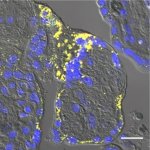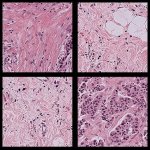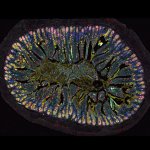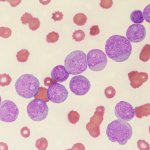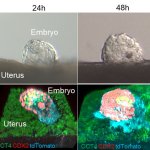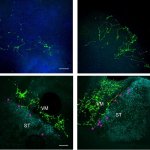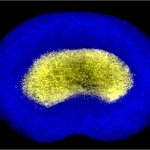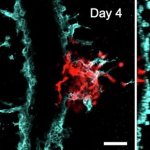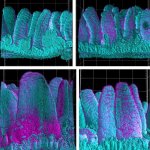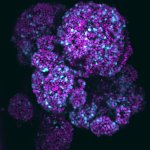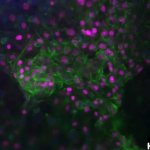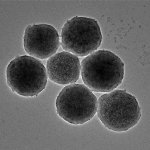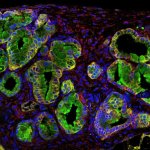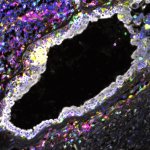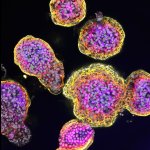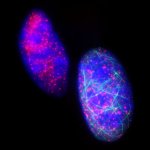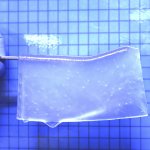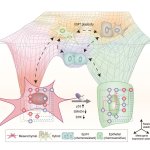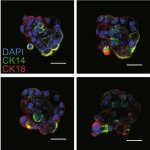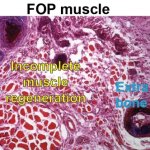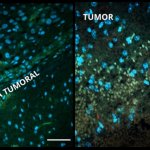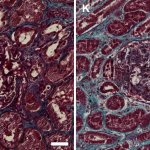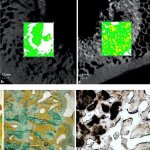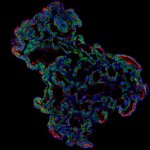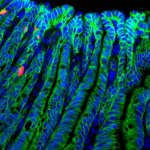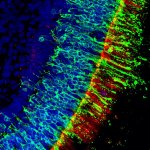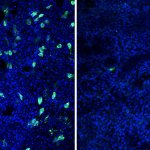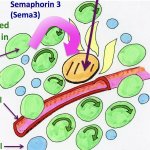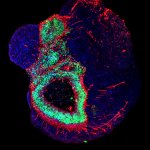
News • Gastric multi-regional assembloid
Lab-grown mini-stomachs to boost understanding of rare diseases
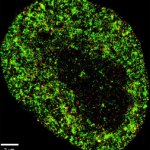
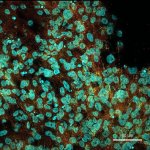
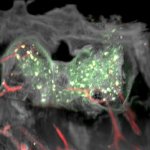
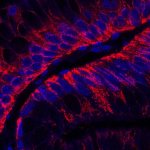
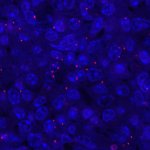
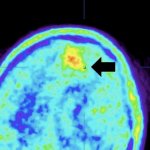
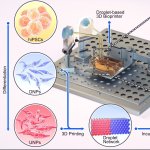
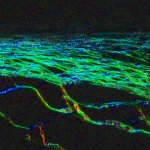
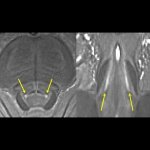
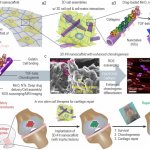
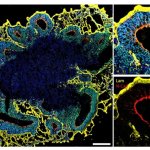
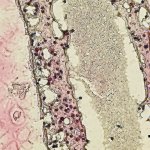
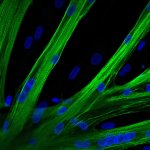
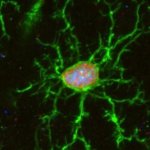
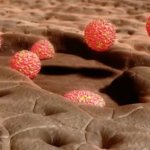
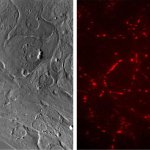
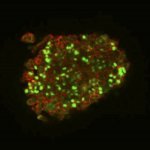
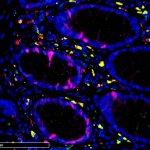
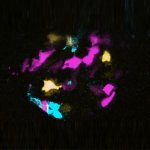
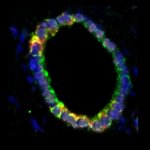
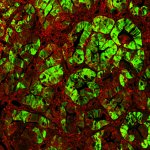
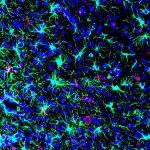
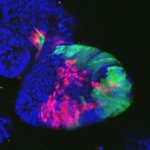
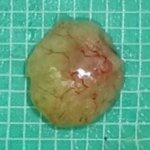
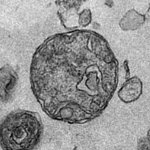
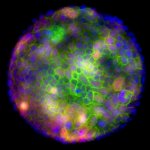
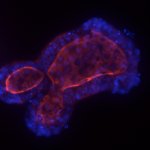
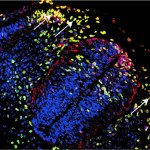
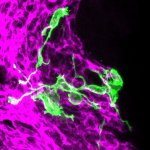
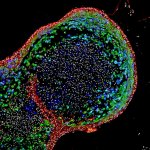
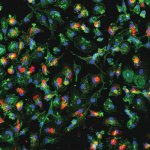
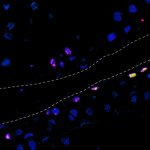
A new type of lab-grown organoid that mimics the behaviour of a human stomach could boost the understanding of rare gastric diseases, researchers say.