News • Research on dopaminergic neurons
Immunotherapy to prevent neuron loss in Parkinson’s disease
Promising new research points to a new immunotherapy approach that could help preserve viable neurons in people with Parkinson’s disease.

Promising new research points to a new immunotherapy approach that could help preserve viable neurons in people with Parkinson’s disease.
A new type of lab-grown organoid that mimics the behaviour of a human stomach could boost the understanding of rare gastric diseases, researchers say.

Analytical and measurement technology copany Horiba has obtained CE IVDR certification for its new Yumizen H500 CRP benchtop hematology analyzer, designed for small laboratories.

Non-specific symptoms such as fatigue, pain or weight loss can be caused by cancer, another serious condition or something completely harmless. A blood test can help provide relevant information.

Symptoms of depression are common among people with asthma, but growing evidence suggests they may arise from biological mechanisms different from those underlying major depressive disorder.

Should younger and older people receive different treatments for the same infection? New research suggests that age-specific treatments may be necessary in ongoing antibiotic resistance crisis.
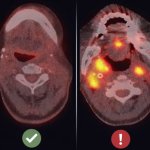
Immunotherapy has been hailed as a breakthrough in cancer treatment. But new research reveals: under sustained treatment pressure, cancer does not simply weaken — it adapts, learns, and fights back.

The immune system’s reaction to the common Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) can ultimately damage the brain and contribute to multiple sclerosis (MS), a new study shows.
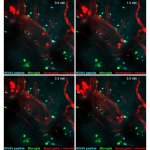
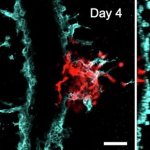
Scientists from Northwestern University have developed an injectable regenerative nanomaterial that helps protect the brain during the vulnerable window after a stroke.

Cardiovascular disease and depression do not co-occur by chance; the TO_AITION project aims to enable earlier diagnosis of comorbidity, better risk prediction and personalised treatment strategies.

New research shows that a harmless strain of Klebsiella – discovered by chance in laboratory experiments – can eliminate infections and reduce gut inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).

Even minor functional impairments of the kidneys can have serious consequences for patients after major surgery. New biomarkers could help identify high-risk patients at an early stage.
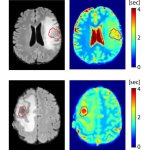
A novel AI-based method can distinguish between progressive brain tumours and radiotherapy-induced necrosis on advanced MRI. This could help clinicians more accurately identify and treat the issues.
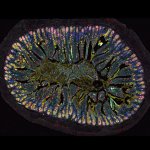
New insights into the intestinal nervous system – or "gut brain" – open new avenues for advancing therapies for allergies, chronic inflammatory bowel diseases and irritable bowel syndrome.

Depression is not only a disease of the mind or the brain, a new study finds: a research team has revealed deep connections to abnormalities in the body's overall immune response.

A team of researchers comprehensively catalogued a new collection of bacteria-eating viruses called phages. These phages could be used to combat Klebsiella pneumoniae - a serious threat in hospitals.

New research reveals why women with long Covid — especially those who develop chronic fatigue syndrome — tend to experience more severe and persistent symptoms than men do.
After a bout of influenza or Covid, the risk of heart attack or stroke may rise dramatically, and chronic infections may increase the long-term risk of serious cardiovascular disease events.

A new approach to PET imaging offers a promising way for physicians to promptly identify patients who are at risk for poor functional recovery after a heart attack, according to new research.

Researchers identified a targeted way to protect the brain from harmful side effects of cranial radiation therapy, potentially preserving the quality of life for millions of brain cancer survivors.
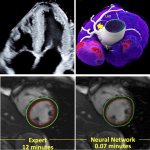
Cardiac imaging is evolving, and new techniques continue to uncover the secrets of the heart for cardiologists who know how to use them. At the ESC 2025 Congress in Madrid, four experts explored cutting-edge developments across different modalities. Ranging from AI-assisted ultrasound image acquisition and accelerated MRI protocols to advanced prognostic tools for CT and nuclear imaging, these…

It is known that depression is linked to increased incidence of metabolic diseases; now scientists have discovered that different types of depression are linked to different cardiometabolic diseases.

Chronic fatigue (ME/CFS) affects millions worldwide, but is poorly understood and has long lacked reliable diagnostic tools. Now, a new blood test claims to diagnose the condition with 96% accuracy.

The heterogeneity of critical illnesses like sepsis, ARDS, and trauma creates immense challenges. A new, unified way to classify patients aims to improve treatment.

GLP-1 receptor agonists are widely prescribed for individuals with diabetes and weight loss. However, these medications may adversely affect the interpretation of cancer imaging, new research finds.
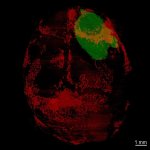
Scientists have shown for the first time that glioblastoma—the deadliest form of brain cancer—affects not just the brain but also erodes the skull, alters the makeup of skull marrow, and interferes with the body’s immune response.
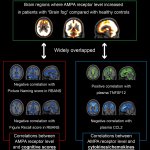
New insights on the mechanisms that cause “brain fog” in Long Covid patients: Researchers use a specialized brain imaging technique to identify a potential biomarker and therapeutic target.
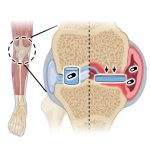
A squishy new ‘artificial cartilage’ material could improve arthritis treatments by releasing anti-inflammatory drugs in response to a flare-up.

Historically, implants to repair bone fractures have been made of metal, donor bone, or 3D-printed material. Now, scientists propose an in-situ printing approach - using a modified glue gun.
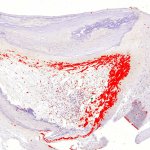
An unexpected trigger for heart attack: Researchers show that dormant bacteria can contribute to atherosclerotic plaques and fatal myocardial infarction, effectively making it an infectious disease.

Studies have found that natural polysaccharides from a medical fungus endemic to Taiwan can not only effectively inhibit inflammation, but also fight the proliferation of lung cancer cells.
Microrobots formed in droplets could enable precision-targeted drug delivery, improving on IV drug delivery that sends only 0.7% of the drug to the target tissue, according to a recent study.
Common respiratory infections such as influenza and Covid-19 can awaken dormant breast cancer cells that have spread to the lungs, setting the stage for new metastatic tumors, new research finds.
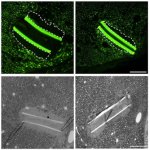
Coating an electronic neural implant with a potent anti-inflammatory drug helps the body better tolerate the implant, improving its long-term performance and stability, according to new research.
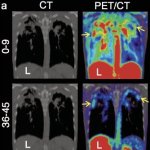
A new PET imaging technique can accurately detect and monitor Mycobacteroides abscessus lung infections—one of the most difficult-to-diagnose conditions in patients with lung diseases.

Newborns, especially those born prematurely, are vulnerable to conditions such as sepsis. A new device profiles an infant’s immune function from a single drop of blood to improve neonatal care.
At the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium (SABCS), three experts presented new approaches and study results for the treatment of breast cancer in young women.
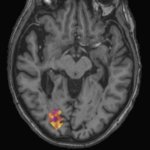
A new biomarker for multiple sclerosis: the inflammatory cell rim from microglial cells surrounding brain lesions was found to directly correlate with the severity and speed of disease progression.

Multiple sclerosis often transitions from a relapsing-remitting to secondary progressive form, which requires different treatment. Now, an AI model can determine this change with 90% certainty.

Researchers have succeeded in mapping how blood vessels in the brain react after a stroke. This new insight can lead to more effective treatment and fewer complications for patients.

An international research team has developed an intelligent device capable of monitoring the skin continuously and accurately detect temperature variations associated with inflammation and infection.

New research has revealed how Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) also profoundly affects the brain, leading to cognitive and behavioural challenges that are very diverse and some could be reversible.
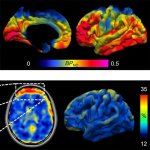
Using the COX-2 enzyme, a new PET imaging approach offers a never-before-seen view of inflammation in the brain, opening the door for clinical and research settings for various brain disorders.
Researchers have developed ‘sponge-like’ microneedle patches that deliver bioactive ingredients and reduce inflammation in slow- and non-healing diabetic wounds.
Leveraging bioink from pancreatic tissue and 3D bioprinting, researchers developed a structure closely mimicking the structure of a pancreas, in which cultured cells can resume insulin production.

Giving separated blood plasma improves outcomes in patients with traumatic brain injury (TBI) or shock, whereas unseparated or “whole” blood may be best for patients with traumatic bleeding.

The gastrointestinal microbiome holds valuable information that can help predict whether immunotherapy will be successful against melanoma. A new “gut-on-a-chip” is designed to do exactly that.
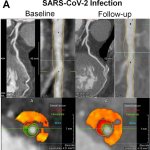
The virus behind Covid-19 initially causes acute lung injury and respiratory failure. However, new evidence indicates the virus also involves inflammation that can affect the cardiovascular system.
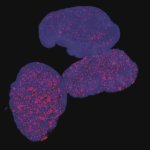
Persister cells arise as a result of cancer treatment and are often responsible for tumour relapse. Researchers identified a distinctive feature of persister cells, paving the way for new treatments.
Dying cells prick their neighbors with a lethal message. This may worsen sepsis, Vijay Rathinam and colleagues report. Their findings could lead to a new understanding of this dangerous illness.
Helping the brain repair itself after a stroke: A new study based on unique tissue samples from Denmark's Brain Bank may pave the way for new treatments that support brain regeneration.

A new study has shown that the molecular signature of long Covid can be found in blood samples of children. Using an AI tool, the researchers were capable of diagnosing the condition with 93% accuracy.

The immune system of children reacts differently to cancer than that of adults. New insights into these differences have the potential to lead to new tailored treatments for children with cancer.

More than just a sports injury: A new study shows that head trauma may activate latent viruses, leading to neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.
Women with breast implants should regularly attend follow-up care to avoid the risk of "silent" implant ruptures and their long-term complications, experts caution in a new publication.
A new type of photocurrent-responsive coating has been shown to shorten the bone-to-implant integration time after orthopaedic surgery to just two weeks.
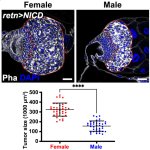
Tumors in female fruit flies grow significantly larger than in male ones, a new study finds. The findings could lead to a better understanding of how the biological sex impacts cancer development.
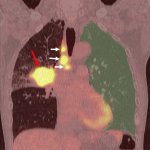
PET/CT image analysis using artificial intelligence (AI) can predict the occurrence of interstitial lung disease, a serious side effect of immunotherapy in lung cancer, a new study shows.

Skills shortages and digitalization, trends in cardiology and oncology, future prospects in laboratory medicine, and healthy aging – these pressing topics are at the forefront of discussions at this year’s Medica Labmed Forum.

Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) treatments could offer relief to breast cancer patients who experience late toxicities following radiotherapy treatment. To date, the handful of completed clinical trials only produced inconclusive or contradictory results. Therefore, results from the latest trial, named HONEY (Effect of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on Breast Cancer Patients with Late Radiation…
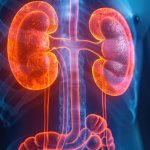
New research has revealed that the connection between PFAS, and kidney damage may be tied to dysregulation of the gut microbiome.
Scientists at the University of Geneva (UNIGE) and the Geneva University Hospitals (HUG) have developed CAR-T cells capable of targeting malignant gliomas while preserving healthy tissue.
Brazilian researchers have identified a key mechanism of Sars-CoV-2 to manipulate its host’s immune defense. This discovery could pave the way for the development of novel therapies.
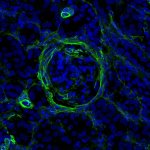
Systemic lupus erythematodes can lead to severe kidney damage. However, until now, the cause for this remained unclear. New research has now revealed the underlying mechanism.
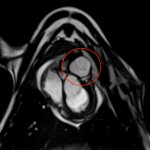
A new heart valve comprised of biological material obtained from human cells, opens up new therapeutic avenues for patients with paediatric heart diseases, such as tetralogy of Fallot.

Enzyme-driven nanorobots could be used in the treatment of joint diseases such as arthritis. A new research project explores the potential of this technology.
Why do aortic aneurysms form where they typically do, at the upper arch or in the abdominal cavity? A new study explores the predilection of these sites for vascular dilatations.

Analytical and measurement technology specialist Horiba has expanded its compact hematology instrument range with the launch of new models with Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) on board.

The IRCCS in Bologna has inaugurated a state-of-the-art integrated PET/CT system. This cutting-edge technology allows for the entire human body to be studied in a single scan, even detecting the smallest tumour cells.

A new study suggests that tattoos could be a risk factor for cancer in the lymphatic system, or lymphoma. Now, the researchers underline the need for more research on the topic.
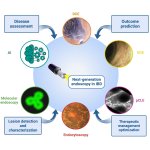
Endoscopy is pivotal in diagnosing and managing ulcerative colitis. Recent technology advances allow for early cancer detection, precise disease assessment and targeted biopsies, improving diagnosis and monitoring. The following article takes a look at the latest advancements.

New research provides cause for optimism that long Covid can resolve over time. Following people from the first wave of Covid-19, it monitored the longevity of immune abnormalities after an infection.

Findings from the largest UK study of patients hospitalised with Sars-CoV-2 infection show that long Covid leads to ongoing inflammation which can be detected in the blood.

Researchers discovered three distinct immunological endophenotypes of multiple sclerosis, defined by specific blood immune signatures. This opens new avenues for personalized treatment strategies.

A team of Northwestern University scientists has developed the first wireless, implantable temperature sensor to detect inflammatory flareups in patients with Crohn’s disease.

Researchers have now shown that a noninvasive treatment that stimulates gamma frequency brain waves may hold promise for treating memory impairment and other cognitive effects of chemotherapy.

A team of researchers has discovered a new method of measuring levels of cortisol directly from a blood sample - a significant step forward in diagnosis and treatment of a wide range of diseases.
Researchers have identified how cells work to resolve "frozen shoulder", a painful and disabling condition affecting the ligaments that form the shoulder joint capsule.
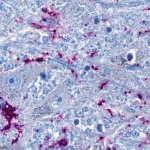
How does a coronavirus infection cause neurological symptoms such as headaches, memory problems, and fatigue? A new study points to a different reason than previously assumed.
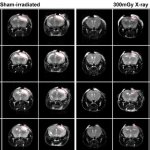
Neuroscientists recently discovered that low-dose ionizing radiation (LDIR) can reduce lesion size and reverse motor deficits in TBI and ischemic stroke mice, demonstrating its therapeutic potential.

Contraception, wound healing, arthritis treatment: Here are three recent papers published in ACS journals that could expand the beneficial uses for nanoparticles, based on results in rats.
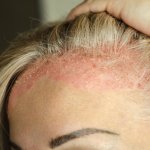
Scientific articles about psiorasis suffer from a shortage of actual patient images, according to a new study. This makes it hard for patients to grasp the condition, the authors argue.
A new study found that the antibody response of infants and young children against Sars-CoV-2 deviates from that of adults in a small, but very significant way.

Using placebos in primary care to reduce overprescribing, conserve existing antibiotics and limit further resistance, is publicly acceptable, a new study shows.
After pelvic radiotherapy, patients may live with low-grade chronic inflammation of the lower intestine 20 years after the treatment, a new study shows.

US researchers have discovered that radiation therapy combined with two types of immunotherapy can control tumors in preclinical models of triple negative breast cancer.
Two out of the four screening tools used by emergency medical services are inadequate for recognising sepsis, according to new research presented at the EUSEM Congress.
A newly discovered mechanism involving exosomes can drive inflammation and impair healing of wounds in diabetes patients, according to a new study led by University of Pittsburgh and UPMC researchers.
A new research breakthrough could lead to the development of new treatments for people with compromised immune systems, such as those with cystic fibrosis.
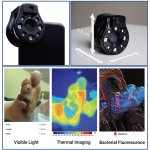
Scientists have developed a device that works with a smartphone or tablet to capture medical images which can identify infected wounds through thermal and fluorescence imaging.

Researchers at Mayo Clinic have developed a 3D prototype of human skin bioprinted to model inflammatory skin disease such as atopic dermatitis — more commonly known as eczema.
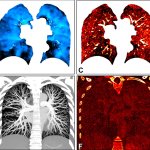
Photon-counting CT allows for a comprehensive, simultaneous evaluation of lung structure and function, something not possible with standard CT, according to a new study.
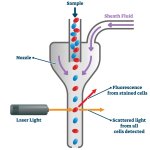
Plastics are a part of everyday life, and an increasingly concerning factor of global environmental pollution. They also have infiltrated our bodies as microparticles (MPs) and nanoparticles (NPs), found even in placentas supporting foetal life. And they are in our blood. Now, researchers in Spain have developed a new method to detect and measure nanoparticles in human peripheral blood that is…
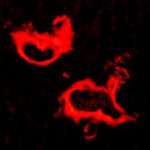
A research team from Barcelona studied the liver of Alzheimer's disease mice models, and demonstrated the importance of the liver-brain axis regarding the psychological symptoms of the disease.
New research has found molecular signature differences in the blood of patients who fully recover from Covid-19 and those who develop long Covid.
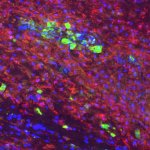
Multiple sclerosis affects three women for every one man. French scientists are studying the role of the sex hormones in order to better understand this discrepancy.
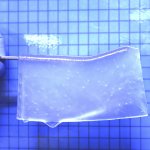
Synthetic hydrogels were shown to provide an effective scaffold for neuronal tissue growth in areas of brain damage, providing a possible approach for brain tissue reconstruction.

January 28 saw the celebration of the “Data Protection Day” as it is called in Europe, or respectively the “Privacy Day” as it is referred to outside of Europe. It marks the date on which the Council of Europe’s data protection convention, known as “Convention 108” was opened for signature back in 1981. According to the Council of Europe, it is the ‘only international,…

In a promising study, Canadian researchers have shown for the first time in mice that modifying intestinal flora before surgery could reduce postoperative complications in colorectal cancer patients.

Canadian researchers are developing a new, ultra-sensitive biosensor to screen for Alzheimer’s disease and other diseases. The device has successfully completed the proof-of-concept stage.
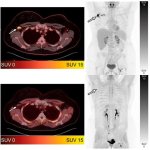
A novel imaging agent can reduce the number of false-positive PET/CT findings among cancer patients recently vaccinated for Covid-19. This may mitigate the issue of tracer uptake in lymph nodes associaed with the vaccine.
Findings of bacteria with anti-inflammatory effects in the intestines of MS patients with no evidence of active disease indicate that diet, bacteria and disease progression are linked.
After an infection with SARS-CoV-2, some people fail to recover their sense of smell. US researchers took a closer look at the olfactory nerve cells to find the reason for Covid-19-induced anosmia.

Researchers use AI to develop personalized 3D-printed joint implants so that these delicate finger parts can be replaced when necessary (e.g. after illness or injury).
Periprosthetic infections and revisions are on the rise in Germany and worldwide, with significant consequences for affected patients as well as for the healthcare systems. Precisely because the number of patients at higher risk of infection in arthroplasty continues to rise, attention is increasingly focused on how this dreaded complication can be avoided.
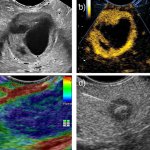
Endosonography poses unique challenges for medical professionals, because two demanding disciplines have to be mastered at the same time. The use of artificial intelligence (AI) could help speed up the notoriously slow learning curve of the procedure, says Prof Dr Christoph F. Dietrich. At the Visceral Medicine Congress in Hamburg, the expert explained how AI can help endosonography achieve…
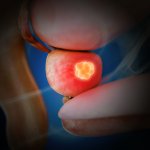
A new randomized study confirms that men with high-risk prostate cancer can be treated with a moderately shortened course (5 vs. 8 weeks) of radiation therapy.
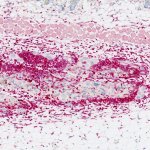
Researchers from Barcelona report that vaccination with senescent cells shows promise in experimental models of melanoma and pancreatic cancer.
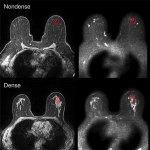
The risk of developing breast cancer is higher in breasts with high density. But why is that? Researchers at Linköping University have shown major biological differences that promote cancer growth.
Colorectal cancer is one of the most common cancers. A team from the University of Geneva has found an alternative for patients who have developed resistance to chemotherapy treatments.

Renal cell carcinoma is among the fifteen most common cancers worldwide. Dr Titus Brinker, from the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), looked at whether a convolutional neural network (CNN) can extract relevant image features from a typical H&E-stained slide to predict 5-year overall survival.

Researchers have shown that when brain cells are directly exposed to blood taken from Covid-19 patients with delirium, there is an increase in cell death and a decrease in the generation of new brain cells.

A newly developed capsule that tunnels through mucus in the GI tract could be used to orally administer large protein drugs such as insulin.
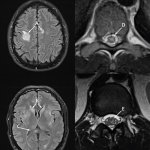
As the monkeypox outbreak continues to spread around the globe, a rare but potentially serious complication of the virus has been discovered.

German researchers present a novel method for testing chemical agents that could help in the development of drugs against neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's.

Two-dimensional (2D) cultured cell lines and animal models have been the principal research tools for the past decade, but have several shortcomings. Three-dimensional cell cultures, or organoids, show great promise here.
Development of effective live bacterial therapeutics may depend more on using and re-introducing native microbes that can stick around than how the microbes are modified.
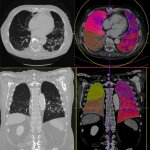
As knowledge about Covid-19 advances, so does the arsenal of techniques to predict, diagnose and follow up on the disease. At ECR, researchers presented a range of promising imaging modalities to keep track of Covid-19 symptoms, severity, and mortality, often including AI support to enhance or accelerate diagnostics.

Researchers are seeking alternatives to gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) to help raise levels of patient safety. An open hybrid session at ECR in Vienna heard how research across several centres has been examining the options of new approaches to reduce reliance on GBCAs.
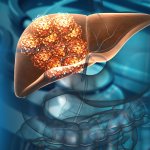
Newly engineered in vitro tumour models open ways to better understand the crosstalk between liver cancer cells and their microenvironment, researchers from Singapore found.
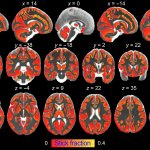
Researchers visualize brain inflammation using diffusion-weighted MRI. This detailed "X-ray" of inflammation cannot be obtained with conventional MRI, but requires data acquisition sequences and special mathematical models.

When a virus makes its way into the body, one of the immune system’s first responders is a set of pathogen-removal cells called macrophages. But they don’t all target viruses in the same way.

Wireless bioresorbable pacemaker bypasses need to extract non-biodegradable leads, eliminating additional risk to the patient.
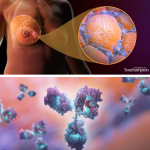
"Crown-like structures" surrounding breast tumors in overweight and obese patients could hinder their response to therapy. The findings of this study could potentially be used to improve personalized treatment for patients.
Scientists at the La Jolla Institute for Immunology discover new drug target for severe asthma and fibrosis.

Researchers have developed advanced computer models, or “digital twins”, of diseases, with the goal of improving diagnosis and treatment.

Cognitive impairment as a result of severe Covid-19 is similar to that sustained between 50 and 70 years of age and is the equivalent to losing 10 IQ points, scientists found.
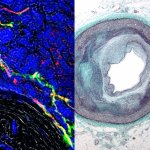
An international team has for the first time demonstrated that nerve signals are exchanged between clogged up arteries and the brain.

An international research team has now found an approach to lower the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) and reduce the associated development of liver fibrosis.

Using mass spectrometry and chromatography techniques, UK researchers have developed an approach to predict infection severity among Covid-19 patients, as well as potential outcomes.

For people with atrial fibrillation, one of our most common cardiac disorders, dementia risk is elevated.
Reducing inflammatory mediators in the blood before surgical treatment of cardiac bacterial infection does not improve clinically relevant outcome, a new study shows.

People who were bedridden for at least a week due to Covid-19 are more likely to experience anxiety and depression for up to 16 months after the infection, a new study shows.
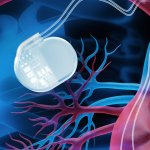
An anti-inflammatory drug incorporated into the coating around an implantable electronic medical device – such as a pacemaker – can reduce the body’s "foreign body" reaction.

Bioengineers have shown they can eradicate advanced-stage ovarian and colorectal cancer in mice in as little as six days with a treatment that could be ready for human clinical trials later this year.
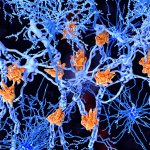
Nerve damage in multiple sclerosis can be detected via the concentration of neurofilament light chain in the blood. This could offer valuable information on future disease course and therapy effectiveness.
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) develop a protocol to transplant 3D cellular structures that could regenerate damaged intestine.
A connection between the Epstein-Barr virus and multiple sclerosis has long been suspected. A new study provides ‘compelling evidence of causality’.

Even as we battle one pandemic (Covid-19), we sit on the cusp of another. Europe has one of the highest burdens of chronic liver disease (CLD) in the world, driven largely by alcohol overconsumption, viral hepatitis, and obesity. Furthermore, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is increasingly common and is a significant contributor to CLD – especially in people with diabetes, where its…

A research team led by Professor Lim Chwee Teck from the National University of Singapore’s (NUS) Department of Biomedical Engineering and Institute for Health Innovation & Technology (iHealthtech), in collaboration with clinical partners from Singapore General Hospital, has developed a smart wearable sensor that can conduct real-time, point-of-care assessment of chronic wounds wirelessly…
Researchers at the DZNE and the University Medical Center Göttingen (UMG) have identified molecules in the blood that can indicate impending dementia. Their findings, which are presented in the scientific journal “EMBO Molecular Medicine”, are based on human studies and laboratory experiments. Various university hospitals across Germany were also involved in the investigations.

Long COVID symptoms rarely persisted beyond 12 weeks in children and adolescents unlike adults.
Hospitalized Covid-19 patients are substantially more likely to harbor autoantibodies — antibodies directed at their own tissues or at substances their immune cells secrete into the blood — than people without Covid-19, according to a new study.
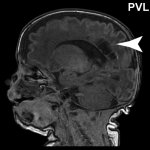
Extremely premature infants are at a high risk for brain damage. Researchers at the University of Vienna and the Medical University of Vienna have now found possible targets for the early treatment of such damage outside the brain: Bacteria in the gut of premature infants may play a key role.
Cartilage cells from the nasal septum can not only help repair cartilage injuries in the knee, they can also withstand the chronic inflammatory tissue environment in osteoarthritis and even counteract the inflammation – according to researchers from the University of Basel and the University Hospital Basel.

Molecular imaging, guided by novel tracers, is emerging as an important diagnostic and therapeutic tool in cardiovascular medicine. Delegates at ICNC-CT, the online International Conference on Nuclear Cardiology and Cardiac CT, also heard that cardiology can learn from fields such as oncology and neurology that have already made important advances in this area. Professor Frank Bengel, who is…

Combining imaging modalities is helping to achieve better diagnostic and therapeutic outcomes for heart patients. The topic, discussed in detail by experts at the ICNC-CT online International Conference on Nuclear Cardiology and Cardiac CT, examined hybrid/fusion imaging as the standard in cardiovascular imaging, and its value in clinical practice. Professor Terrence Ruddy spoke about the role of…

An AI-led device to assess coronary CT angiographs has been designed to assess cardiac plaque that may lead to myocardial infarction (MI). In his presentation ‘Vascular inflammation and cardiovascular risk assessment using coronary CT angiography’ (CCTA), Charambalos Antoniades, Professor of Cardiovascular Medicine at the University of Oxford, presented the research team’s findings during…

In a new study, researchers at Lund University and Uppsala University have seen a clear connection between how long a person sleeps and a number of biomarkers linked to cardiometabolic diseases such as cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes.
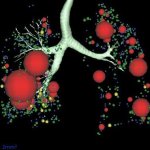
A novel CT scan-based approach has revealed significant changes in a parameter indicating lung destruction in some asthmatics. This finding could lead to more personalized treatments for asthma accompanied by persistent airflow limitation. Clinicians have long thought that some people with asthma experience declines in their lung function, called fixed airflow obstruction (FAO), due to changes to…
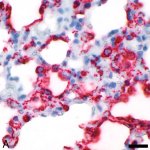
Covid-19 disease severity is determined by the individual patient’s immune response. The precise mechanisms taking place inside the lungs and blood during the early phase of the disease, however, remain unclear. Researchers from Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, the Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine (MDC) and Freie Universität Berlin have now studied the cellular mechanisms…

Beige is considered a calming paint color, and scientists have new evidence that beige fat has a similar impact on the brain, bringing down the inflammation associated with the more common white fat and providing protection from dementia. They have found that beige fat cells, which are typically intermingled with white fat cells in the subcutaneous fat present on “pear shaped” people, mediate…
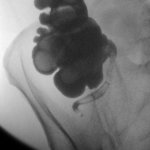
Long considered an unnecessary organ, the appendix is now the focus of several studies that aim to better understand its role. Present in many mammals, including humans, it appears to have developed at least 16 times over the course of the evolutionary history of mammals, suggesting that its function must confer a positive selective advantage on those that have it. A new study carried out by…
Home test kits to check for Covid-19 spike proteins and anti-Covid-19 antibodies are fast and simple to use but lack the sensitivity and accuracy of laboratory tests. Researchers from Eindhoven University of Technology with Utrecht University have developed a new type of sensor that combines the sensitivity and accuracy of current laboratory-based measurements with the speed and low-cost of…
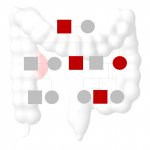
Scientists from the German Cancer Research Center and Heidelberg University Hospital have for the first time been able to delay the development of hereditary colorectal cancer with a protective vaccination. Mice with a hereditary predisposition to colorectal cancer survived significantly longer after vaccination than unvaccinated animals. Combining the vaccination with an anti-inflammatory drug…
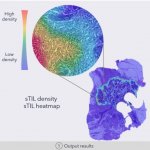
A researcher at the Technical University of Denmark (DTU) has developed a mathematical model for use in automated image analysis of tissue samples. The model provides the possibility for better and more similar cancer prognosis and treatment.
A team of engineers and clinicians has developed an ultra-thin, inflatable device that can be used to treat the most severe forms of pain without the need for invasive surgery. The device, developed by researchers at the University of Cambridge, uses a combination of soft robotic fabrication techniques, ultra-thin electronics and microfluidics.

Researchers at RMIT University in Australia have developed smart wound dressings with built-in nanosensors that glow to alert patients when a wound is not healing properly. The multifunctional, antimicrobial dressings feature fluorescent sensors that glow brightly under UV light if infection starts to set in and can be used to monitor healing progress.
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) reactivation resulting from the inflammatory response to coronavirus infection may be the cause of previously unexplained long Covid symptoms—such as fatigue, brain fog, and rashes—that occur in approximately 30% of patients after recovery from initial Covid-19 infection. The first evidence linking EBV reactivation to long Covid, as well as an analysis of long Covid…

Inspired by kirigami, the Japanese art of folding and cutting paper to create three-dimensional structures, MIT engineers and their collaborators have designed a new type of stent that could be used to deliver drugs to the gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract, or other tubular organs in the body.

New artificial intelligence (AI) technology to scan for heightened blood vessel inflammation can calculate a person’s risk of death from Covid-19 and its variants.
When a cell is infected, SARS-CoV-2 not only causes the host cell to produce new virus particles. The virus also suppresses host cell defence mechanisms. The virus protein nsP3 plays a central role in this. Using structural analyses, researchers at Goethe University in cooperation with the Swiss Paul Scherrer Institute have now discovered that a decomposition product of the virostatic agent…

The largest study of its kind in the UK has identified differences in the immune response to Covid-19 between people with no symptoms, compared to those suffering a more serious reaction to the virus. The research by Newcastle University and collaborators within the Human Cell Atlas initiative found raised levels of specific immune cells in asymptomatic people. They also showed people with more…

Potentially game-changing research led by McMaster University scientists may finally bring relief to millions of people worldwide living with Crohn’s disease. Investigator Brian Coombes said his team identified a strain of adherent-invasive E-coli (AIEC) that is strongly implicated in the condition and is often found in the intestines of people with Crohn’s disease. “If you examine the gut…
Do BMMFs, the novel infectious agents found in dairy products and bovine sera, play a role in the development of colorectal cancer? Scientists led by Harald zur Hausen detected the pathogens in colorectal cancer patients in close proximity to tumors. The researchers show that the BMMFs trigger local chronic inflammation, which can cause mutations via activated oxygen molecules and thus promote…

When airborne pollen levels are higher, increased SARS-CoV-2 infection rates can be observed. These results were determined by a large-scale study conducted by an international team headed by researchers at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) and the Helmholtz Zentrum München. Members of high-risk groups could protect themselves by watching pollen forecasts and wearing dust filter masks.

Working in intensive care units poses special challenges for healthcare workers. They have to safely and reliably detect whether the condition of their seriously ill patients is deteriorating in a life-threatening way, and they have to do so under great time pressure because every minute counts. The stress level increases even more when the patients are children and adolescents. In paediatric…
University of Minnesota Medical School researchers studied SARS-CoV-2 infections at individual cellular levels and made four major discoveries about the virus, including one that validates the effectiveness of remdesivir – an FDA-approved antiviral drug – as a form of treatment for severe Covid-19 disease. “Since the start of the Covid-19 pandemic, the way that each individual responds…
Patients given preventive blood thinning drugs (prophylactic anticoagulants) within 24 hours of admission to hospital with Covid-19 are less likely to die compared with those who do not receive them, a new study finds. Clinical trials are now underway to see if prophylactic anticoagulants could be an effective treatment for Covid-19. In the meantime, the researchers say these findings provide…

Pregnancy complications and early menopause increase women’s future risk of heart disease. Cardiologists, gynaecologists and endocrinologists recommend how to help middle-aged women prevent later heart problems in a European Society of Cardiology (ESC) consensus document published in European Heart Journal, a journal of the ESC.

For several years, scientists worldwide have been investigating the extent to which microorganisms living in and on the human body influence central life processes and thus health and disease. Today they assume that there is a connection between the totality of the microbial colonization in the human body, called the microbiome, and the development of diseases. Chronic inflammatory bowel disease…

Fried-food intake is linked to a heightened risk of major heart disease and stroke, finds a pooled analysis of the available research data, published online in the journal Heart. And the risk rises with each additional 114 g weekly serving, the analysis indicates. It’s clear that the Western diet doesn’t promote good cardiovascular health, but it’s not clear exactly what contribution fried…
One of the most vexing aspects of the Covid-19 pandemic is doctors’ inability to predict which newly hospitalized patients will go on to develop severe disease, including complications that require the insertion of a breathing tube, kidney dialysis or other intensive care. Knowledge of a patient’s age and underlying medical conditions can help predict such outcomes, but there are still…

According to current studies, the Covid-19 disease which is caused by the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus comprises at least five different variants. These differ in how the immune system responds to the infection. Researchers from the German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases (DZNE) and the University of Bonn, together with other experts from Germany, Greece and the Netherlands, present these findings…
An unfortunate truth about the use of mechanical ventilation to save the lives of patients in respiratory distress is that the pressure used to inflate the lungs is likely to cause further lung damage. In a new study, scientists identified a molecule that is produced by immune cells during mechanical ventilation to try to decrease inflammation, but isn’t able to completely prevent…
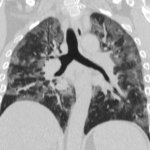
Bacteria or viruses like influenza that cause pneumonia can spread across large regions of the lung within hours. In the modern intensive care unit, these bacteria or viruses are usually controlled either by antibiotics or by the body’s immune system within the first few days of the illness. But in a study published in Nature, investigators at Northwestern Medicine show Covid-19 pneumonia is…
The variety and volume of bacteria in the gut, known as the microbiome, may influence the severity of Covid-19 as well as the magnitude of the immune system response to the infection, suggests research published online in the journal Gut. Imbalances in the make-up of the microbiome may also be implicated in persisting inflammatory symptoms, dubbed ‘long Covid’, the findings suggest. Covid-19…

In some cases, immune cells in the lungs can contribute to worsening a virus attack. In a new study, researchers at Karolinska Institutet describe how different kinds of immune cells, called macrophages, develop in the lungs and which of them may be behind severe lung diseases. The study, which was published in Immunity, may contribute to future treatments for Covid-19, among other diseases.

So far, little research has been done on the risk of children being seriously affected by Covid-19 when the schools were open. A study from Karolinska Institutet has now shown that one child in 130,000 was treated in an intensive care unit on account of Covid-19 during the period March-June. The study has been published in New England Journal of Medicine.
Research conducted at the Health New Orleans Neuroscience Center of Excellence at the Louisiana State University (LSU) reports that a combination of an LSU Health-patented drug and selected DHA derivatives is more effective in protecting brain cells and increasing recovery after stroke than a single drug. The findings are published in Brain Circulation.
A recent review study concludes that nanoplastics change the composition and diversity of gut microbiome in vertebrates and invertebrates. The effects of a widespread and prolonged exposure to nanoplastics observed in animal models can be applied to humans.
Like all viruses, the novel coronavirus is dependent on help from the human host cell. Proteins are the functional units of the cell and enable the virus to enter the host cell or help the virus to replicate. Scientists from Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin and from the Berlin Institute of Health (BIH), along with colleagues from the United Kingdom, Germany and the United States, have…
In a preclinical study, NIH scientists found that the commonly used antibiotic methacycline may be effective at combating the neurological problems caused by Zika virus infections.

Acute stroke in children has the same incidence as brain tumours and can seriously affect a patient’s life. Two kinds of arteriopathies are common drivers of paediatric acute stroke and radiologists must learn to distinguish their signs as early as possible to improve prognosis, according to Béatrice Husson, a paediatric radiologist at Le Kremlin Bicêtre Hospital in Paris.

Pancreatic cancer has the worst survival rate of any cancers, with immunotherapies currently offering negligible treatment benefits for patients. To help identify new therapeutic approaches, researchers from the University of Oxford have been focusing on leukocyte infiltration as a prognostic marker of the disease. Their study and findings were outlined by Dr Shivan Sivakumar during a session…
A novel outpatient procedure offers lasting pain relief for patients suffering from moderate to severe arthritis in their hip and shoulder joints, according to a study presented at the annual meeting of the RSNA.

Alzheimer's disease is the most common cause of dementia. Still incurable, it directly affects nearly one million people in Europe, and indirectly millions of family members as well as society as a whole. In recent years, the scientific community has suspected that the gut microbiota plays a role in the development of the disease.
Asian ethnicity is strongly linked to COVID-related stroke, reveals an analysis of stroke centre activity in England and Scotland during the first wave of the coronavirus pandemic, and accepted for publication in the Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery & Psychiatry.

Costantino Balestra, Professor of Physiology at Haute Ecole Bruxelles-Brabant in Belgium, uses point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) in environments that could not be more different from a typical hospital setting. His expertise lies in studying the effects of extreme conditions on the human body, including temperatures, altitudes, and ambient pressures, for example, in deep oceans. One of his areas…

Over 80 percent of 200 COVID-19 patients in a hospital in Spain have vitamin D deficiency, according to a new study.
The present Coronavirus pandemic with all its effects on society – both health and economic – highlights the urgency of developing new therapies for COVID-19 treatment. At the same time, it demonstrates the necessity to become well prepared for new virus infections we may be facing in the future. To help control the current pandemic and brace for novel pathogens that may cause future…

Researchers at the University of Helsinki and the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute have identified the mechanism behind bone marrow failure developing in children that suffer from Fanconi anaemia. The findings will help to develop new therapies for the disorder.

Although uncommon, sudden permanent hearing loss seems to be linked to COVID-19 infection in some people, warn doctors, reporting the first UK case in the journal BMJ Case Reports. Awareness of this possible side effect is important, because a prompt course of steroid treatment can reverse this disabling condition, they emphasise. Sudden hearing loss is frequently seen by ear, nose and throat…
Adequate levels of vitamin D reduces complications and deaths among COVID-19 patients, reveals new research performed at the Boston University School of Medicine. Hospitalized COVID-19 patients who were vitamin D sufficient, with a blood level of 25-hydroxyvitamin D of at least 30 ng/mL (a measure of vitamin D status), had a significant decreased risk for adverse clinical outcomes including…

An AI (Artificial Intelligence) assisted polyp detector is helping endoscopists find more lesions during colorectal examinations. Leading endoscopists highlighted how the system is improving performance and finding flat or hidden polyps that the human eye could miss, in a webinar entitled “Artificial Intelligence - How to unleash the potential for colorectal polyp detection.” Hosted by the…

On the occasion of this year's World Sepsis Day, we spoke with Elena Sukhacheva, Ph.D., director of medical and scientific affairs at Beckman Coulter, about the status quo and outlook on sepsis diagnostics. With the severity of sepsis symptoms, it’s easy to comprehend why it is invaluable to diagnose this disease properly and in a timely manner. Dr Sukhacheva takes an in-depth look at…
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is the most common muscle disease in children and is passed on by X-linked recessive inheritance. Characteristic is a progressive muscular atrophy. The disease often results in death before the third decade of life. Researchers of the Universities of Maynooth (Ireland) and Bonn have found a connection between dystrophic muscles and the lymphatic system in mice…

In the most comprehensive study of COVID-19 pediatric patients to date, Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and Mass General Hospital for Children (MGHfC) researchers provide critical data showing that children play a larger role in the community spread of COVID-19 than previously thought. In a study of 192 children ages 0-22, 49 children tested positive for SARS-CoV-2, and an additional 18…
Researchers studying tissue removed from patients noses during surgery believe they may have discovered the reason why so many people with COVID-19 lose their sense of smell, even when they have no other symptoms. In their experiments they found extremely high levels of angiotensin converting enzyme II (ACE-2) only in the area of the nose responsible for smelling. This Enzyme is thought to be the…

As the COVID-19 pandemic continues to claim lives around the world, much research has focused on the immune system’s role in patients who become seriously ill. A popular theory has it that the immune system gets so revved up fighting the virus that, after several days, it produces a so-called cytokine storm that results in potentially fatal organ damage, particularly to the lungs.
Disruption of gut bacteria by antibiotics soon after birth can affect the maturation of the immune system, say researchers at Rutgers University-New Brunswick. Even short, single antibiotic courses given to young animals can predispose them to inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) when they are older, according to their research. The study, published in Genome Medicine, provides further evidence…
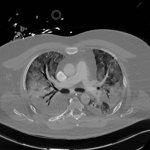
There are major complications from COVID-19 – ARDS, pulmonary embolism and neurological – that imaging can help detect, manage and/or follow up in the long term, radiologists from France and the UK explained during a recent ESR Connect session. ARDS is the most dreaded complication and the number one morbidity in COVID-19 patients. The incidence was up to 30% of patients in initial reports.…
Which patient will develop a severe form of COVID-19? This is an essential question which must be answered in order to improve the individual management and the prognosis of these patients. In a publication in the journal Science, teams from the Assistance publique – Hôpitaux de Paris (AP-HP), Inserm, Université de Paris, Institut Pasteur and Institut Imagine describe a unique and unexpected…

Despite its proximity to China, Taiwan contained COVID-19 successfully, without a lockdown or movement restriction measures introduced elsewhere. With few new cases reported, life almost returned to normal. Behind the scenes, however, efforts have continued to maintain that positive situation.
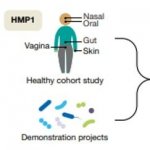
The human species maintains symbiotic relationships with a multitude of microbial organisms that colonise the inside as well as the surface of the body. Scientists, for a long time, underestimated the significance of these organisms for humans.
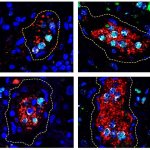
An overactive defense response may lead to increased blood clotting, disease severity, and death from COVID-19. A phenomenon called NETosi is part of an immune response that becomes increasingly hyperactive in people on ventilators and people who die from the disease.
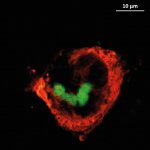
New coatings on implants could help make them more compatible. Researchers at the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) have developed a new method of applying anti-inflammatory substances to implants in order to inhibit undesirable inflammatory reactions in the body. Their study was recently published in the "International Journal of Molecular Sciences".
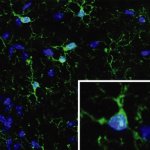
Infections can trigger a particularly strong immune reaction of the body (termed sepsis). In such a sepsis the immune system reacts so strongly that not only the pathogens but also tissues and organs are damaged. In a study with mice, researchers from the Technische Universität Braunschweig were able to show that sepsis can have long-term effects on the brain and learning behaviour even after…
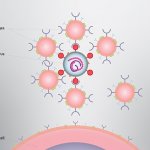
Nanoparticles cloaked in human lung cell membranes and human immune cell membranes can attract and neutralize the SARS-CoV-2 virus in cell culture, causing the virus to lose its ability to hijack host cells and reproduce.
A tuberculosis vaccine developed 100 years ago also makes vaccinated persons less susceptible to other infections. While this effect has been recognized for a long time, it is not known what causes it. Together with colleagues from Australia and Denmark, researchers from Radboud university medical center the universities of Nijmegen and Bonn have now presented a possible answer to this question.
MRI imaging is one of the best ways of examining different body tissue and obtaining information about injuries and illnesses. However, MRI scanners are typically large, heavy, and very expensive devices that need to be operated by specially trained healthcare personnel. Aalto University has just launched a project that studies and builds new magnetic resonance imaging technology, which enables…
Leading immunologists in Japan are proposing a possible molecular mechanism that causes massive release of proinflammatory cytokines, or a cytokine storm, leading to the acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in COVID-19 patients. Their suggestions, published in the journal Immunity, are based on recent findings that explain how SARS-CoV-2 enters human cells.

As Covid-19 spreads throughout the country, much attention has been paid to the devastating effects of the virus on the lungs. But doctors are learning how the virus may affect other organs, including the brain. Some patients with Covid-19 have had neurological symptoms, which may include an increased risk of stroke.

Scientists at the University of Cambridge have found an association between living in an area of England with high levels of air pollution and the severity of COVID-19, the disease caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Because of the urgent need to share information relating to the pandemic, the researchers have published their report on MedRXiv. It has not yet been peer-reviewed. However, the…
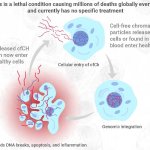
Sepsis—the body's own immune response gone against it—is a major health problem worldwide. It is basically a "hyper" immune response by the body to infection or injury, and is characterized by hyperinflammation, immune system paralysis, cell death, liver and kidney failure, blood clots, and even hemorrhage. An estimated 30 million people suffer from sepsis every year, of which 20%…
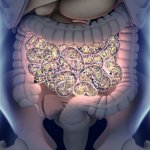
Scientists from the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) and the Hebrew University in Jerusalem demonstrated in mice that intestinal bacteria reprogram DNA activity in cells of the gut mucosa and thus have a considerable impact on the development of the healthy gut.
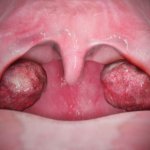
Biomedical researchers in Munich have isolated immune cells from human tonsils obtained following routine surgery, and used them to analyze aspects of the immune response and test the effects of anti-inflammatory agents at the cellular level. Human tissues that have been surgically removed from patients are normally treated as waste, especially when they are derived from a ‘dispensable’ organ…
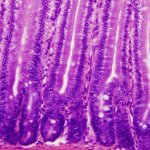
Celiac disease affects 0.3-2.4% of people in most countries world-wide, and approx. 2% in Finland. Celiac patients suffer from a variety of symptoms, typically intestinal complaints, such as diarrhea, but are often symptom-free. Immunologist Tobias Freitag co-developed and tested nanoparticles containing gliadin for the immunomodulatory treatment of celiac disease in Professor Seppo Meri’s…

People who have been treated in intensive care commonly suffer from residual cognitive impairment, but the reason for this is unknown. Researchers at Karolinska Institutet now link cognitive impairment with lasting inflammation and a potential treatment target. The results are presented in the scientific journal Intensive Care Medicine.
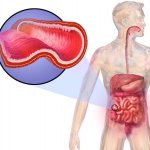
Researchers from Karolinska Institutet, Örebro University and Aarhus University, Denmark, have published the largest study to date on the risk of colorectal cancer in Crohn's disease. The article is published in the journal The Lancet Gastroenterology Hepatology. Crohn's disease is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Several previous studies have reported an increased risk of colorectal…
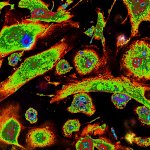
Researchers discover a novel checkpoint in immune cells with the potential to treat the cancer cell microenvironment. The recognition of bacterial infections or foreign substances is mediated and controlled by the human immune system. This innate and adaptive immune system comprises the most important metabolic and cellulare processes to fight against infections and other diseases. Paradoxically,…
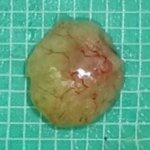
A team of researchers from Osaka University, Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine, and Toppan Printing Co., Ltd. succeeded in reconstructing adipose tissue balls (“mini-breasts”) with a functional vascular network using patient-derived cells, achieving a high graft survival rate in small animal models. So far, silicone breast implants were primarily used in breast reconstruction following…

One of the causes of breast cancer may be inflammation triggered by harmful bacteria say researchers. Scientists say their idea – as yet unproven – is supported by the available evidence, which is that bacterial induced inflammation is linked to cancer. The paper in the journal Medical Hypotheses is by Lancaster University medical student Auday Marwaha, Professor Jim Morris from the…

Computed tomography (CT) plays an increasingly important role in assessing pelvic disease, particularly when patients present with acute abdominal pain. In addition, radiomic approaches on CT are being developed to increase the characterisation of ovarian cancer for optimising treatment planning.
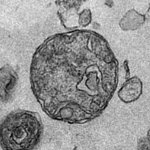
Does the blood we thought to know so well contain elements that had been undetectable until now? The answer is yes, according to a team of researchers. The scientistts from Inserm, Université de Montpellier and the Montpellier Cancer Institute (ICM) working at the Montpellier Cancer Research Institute (IRCM), have revealed the presence of whole functional mitochondria in the blood circulation.…

Diseases such as cardiovascular diseases, cancer or certain lung diseases are among the most common non-natural causes of death today and account for about 70 percent of deaths worldwide. They are defined by the World Health Organization (WHO) as non-communicable because they are assumed to be caused by a combination of genetic, lifestyle and environmental factors and cannot be transmitted…

When the heart valve between the aorta and the left ventricle is narrowed, i.e. aortic valve stenosis is present, different genes are active in men than in women. Scientists of the German Centre for Cardiovascular Research (DZHK) at Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin have discovered this for the first time. Future research can be planned more precisely according to these results and could…

Researchers at Lund University in Sweden have developed a new hydrogel based on the body’s natural peptide defense. It has been shown to prevent and treat infections in wounds. The formulation kills multi-resistant bacteria, something that is increasing in importance with antibiotic resistance growing globally. “The ability to effectively heal wounds is key for our survival in evolutionary…
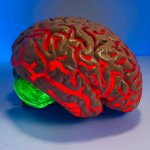
A new multicentre study will investigate the link between brain inflammation and psychosis, and use artificial intelligence techniques to identify patients that might benefit most from novel treatments. The study, funded by UKRI Medical Research Council, is led by the Universities of Birmingham and Cambridge. Researchers will examine how and if activated inflammatory cells may act differently in…
In animals, a vaccine modifying the composition and function of the gut microbiota provides protection against the onset of chronic inflammatory bowel diseases and certain metabolic disorders, such as diabetes and obesity. This research was conducted by the team of Benoît Chassaing, Inserm researcher at Institut Cochin (Inserm/CNRS/Université de Paris), whose initial findings have been…

Inflammation drives the progression of neurodegenerative brain diseases and plays a major role in the accumulation of tau proteins within neurons. An international research team led by the German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases (DZNE) and the University of Bonn comes to this conclusion in the journal “Nature”. The findings are based on the analyses of human brain tissue and further lab…
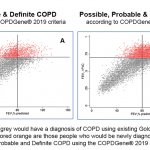
Researchers at National Jewish Health and dozens of leading institutions around the nation have proposed new criteria for diagnosing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), the fourth leading cause of death in the United States. The proposal expands diagnostic criteria from a single measure of lung function to include environmental exposure, symptoms, and abnormal CT scans.

Chronic inflammatory diseases, such as allergies and asthma, are not only an acute problem but also a major research and prevention challenge. We spoke with Professor Harald Renz, Director of the Institute for Laboratory Medicine at the University Hospital Gießen/Marburg, Germany, and discussed the major reason for increases in the number of these widespread diseases.
The results of a major study across 195 countries, presented at UEG Week Barcelona 2019, indicate that global death rates for pancreatic cancer and incidence rates for colorectal cancer both increased by 10% between 1990 and 2017. The Global Burden of Disease study, is the first to provide comprehensive worldwide estimates of the burden, epidemiological features and risk factors of a number of…
Scientists have uncovered a novel antibiotic-free approach that could help prevent and treat one of the most widespread bacterial pathogens, using nanocapsules made of natural ingredients. Helicobacter pylori is a bacterial pathogen carried by 4.4 billion people worldwide, with the highest prevalence in Africa, Latin America and the Caribbean. Although the majority of infections show no symptoms,…

Biologists from the University of California, Irvine have made a major finding on combating inflammation linked to Alzheimer's disease. The School of Biological Sciences researchers’ discovery about the role of a protein called TOM-1 heralds a shift toward examining the molecular underpinnings of Alzheimer’s processes. Their study appears online in Proceedings of the National Academy of…
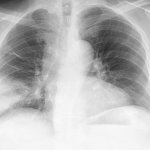
Spanish researchers in Valencia have identified specific fragments of genetic material that play a role in the development of respiratory failure and sepsis in pneumonia patients. Presenting the research at the European Respiratory Society International Congress, Dr Francisco Sanz said the findings could enable doctors to test quickly for these biological markers when a patient is admitted to…

For decades now, the Fraunhofer Institute for Organic Electronics, Electron Beam and Plasma Technology FEP has been developing processes and systems for cleaning, sterilization, and surface modification. The newly in-house developed process, called SULEEI, makes it possible to sterilize (S) and preserve decellularized pericardial tissue by means of photo-initiated ultraviolet (U) crosslinking…
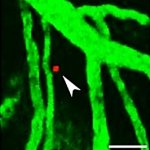
Lymphomas in the central nervous system are rare but dangerous. Scientists at the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) have now discovered which molecular mechanism leads to lymphomas forming metastases in the central nervous system.

Pathology is embracing digitisation just as radiology did over 20 years ago and both specialties are looking at new ways to integrate each other in their workflows. AI could fuel this sparkling alliance, giving it further means to improve cancer treatment.

A study of nearly half a million people has found for the first time that those with heart or blood vessel problems benefit more from having a physically active lifestyle than do healthy people without cardiovascular disease (CVD). Increased physical activity reduced the risk of dying during a six-year follow-up period for people with and without CVD, but the researchers found the greatest…

Fourteen metabolic biomarkers can predict long term mortality in individuals helping to determine life expectancy in general populations, a new study in the journal Nature Communications reports. In the largest study of its kind, researchers from Leiden University Medical Center in the Netherlands and the University of Surrey investigated predictors of long-term mortality risk. Current predictors…

Vincent Vidal (Marseille, France) and colleagues have demonstrated the in vivo feasibility of arterial embolization with permanent and absorbable suture fragments, leading them to propose what they have termed the “FAIR-Embo” concept to the wider interventional radiology (IR) community. Writing in Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiology (CVIR), they conclude: “Embolization by absorbable…

The World Health Organisation's (WHO) Essential Medicines List and List of Essential Diagnostics are core guidance documents that help countries prioritize critical health products that should be widely available and affordable throughout health systems. Now, updated versions of the two lists have been published, focusing on cancer and other global health challenges, with an emphasis on effective…
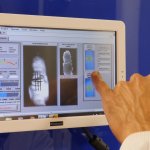
A new way of detecting rheumatoid arthritis using infrared light could offer an objective way of diagnosing the disease and monitoring treatment effectiveness, a University of Birmingham study shows. The rapid, non-invasive technique could help clinicians diagnose the disease earlier, and assess how effectively the selected treatment is controlling the progression of the disease. Rheumatoid…
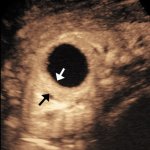
The pros and cons of CT (computed tomography), MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) and CEUS (contrast enhanced ultrasound) for emergency abdominal use were highlighted by speakers in an ECR 2019 session under the broader heading: ‘Abdominal Emergencies: advanced imaging in daily routine’.

Image analysis of prostate cancer is a challenging area for clinicians. The disease shows a low mutation burden compared to melanoma and stomach cancer, for example, making morpho-molecular correlation more difficult, and there is often very low inflammation. With the role of tumour infiltrating lymphocytes in prostate cancer currently unclear – and with the advent of new approaches to prostate…
Immuno-oncology is a therapy in which the body’s immune system treats a tumour. Dr Eric Borges, from the Research and Development Centre at Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH in Germany, explains why this is revolutionary. Unlike conventional cancer therapies, with immuno-oncology the tumour cell is not the direct target, it’s the patient’s immune system. The medication stimulates this to…
An anti-inflammatory drug called ketorolac, given before surgery, can promote long-term survival in animal models of cancer metastasis, a team of scientists has found. Furthermore, so-called "pro-resolution" therapies can also trigger the immune system to eliminate metastatic cells. The research also suggests that flanking chemotherapy with anti-inflammatory drugs can unleash anti-tumor…

The migrant population is fast growing and heterogeneous. Experts at a session held during the European Congress of Radiology (ECR 2019) concluded that radiologists can play a key role in detecting and differentiating related diseases. Migration is a growing phenomenon and has an impact on health, according to Jozef Bartovic from the World Health Organisation (WHO) in Copenhagen, Denmark.…