News • Research
High-cholesterol diet leads to colon cancer – let's find out why
New research from the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) could help explain the link between a high-cholesterol diet and an elevated risk for colon cancer.
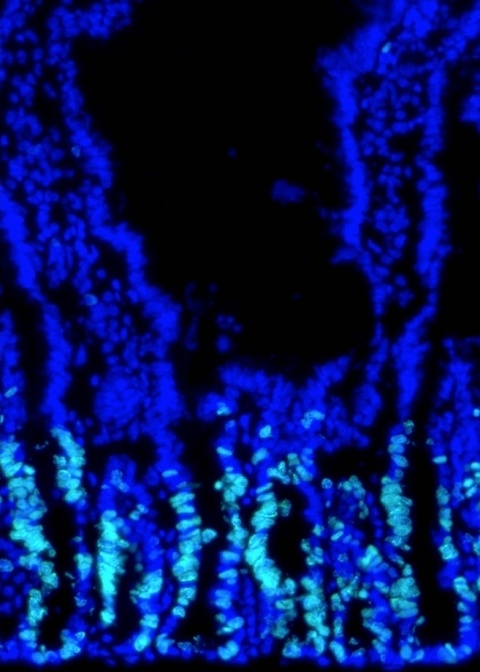
In a study of mice, scientists from the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA discovered that boosting the animals’ cholesterol levels spurred intestinal stem cells to divide more quickly, enabling tumors to form 100 times faster. Published online in Cell Stem Cell, the study identifies a new drug target for colon cancer treatment. “We were excited to find that cholesterol influences the growth of stem cells in the intestines, which in turn accelerates the rate of tumor formation by more than 100-fold,” said Dr. Peter Tontonoz, the medical school’s Frances and Albert Piansky Professor of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine. “While the connection between dietary cholesterol and colon cancer is well established, no one has previously explained the mechanism behind it.”
The scientists increased cholesterol in the intestinal stem cells in some of the mice by introducing more of the substance into their diets. In others, the researchers altered a gene that regulates phospholipids, the primary type of fat in cell membranes, which spurred the cells into producing more cholesterol on their own. The stem cells’ ability to multiply was increased in both groups. The UCLA team will explore whether the phospholipid-cholesterol interaction they uncovered plays a similar role in speeding the growth of other cancers.
Source: University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), Health Sciences
26.01.2018