Image source: Osaka University
News • After mastectomy
Promising approach for breast regeneration
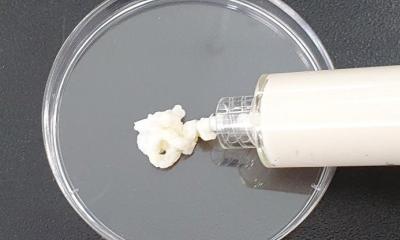
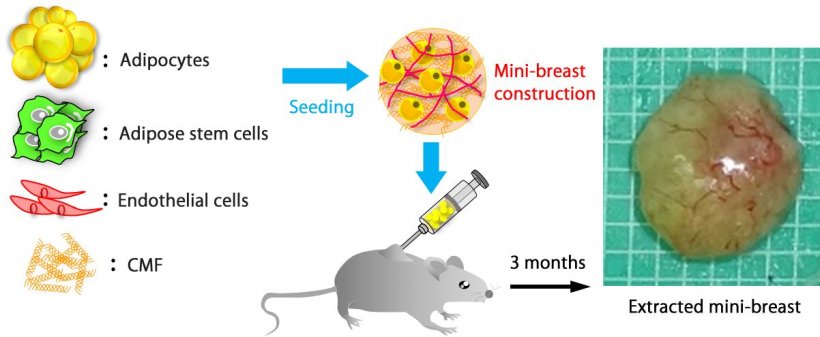
A team of researchers from Osaka University, Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine, and Toppan Printing Co., Ltd. succeeded in reconstructing adipose tissue balls (“mini-breasts”) with a functional vascular network using patient-derived cells, achieving a high graft survival rate in small animal models.
So far, silicone breast implants were primarily used in breast reconstruction following mastectomy. In Japan, the breast implant manufactured by Allergan was the only product approved by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. In July 2019, however, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) requested Allergan to recall its breast implants due to risk of breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma (BIA-ALCL), and their production was discontinued.
The technique used in this study was published in the journal Acta Biomaterialia.
Recommended article
News • BIA-ALCL
Breast implant cancer risks: are women aware?
Breast surgeons across the UK must ensure women are aware of BIA-ALCL, a non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma that is associated with implants; and more responsibility must be taken to diagnose and report cases, surgeons attending the 2018 London Breast Meeting have warned. Hundreds of breast specialists from around the world met at the Royal College of Physicians for the four-day conference this autumn,…
Although autologous tissue-based breast reconstruction, in which the patient’s fat cells are collected and injected, has also been performed, the graft survival rate is low and outcomes vary with the patient’s background. Some patients have to undergo several transplant surgeries.
Our findings will lead to a new, highly safe breast regenerative medicine that can replace the conventional fat cell injection and implantation
Michiya Matsusaki
In this study, the research team used type I collagen microfibers (CMFs) and applied their unique tissue engineering technique to the production of mini-breasts. CMFs act as a scaffold for adipocytes, adipose-derived stem cells, and vascular endothelial cells. The fabricated vascular network supplies the cells with nutrients and oxygen, and connection between the mini-breast and the patient’s blood vessels was also established. Transplanting this mini-breast into small animals resulted in a graft survival rate twice as high as that of conventional aspirated fat tissue transplantation.
Since cells derived from patients are used, no inflammatory reaction was observed, indicating that the mini-breasts are highly safe. Furthermore, the volume of the mini-breast to be implanted is adjustable by in vitro culture. “Our findings will lead to a new, highly safe breast regenerative medicine that can replace the conventional fat cell injection and implantation,” says Prof. Michiya Matsusaki, who lead the study.
Source: Osaka University
04.02.2020