorship: Dr Damini Dey). His research focuses on the application of artificial intelligence and advanced analytics techniques to plaque imaging with CCTA.
28.08.2021